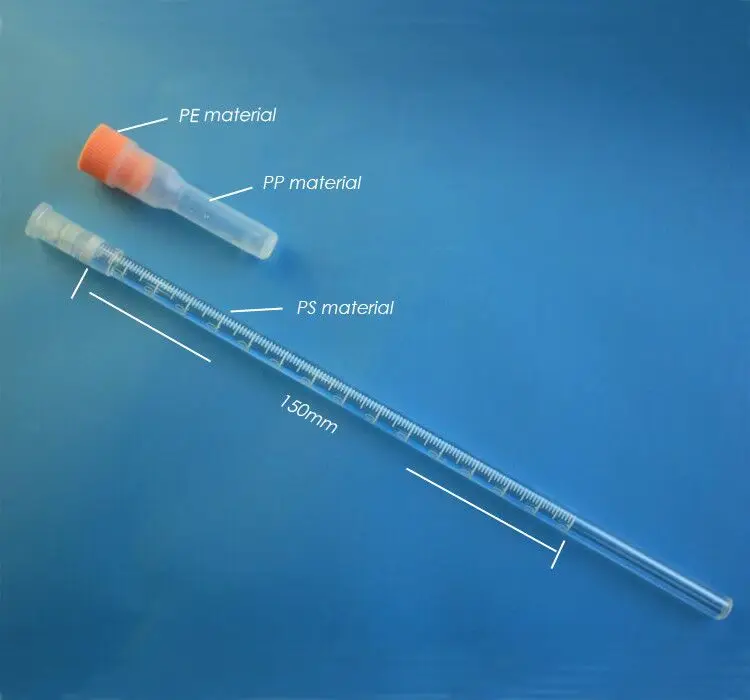
What is the ESR of Westergren’s tube?
It is expressed as ESR (Wintrobe, 1st hour) = …… mm. The Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a measure of settling of the red blood cells in an anti-coagulated whole blood sample which is allowed to stand in a narrow vertical tube during a specified period of time. Westergren’s tube is used to measure ESR in this method:
What is the diameter of a Westergren tube?
Tube handling The Westergren method uses standardized colorless, circular glass or plastic tubes, with an inner diameter of at least 2.55 mm and sufficient length to include a 200 mm sedimentation scale. The inner diameter should be constant (± 5%) over the whole length; a so called Westergren tube.
What is the Westergren test?
It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of inflammation . To perform the test, anticoagulated blood is traditionally placed in an upright tube, known as a Westergren tube, and the distance which the red blood cells fall is measured and reported in mm at the end of one hour.
What is a Westergren rack used for?
The westergren rack is a student physiology practical apparatus that holds the westergren tube and is used in the determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate ESR. When performing a sedimentation rate the wintrobe or westergren tube is filled to the level marked?

What is the Wintrobe tube?
A Wintrobe tube is a narrow glass tube measuring 110-mm-long, with graduation from 0 to 100 mm in both ascending and descending order. This method has been succeeded by the “micro-hematocrit” method which uses a small capillary tube instead of a Wintrobe hematocrit tube.
What is meant by Westergren?
[ wĕs′tər-grĕn′, vĕs′- ] n. A method for estimating the sedimentation rate of red blood cells in whole blood by mixing venous blood with an aqueous solution of sodium citrate and allowing the mixture to stand in an upright standard pipet and, after one hour, reading the millimeters the cells have descended.
What is Wintrobe and Westergren tube?
Wintrobe method: The Wintrobe method is performed similarly except that the Wintrobe tube is smaller in diameter than the Westergren tube and only 100 mm long. EDTA anticoagulated blood without extra diluent is drawn into the tube, and the rate of fall of red blood cells is measured in millimeters after 1 hour.
What does ESR Westergren measure?
The ESR test measures the rate at which the red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, in a sample of whole blood, fall to the bottom of the Westergren tube.
What diseases cause high ESR?
If your ESR is high, it may be related to an inflammatory condition, such as:Infection.Rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatic fever.Vascular disease.Inflammatory bowel disease.Heart disease.Kidney disease.Certain cancers.
Why ESR is high in female?
PIP: In healthy subjects, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is higher in women than in men, and in both sexes, a rise occurs with age. It is well-established that pathological elevation of the ESR may be due to elevation of the fibrinogen level.
Which is better Wintrobe or Westergren?
A comparison was made of two methods of estimating the erythrocyte sedimen- tation rate on fifty samples of blood. The results tend to confirm the view that Westergren's method is superior to Wintrobe's.
What are the three stages of ESR?
There are 3 stages in erythrocyte sedimentation 1) Stage 1 : Rouleaux formation - First 10 minutes 2) Stage 2 : Stage of sedimentation or settling - 40 mins 3) Stage 3 : Stage of packing - 10 minutes, sedimentation slows and cells start to pack at the bottom of the tube.
What is the normal range of ESR?
The normal range is 0 to 22 mm/hr for men and 0 to 29 mm/hr for women.
What happens when ESR is high?
This makes them heavier, so they settle faster. The faster your red blood cells settle and fall, the higher your ESR. A high ESR tells your healthcare provider that you may have an active disease process in your body.
What does high ESR mean?
If an ESR is abnormally high, it means that the RBCs fell faster than expected. This usually happens when the RBCs have more protein within them, which causes them to stick together. Many conditions can cause an ESR to become elevated.
Is ESR 40 high for female?
ESR values of 40 and 60 mm/h clearly indicate a state of heightened systemic inflammation among people who already have an inflammatory disease. We also examined whether the increase in ESR was accompanied with disease flares, and our results suggest that this may be the case.
Is ESR 40 high?
ESR values of 40 and 60 mm/h clearly indicate a state of heightened systemic inflammation among people who already have an inflammatory disease. We also examined whether the increase in ESR was accompanied with disease flares, and our results suggest that this may be the case.
What is ESR normal range?
The normal range is 0 to 22 mm/hr for men and 0 to 29 mm/hr for women.
What is normal sed rate by modified Westergren?
For adults (Westergren method): Men under 50 years old: less than 15 mm/hr. Men over 50 years old: less than 20 mm/hr.
What is Westergren pipette used for?
Westergren sedimentation rate tubes may be used for the standard procedure, by drawing blood in a liquid sodium citrate vacuum tube, or the modified procedure, using a saline-diluted EDTA vacuum tube. ESR tubes measure the rate at which red blood cells settle out of plasma.
What is ESR in blood?
ESR is a measure of settling down of RBCs in an anticoagulated specimen of whole blood during a specified period of time.
How long does it take to test for ESR?
If the anticoagulant used is ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) and the sample is refrigerated then it can be tested for ESR upto 12 hours after collection of the sample. The temperature of the blood sample should be brought at room temperature before doing the test.
What tube is used to measure ESR?
Westergren’s tube is used to measure ESR in this method:
What is the markings from 0-100 mm?
Markings from 0-100 mm from upto down are used for reading ESR and markings from bottom to upward used for reading PCV (hematocrit).
Why should a rack be leveled?
The rack should be leveled because slight tilt of the rack can give high ESR values.
How far is a tube graduated?
Tube is graduated along the lower 2/3 portion, 0-200 mm from up to down.
What is the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes?
The Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a measure of settling of the red blood cells in an anti-coagulated whole blood sample which is allowed to stand in a narrow vertical tube during a specified period of time.
What is the gold standard for measuring erythrocytes?
Erythrocytes usually aggregate into clumps that resemble a stack of coins and are called rouleaux. (page 4,5) The Westergren method is the gold standard and adopted as the reference method for ESR measurement by the International Council for Standardization in Hæmatology (ICSH).
What increases ESR in women?
ESR values are higher for women than for men and increase progressively with age. Pregnancy also increases ESR. During acute phase reactions, macromolecular plasma proteins, particularly fibrinogen, are produced that decrease the negative charges between erythrocytes and thereby encourage rouleaux formation. Paraproteins are positively charged molecules that are abundantly present in multiple myeloma and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia patients. Like fibrinogen, paraproteins decrease the negative charges between erythrocytes and increase rouleaux formation. As described earlier the aggregation based ESR tests (Test-1 and iSED) typically miss detecting these disorders, see paragraph above on “Aggregation versus Sedimentation”. (Raijmakers, Kuijper, Bakkeren, & Vader, 2008) High protein concentrations increase plasma viscosity, which slows down the fall rate and thus ESR. However, the effects of fibrinogen and paraproteins on the negative charges between erythrocytes and rouleaux formation far outweigh the effect of increased plasma viscosity, resulting in a strong net increase of ESR. In anemia, erythrocyte numbers are reduced, which increases rouleaux formation. In addition, the reduced hematocrit affects the velocity of the upward plasma current so that erythrocyte aggregates fall faster. In macrocytosis, erythrocytes are changed into a shape with a small surface-to-volume ratio, which leads to a higher sedimentation rate. (Saadeh, 1998) (Bridgen, 1999)
What are the stages of sedimentation?
The sedimentation process can be divided into three stages: A. Lag stage-rouleaux formation (10 min) Erythrocytes start to aggregate and form rouleaux. The presence of acute phase proteins encourages rouleaux formation. During this phase, no sedimentation occurs. B. Decantation stage-sedimentation (40 min) Erythrocyte aggregates fall to the bottom under influence of gravity at a constant rate. Large aggregates fall faster than small aggregates or single cells. Falling aggregates induce an upward plasma current that slows down sedimentation. C. Packing stage (10 min) The rate of sedimentation slows down to zero and cells start to pack in the bottom of the tube.
What are the factors that affect erythrocyte sedimentation?
Erythrocyte sedimentation is governed by factors that stimulate or inhibit erythrocyte aggregation and sedimentation. Normal erythrocytes are negatively charged and repel each other, which limits the sedimentation rate. Large clumps fall faster than small ones, so factors that increase aggregation will increase sedimentation. Erythrocytes usually aggregate into clumps that resemble a stack of coins, which are called rouleaux.
How does a tube affect ESR?
A tube that is not held completely vertical can lead to increased sedimentation rates and is one of the technical factors that can affect ESR readings. But could this knowledge be used to increase ESR and develop a rapid ESR method? DM Dissanayake of the University of Peradenya in Sri Lanka has tested whether it was possible to use an inclined tube to get a faster reading of the ESR. Dissanayake tilted tubes at an angle of 45 degrees and registered sedimentation distances every 30 seconds from 4 to 13 minutes by reading the lowest level of the meniscus. These results were compared with a traditional Westergren reading of the same sample in another tube that was kept vertically. The experiment contained a wide range of ESR readings, from 0 mm/hr to well over 150 mm/hr. The correlation between the traditional Westergren reading and the tilted tube was maximal between 10 and 11.5 minutes (correlation coefficient=0.985-0.986) for both low and high ESR readings. (Dissanayake, 2006) The accuracy of the r esults was considered acceptable. It demonstrates however that a tilted
How much can a deviation of 3 degrees accelerate ESR?
A deviation of 3 degrees can accelerate ESR up to 30%.
How does reduced hematocrit affect erythrocytes?
In addition, the reduced hematocrit affects the velocity of the upward plasma current so that erythrocyte aggregates fall faster. In macrocytosis, erythrocytes are changed into a shape with a small surface-to-volume ratio, which leads to a higher sedimentation rate. (Saadeh, 1998) (Bridgen, 1999) .
Stages
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is the measure of ability of erythrocytes ( red blood cell) to fall through the blood plasma and accumulate together at the base of container in one hour.
Causes of elevation
The rate of erythrocyte sedimentation is affected by both inflammatory and non-inflammatory conditions.
Causes of reduction
An increased number of red blood cells (polycythemia) causes reduced ESR as blood viscosity increases. Hemoglobinopathy such as sickle-cell disease can have low ESR due to an improper shape of red blood cells that impairs stacking.
Medical uses
ESR can sometimes be useful in diagnosing diseases, such as multiple myeloma, temporal arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, various auto-immune diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and chronic kidney diseases. In many of these cases, the ESR may exceed 100 mm/hour.
Relation to C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase protein. Therefore, it is a better marker for acute phase reaction than ESR. While ESR and CRP generally together correlate with the degree of inflammation, this is not always the case and results may be discordant in 12.5% of the cases.
History
The test was invented in 1897 by the Polish pathologist Edmund Biernacki. In some parts of the world the test continues to be referred to as Biernacki's Reaction ( Polish: odczyn Biernackiego, OB). In 1918, Dr Robert Fåhræus noted that ESR differed only during pregnancy. Therefore, he suggested that ESR could be used as an indicator of pregnancy.
Research
According to a study released in 2015, a stop gain mutation in HBB gene (p. Gln40stop) was shown to be associated with ESR values in Sardinian population. The red blood cell count, whose values are inversely related to ESR, is affected in carriers of this SNP.
What Is a Sedimentation Rate (Sed Rate)?
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR, or "sed rate") measures how quickly red blood cells fall to the bottom of a test tube. Typically, the higher the sed rate, the more inflammation there is in the body.
What Are the Reasons for Performing a Sedimentation Rate Test?
Doctors use the sedimentation rate to help to determine if inflammation is present in the patient. Additionally, the sedimentation rate can be a convenient method of monitoring the progress of treatment of diseases that are characterized by inflammation.
Who Performs a Sedimentation Rate Test?
The sedimentation rate is typically measured in a laboratory that does testing of blood samples.
How Is a Sedimentation Rate Test Performed?
A sedimentation rate is performed by measuring how long it takes red blood cells (RBCs) to settle in a test tube. The RBCs become sediment in the bottom of the test tube over time, leaving the blood serum visible above.
What Are Normal Sedimentation Rates?
The normal sedimentation rate (Westergren method) for males is 0-15 millimeters per hour,
From
Firestein, Gary S., et al. Kelley & Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology, 10th Ed. China: Elsevier, 2016.