Why does bond price decrease when yield to maturity increases?
Yields and Bond Prices are inversely related. So a rise in price will decrease the yield and a fall in the bond price will increase the yield. The calculation for YTM is based on the coupon rate, the length of time to maturity and the market price of the bond. YTM is basically the Internal Rate of Return on the bond.
How can we calculate yield on debt?
- To calculate the present value of your interest payments, you calculate the value of a series of equal payments each year over time. ...
- The formula for present value requires you to separate your annual interest payments into the smaller amounts you receive during the year. ...
- The sooner you are able to receive any payment, the more valuable it is to you. ...
How to calculate yield to maturity?
Yield to Maturity (YTM) – otherwise referred to as redemption or book yield Yield Yield is defined as an income-only return on investment (it excludes capital gains) calculated by taking dividends, coupons, or net income and dividing them by the value of the investment.
Are bonds with higher yield to maturity better?
Yes, high-yield corporate bonds are more volatile and, therefore, riskier than investment-grade and government-issued bonds. However, these securities can also provide significant advantages when analyzed in-depth. It all comes down to money.
What is yield to maturity and why is it important?
Yield to maturity (YTM) is a term that is related very closely to bonds and measures the cash flow of the investment over a period of time. It is the total return expected on a bond when the bond matures and is expressed as an annual return, which is why it is considered a long term bond yield.
Is it better to have a higher or lower YTM?
As you can see, the lower the bond price, the higher the YTM. Our bond with a $1,000 par value, 5% coupon and 3-year maturity is scheduled to pay out $1,150 in 3 years. As these payment amounts are fixed, you would want to buy the bond at a lower price to increase your earnings, which means a higher YTM.
Why is yield to maturity cost of debt?
The YTM refers to the internal rate of return (IRR) of a bond, which is a more accurate approximation of the current, updated interest rate if the company tried to raise debt as of today. Hence, the cost of debt is NOT the nominal interest rate, but rather the yield on the company's long-term debt instruments.
What does a high yield to maturity mean?
The relationship between the current YTM and interest rate risk is inversely proportional, which means the higher the YTM, the less sensitive the bond prices are to interest rate changes. The most noteworthy drawback to the yield to maturity (YTM) measure is that YTM does NOT account for a bond's reinvestment risk.
Is high YTM good or bad?
High yield bonds are not intrinsically good or bad investments. Generally, a high yield bond is defined as a bond with a credit rating below investment grade; for example, below S&P's BBB. The bonds' higher yield is compensation for the greater risk associated with a lower credit rating.
Is yield to maturity the same as interest rate?
Yield to maturity (YTM) is the overall interest rate earned by an investor who buys a bond at the market price and holds it until maturity. Mathematically, it is the discount rate at which the sum of all future cash flows (from coupons and principal repayment) equals the price of the bond.
What is the formula for yield to maturity?
What is the formula for yield to maturity? YTM formula is as follows: YTM = APR + ((Face value - current market price) divided by the number of years until maturity). Then take that value and divide it by (Face value + market price) / 2.
How do you know if a bond is good to buy?
The most important aspects are the bond's price, its interest rate and yield, its date to maturity, and its redemption features. Analyzing these key components allows you to determine whether a bond is an appropriate investment.
Why is yield to maturity better than coupon rate?
The major difference between coupon rate and yield of maturity is that coupon rate has fixed bond tenure throughout the year. However, in the case of the yield of maturity, it changes depending on several factors like remaining years till maturity and the current price at which the bond is being traded.
Can YTM be negative?
For the YTM to be negative, a premium bond has to sell for a price so far above par that all its future coupon payments could not sufficiently outweigh the initial investment. For example, the bond in the above example has a YTM of 16.207%. If it sold for $1,650 instead, its YTM goes negative and plummets to -4.354%.
Why is YTM and price inversely related?
The yield and bond price have an important but inverse relationship. When the bond price is lower than the face value, the bond yield is higher than the coupon rate. When the bond price is higher than the face value, the bond yield is lower than the coupon rate.
What is the relationship between yield to maturity and bond price?
The yield-to-maturity is the implied market discount rate given the price of the bond. A bond's price moves inversely with its YTM. An increase in YTM decreases the price and a decrease in YTM increases the price of a bond. The relationship between a bond's price and its YTM is convex.
When a bond's yield to maturity is less than the bond's coupon rate the bond?
When a bond's yield to maturity is less than the bond's coupon rate, the bond: is selling at a premium. A bond has a $1,000 face value, a market price of $1,036, and pays interest payments of $70 every year.
What is yield to maturity example?
Example of Yield to Maturity After every six months, an investor who is also the bondholder receives a coupon payment of (5% x $ 100)/2= $5. In total, the investor would get 5 payments of $5, plus $100 being the face value of the bond due at maturity.
Why is YTM and price inversely related?
The yield and bond price have an important but inverse relationship. When the bond price is lower than the face value, the bond yield is higher than the coupon rate. When the bond price is higher than the face value, the bond yield is lower than the coupon rate.
What is the relationship between a bondholder's rate of return and the bond's yield to maturity if he does not hold the bond until it matures?
What is the relationship between a bondholder's rate of return and the bond's yield to maturity if he does not hold the bond until it matures? - The rate of return will be higher than the yield to maturity.
Why is yield to maturity important?
The primary importance of yield to maturity is the fact that it enables investors to draw comparisons between different securities and the returns they can expect from each. It is critical for determining which securities to add to their portfolios.
What is yield in investing?
Yield Yield is defined as an income-only return on investment (it excludes capital gains) calculated by taking dividends, coupons, or net income and dividing them by the value of the investment. Expressed as an annual percentage, the yield tells investors how much income they will earn each year relative to the cost of their investment.
What is YTM interest rate?
YTM is typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR) Annual Percentage Rate (APR) The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is the yearly rate of interest that an individual must pay on a loan, or that they receive on a deposit account.
What is fixed rate bond?
or interest rate of a fixed-rate security, such as a bond. Bonds Bonds are fixed-income securities that are issued by corporations and governments to raise capital. The bond issuer borrows capital from the bondholder and makes fixed payments to them at a fixed (or variable) interest rate for a specified period. .
What is the Yield-to-Maturity (YTM)?
The Yield-to-Maturity (YTM) represents the expected annual rate of return earned on a bond under the assumption that the debt security is held until maturity.
Why do investors project yield to maturity?
Considering yields rise when prices drop (and vice versa), investors can project the yield-to-maturity (YTM) on portfolio investments to guide better decision-making.
What is the difference between a bond's YTM and its coupon rate?
An important distinction between a bond’s YTM and its coupon rate is the YTM fluctuates over time based on the prevailing interest rate environment, whereas the coupon rate is fixed.
What is YTM in finance?
The yield to maturity (YTM), as mentioned earlier, is the annualized return on a debt instrument based on the total payments received from the date of initial purchase until the maturation date.
How to calculate semi annual coupon rate?
Given those inputs, the next step is to calculate the semi-annual coupon rate, which we can calculate by dividing the annual coupon rate by two.
What is the most commonly used metric for evaluating potential investments by bond and fixed income investors?
One of the most frequently used metrics for evaluating potential investments by bond and fixed income investors is the yield to maturity (YTM).
What is the relationship between the current YTM and interest rate risk?
The relationship between the current YTM and interest rate risk is inversely proportional, which means the higher the YTM, the less sensitive the bond prices are to interest rate changes.
What is yield to maturity?
Yield To Maturity is an indicator of returns for Debt Funds, however, it keeps changing with changing market conditions. In real life, the YTM of an open-ended Debt Fund is often different from the actual returns generated by the scheme.
What is Yield to Maturity (YTM) and Its Formula?
As Debt Funds invest in multiple Bonds, so the Yield To Maturity (YTM) of a Debt Fund is the weighted average yield of all the Bonds included in the scheme’s portfolio. But to simplify this, let us first consider what YTM means with respect to an individual bond. In the case of a Bond, YTM is defined as the total rate of return that a Bond Holder expects to earn if a Bond is held till maturity.
What does YTM mean in debt?
The YTM of a Debt Fund does more than just provide an indication of the potential returns you might get from your investment. It can also act as an indicator of the Credit Risk and Liquidity Risk associated with the Debt Fund.
What is the downside of low credit rating bonds?
There is however a downside – Bonds with low Credit Rating carry a higher level of Liquidity Risk and Credit Risk as compared to High-Quality Bonds. So Debt Funds with high exposure to Low-Quality Bonds carry a higher degree of risk for investors as compared to schemes that invest primarily in High-Quality Bonds.
Can you predict the future returns of a debt fund?
While the exact future returns of a Debt Fund cannot be predicted , it is possible to estimate your future Debt Fund returns using Fund data such as Yield To Maturity (YTM), Expense Ratio, Modified Duration, etc., and taking into account the RBI Interest Rate Cycle.
Can a debt fund invest in multiple bonds?
However, the extent of this YTM change for the fund will depend on the weightage of the individual Bond in the Debt Fund ’s portfolio.
How do you find out if a company has debt?
The first approach is to look at the current yield to maturity or YTM of a company’s debt. If a company is public, it can have observable debt in the market. An example would be a straight bond Fixed Income Trading Fixed income trading involves investing in bonds or other debt security instruments.
How do you estimate the cost of debt?
There are two common ways of estimating the cost of debt. The first approach is to look at the current yield to maturity or YTM of a company’s debt. If a company is public, it can have observable debt in the market.
What is the approximate yield to maturity?
Yield to Maturity FormulaC = Coupon/interest paymentF = Face valueP = Pricen = Years to maturity
How to calculate the effective after-tax yield?
Remember to convert your percentages to decimals when calculating the after tax yield. Convert by dividing by 100. …For example, with the 6% corporate bond and the 28.8 percent marginal tax rate, your after-tax yield would be calculated using the following equation: A T Y = 0.06 ∗ …This calculations gives an after-tax yield of 0.0427, or 4.27%.
What are some uses of yield to maturity?
Uses of Yield to Maturity (YTM) Yield to maturity can be quite useful for estimating whether buying a bond is a good investment. An investor will determine a required yield (the return on a bond …
How do you calculate actual yield?
Steps to Calculate Theoretical YieldBalance the Chemical Equation. The first step is to balance the chemical equation. …Express Mass of the Reactants in Terms of Moles. …Find the Limiting Reagent. Now, the next step is to determine which of the two reactants is the limiting reagent. …Find the Theoretical Yield. …Find the Percentage Yield. …
How to determine debt capacity for a company?
What is Debt Capacity?Assessing Debt Capacity. Balance Sheet The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. …Credit Metrics. Credit metrics are extremely useful to determine debt capacity, as they directly reflect the book values of assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity.Download the Free Template.
What is debt yield?
Debt yield refers to the rate of return an investor can expect to earn if he/she holds a debt instrument until maturity. Such instruments include government-backed T-bills. Bonds Bonds are fixed-income securities that are issued by corporations and governments to raise capital.
What is a bond?
Bonds Bonds are fixed-income securities that are issued by corporations and governments to raise capital. The bond issuer borrows capital from the bondholder and makes fixed payments to them at a fixed (or variable) interest rate for a specified period. , private debt agreements, and other fixed income securities.
What is convertible bond?
Convertible Bond A convertible bond is a type of debt security that provides an investor with a right or an obligation to exchange the bond for a predetermined number of shares in the issuing company at certain times of a bond’s lifetime. A convertible bond is a hybrid security. Risk-Free Rate. Risk-Free Rate The risk-free rate ...
What is MMY in banking?
MMY calculates the return on highly liquid, short-term debt instruments such as certificates of deposits, commercial paper, or T-bills. MMY is different from BDY, as it computes yield based on the purchase price of the security rather than on the security’s face value. The equation for MMY is:
What is HPY in finance?
HPY measures any capital gains and/or losses from debt investments that have occurred over a specified holding period. The formula for calculating HPY is:
Why is it important to calculate bond maturity?
This calculation is useful for investors looking to maximize profits by holding a bond until maturity, because it includes the interest that could be earned if annual coupon payments were reinvested, thereby earning additional interest on investment income .
What is bond debt?
Bonds are debt instruments that pay interest to investors, who essentially function as creditors to issuers. These interest payments constitute a bond's yield.
How to calculate current yield?
The current yield of a bond is calculated by dividing the annual coupon payment by the bond's current market value. Because this formula is based on the purchase price rather than the par value of a bond, it more accurately reflects the profitability of a bond, relative to other bonds on the market. The current yield calculation helps investors drill down on bonds that generate the greatest returns on investment each year. This is especially helpful for short-term investments .
What is YTM bond?
Yield to maturity (YTM) is the total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until its maturation date.
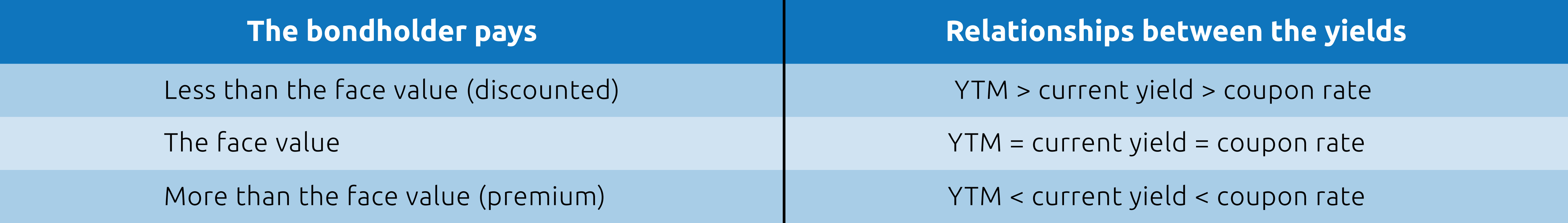
What is the difference between a premium bond and a discount bond?
Conversely, when a bond sells for less than par, which is known as a discount bond, its current yield and YTM are higher than the coupon rate . Only on occasions when a bond sells for its exact par value are all three rates identical.
What is holding period yield?
By definition, the holding period yield (HPY) is solely calculated on a holding period basis, therefore there is no need to include the number of days—as one would do with the bank discount yield. In this case, you take the increase in value from what you paid, add on any interest or dividend payments, ...
Why is understanding yields important?
Understanding how each of these yields is calculated is essential to grasping an investment’s actual return on an instrument.
What is EAY in investing?
The effective annual yield (EAY) can give a more accurate yield, especially when alternative investments are available which can compound the returns. This accounts for interest earned on interest.
How does the debt market work?
The debt market uses several calculations to determine the yield. Once the best way is decided, the yields from these short-term debt markets can be used when discounting cash flows and calculating the real return of debt instruments, like T-Bills.
Is annualized yield a 360 day year?
But there are problems inherent with using this annualized yield in determining returns. For one thing, this yield uses a 360-day year to calculate the return an investor would receive. But this doesn't take into account the potential for compounded returns .
