
[8]
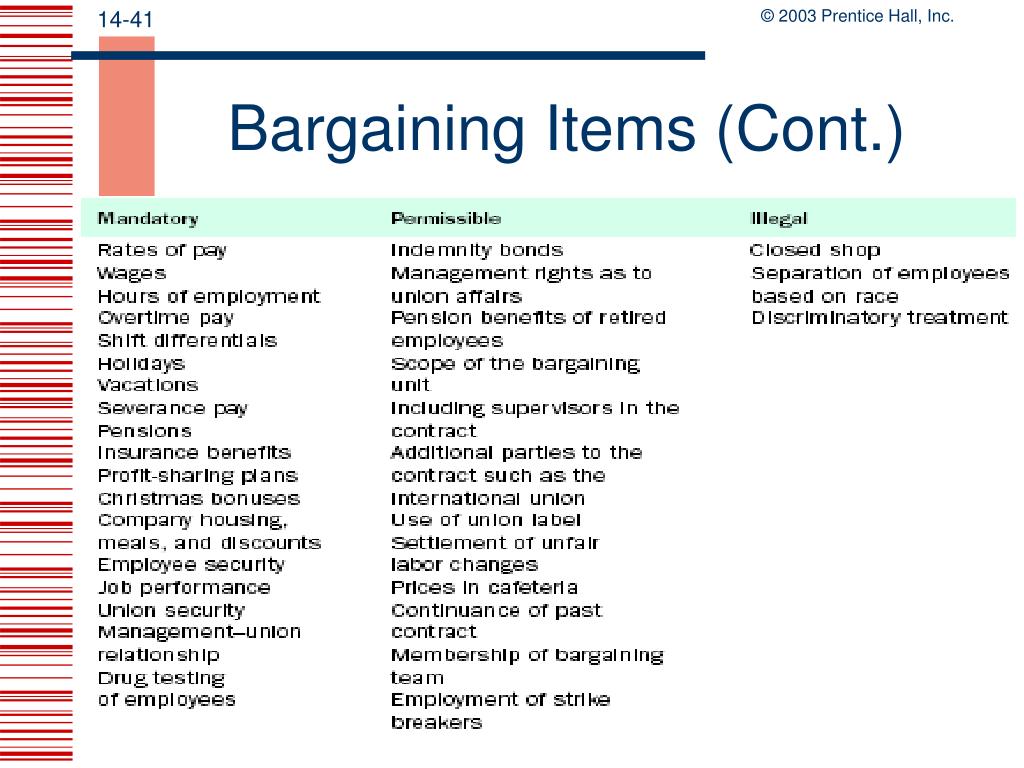
- Mandatory subjects, broadly speaking, relate to wages, hours, pensions, healthcare and working conditions. ...
- Permissive subjects are non-mandatory subjects of bargaining, meaning employers are not required to bargain over them. ...
- Finally, illegal bargaining subjects are those that violate the NLRA, such as a closed-shop provision in a right-to-work state. ...
What are the mandatory subjects of bargaining?
Some Mandatory Subjects of Bargaining That Might Surprise You: What constitutes “wages, hours and terms and conditions of employment” for purposes of deciding whether a subject is a mandatory or permissive subject of bargaining is determined on a case-by-case basis. Wages and hours are clearly covered by a duty to bargain.
What is an illegal subject of collective bargaining?
Insist to impasse on an illegal subject of bargaining, or include an illegal clause in a collective-bargaining agreement. Illegal subjects include, for example, closed-shop provisions, hiring-hall provisions granting referral preference for union members, and provisions inconsistent with your duty of fair representation.
Can a collective bargaining agreement be conditioned on a permissive subject?
In contrast, the law prohibits both the employer and the union from conditioning a collective bargaining agreement on the other party’s acceptance of a proposal on a permissive subject of bargaining. The bargaining parties also cannot make agreement on a permissive subject a condition to agreement on a mandatory subject.
Can a Union refuse to sign a collective bargaining agreement?
A union must bargain in good faith on behalf of employees it represents, and it is unlawful for a union to fail to do so. Examples of failing to do so include insisting to impasse on a nonmandatory subject of bargaining, or reaching a collective-bargaining agreement with an employer but then refusing to sign it.
What are the three categories of collective bargaining?
How does collective bargaining work?
What is the importance of collective bargaining?
What are the three main categories of bargaining topics?
How many steps are involved in collective bargaining?
When does a strike occur?
Why is it important to have a positive relationship with a union?
See 4 more
About this website
Which of the following is a mandatory subject during collective bargaining?
Mandatory subjects are those that directly affect – wages, hours or working conditions (or terms and conditions of employment). Both parties must bargain these subjects if either party submits a proposal that addresses these subjects.
Why is collective bargaining illegal?
Is Collective Bargaining Illegal? Collective bargaining is not illegal. According to the International Labour Organization, employers have the right to form unions to represent them and their interests and the right to collective bargaining.
What are the 3 major topics covered during collective bargaining?
There are three main classification of bargaining topics: mandatory, permissive, and illegal. Wages, health and safety, management rights, work conditions, and benefits fall into the mandatory category. Permissive topics are those that are not required but may be brought up during the process.
What are non mandatory subjects of bargaining?
Permissive subjects include, for example, unit scope, selection of a bargaining representative, internal union affairs, and settlement of unfair labor practice charges. Insist to impasse on a proposal concerning an illegal subject of bargaining, or include an illegal clause in a labor contract.
What are the 5 mandatory subjects of bargaining?
Examples of subjects that are mandatory for bargaining include wages, benefits such as health care and pension, grievance and arbitration procedures, contract length, seniority, union security clauses, strikes and lock outs, management rights clauses, and other terms and conditions of employment.
What are the 5 core steps of collective bargaining?
The 5 Stages of Collective BargainingPreparing for bargaining. ... Conducting negotiations. ... Ratifying the contract. ... Resolving a contract dispute. ... Changing or clarifying the contract.
What is the difference between mandatory and permissive bargaining items?
Mandatory – both parties (management and labor) have a statutory obligation to bargain these subjects. Permissive– both parties may choose to (or refuse to) bargain these subjects. Illegal– both parties must refrain from bargaining these subjects.
What is involved in the collective bargaining process?
Collective bargaining is the process in which working people, through their unions, negotiate contracts with their employers to determine their terms of employment, including pay, benefits, hours, leave, job health and safety policies, ways to balance work and family, and more.
What are the three types of bargaining issues?
Bargaining issues are divided into three basic categories: mandatory, permissive and illegal subjects of bargaining. Mandatory issues of bargaining are those subjects that directly impact "wages, hours or working conditions." These subjects have also been referred to as those that "vitally affect" employees.
What is mandatory subject?
A compulsory subject is one within your program structure that must be completed in order to fulfil the requirements of the program. You will not be eligible to graduate unless you meet all of the requirements for your program.
Is an illegal subject for collective bargaining quizlet?
Union security is an illegal subject for collective bargaining.
Are video cameras a mandatory subject of bargaining?
Installation and use of video surveillance cameras is a mandatory subject of collective bargaining and is an unfair labor practice if bargaining does not occur prior to their installation.
Is collective bargaining a human right?
The right to collectively bargain is recognized through international human rights conventions. Article 23 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights identifies the ability to organize trade unions as a fundamental human right.
What are collective bargaining issues?
Typical issues on the bargaining agenda include wages, working time, training, occupational health and safety and equal treatment. The objective of these negotiations is to arrive at a collective agreement that regulates terms and conditions of employment.
Is collective bargaining a constitutional right?
What laws protect the right to collective bargaining? The National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) is the federal statute that grants most private sector employees the right to join a union and engage in collective bargaining.
Are collective agreements legally enforceable?
Not only are collective agreements presumed not to be intended to be legally enforceable unless they are in writing and contain a provision to that effect, but provisions exist that the same shall apply to any part(s) of such agreement.
Collective Bargaining Process: 7 Step by Step Process
ADVERTISEMENTS: Everything you need to know about the process of collective bargaining. Collective bargaining is a process by which employers and employees confer in good faith and come to an understanding about the terms and conditions of work and other related aspects. The objective of bargaining is to settle matters on discussion tables with mutual […]
STRATEGIC COLLECTIVE BARGAINING - International Labour Organization
MODULE 1 - INTRODUCTION 2 c. Module 3: The Law Complying with the law is critical for successful collective bargaining and also offers the prospect of improving commercial outcomes for employers in many
4 Strategies for Collective Bargaining in Today’s Economy
Gary Furlong has extensive experience in labour mediation, alternative dispute resolution, negotiation, and conflict resolution. He has delivered collective bargaining negotiation skills training for both management and union bargaining teams across Canada, bringing a strong focus of effective and collaborative skills to the table.
What is an illegal subject in a collective bargaining agreement?
Illegal subjects include, for example, closed-shop provisions, hiring-hall provisions granting referral preference for union members, and provisions inconsistent with your duty of fair representation.
How long does it take to terminate a collective bargaining agreement?
Terminate or modify a collective-bargaining agreement without giving notice to federal and state mediators within 30 days (60 days if collective bargaining involves employees of a healthcare institution) of serving written notice on the employer that you are terminating or modifying the contract.
How long do you have to strike a contract?
Engage in a strike before 60 days (90 days if collective bargaining involves employees of a healthcare institution) have passed after you serve written notice on the employer that you are terminating or modifying the contract or before the expiration date of the contract, whichever is later. Failure to comply renders strikers vulnerable to discharge. (Does not apply to unfair labor practice strikes.)
What are some examples of unions failing to do so?
Examples of failing to do so include insisting to impasse on a nonmandatory subject of bargaining, or reaching a collective-bargaining agreement with an employer but then refusing to sign it.
How much notice do you need to give to a mediator?
Give at least 30 days notice to federal and state mediators of the existence of a dispute, where you are bargaining for an initial collective-bargaining agreement.
What is Section 8 D?
Section 8 (d) of the Act sets forth what is encompassed within the duty to bargain collectively. Section 8 (b) (3) of the Act makes it unlawful for a labor organization or its agents to refuse to bargain collectively with an employer whose employees you represent. For example, you may not
What does it mean to strike an employer?
Engage in a strike to pressure an employer to consent to a midterm contract modification.
What is collective bargaining?
Collective bargaining rights. The National Labor Relations Act gives you the right to bargain collectively with your employer through a representative that you and your coworkers choose. What does that mean?
What happens when negotiations reach an impasse?
If negotiations reach an impasse, an employer can impose terms and conditions so long as it offered them to the union before impasse was reached. Once a contract is in place, neither party may deviate from its terms without the other party’s consent, absent extraordinary circumstances.
What are mandatory bargaining issues?
Mandatory bargaining issues refer to subjects or issues that directly affect the terms and conditions of employment with examples such as wages pay for training, promotions, and bonuses (Degni et al. 35). These are the issues that the two parties (employer and employee) must bargain over in case a proposal is made. The employee must be part of a union which will put forward the proposal for example wage increment. The duty to bargain is only limited to the mandatory subjects, and in other cases, the parties are free to bargain or not to bargain and to agree or not to agree (Degni et al. 37). Mandatory bargaining issues fall in the statutory phrase and are meant to settle the aspect of the relationship between employers and employees. The two parties do not have to necessarily reach an agreement when a proposal is made although they must bargain in good faith over the subject (Degni et al. 37). Subjects such as pensions and job duties may be considered as non-issues, yet they are the are the primary causes of strikes, hence the need to address them once they arise.
What is the process of negotiating a lawfully binding agreement between a union and an employer?
Bargaining is the process of negotiating a lawfully binding agreement between a union and an employer, with the focus on overseeing the wages, working hours and the other terms and conditions of employment. For bargaining to take place successfully, the subjects or issues raised have to be categorized as mandatory, voluntary, or illegal (Degni et al. 32).
Why was the closed shop agreement banned?
41). This is because of the belief that all employees received greater benefits from collective bargaining overseen by closed shops as compared to individual employees.
What are some examples of mandatory bargaining?
Other less than obvious mandatory subjects of bargaining include, for example, employee background checks, discipline policies (including what constitutes grounds for discipline), free-meal policies, changes to policies regarding transportation to work, requirements that employees sign in and out of work, and relocation decisions.
Why are unilateral changes in working conditions unlawful?
Commonly seen unilateral changes in working conditions that may be unlawful because they involve mandatory subjects of bargaining include changes to policies such as harassment policies and work rules . By way of example, suppose in the second year of a three-year agreement, management suddenly decides to announce a work rule banning all iPads and cell phones onstage during rehearsals, claiming that they are a distraction to other musicians and an annoyance to the conductor. Is this a mandatory subject of bargaining? Most likely it is. It directly impacts the terms and conditions of employment. This sort of work rule change is not intrinsically within management’s rights. Employers need to bargain about changes in working conditions before implementing them. Most collective bargaining agreements contain dozens of rules regulating rehearsals, and this one is no different. The employer must bargain about changes to those rules, assuming the employer has not waived the right to make such changes during the midterm of a contract and assuming the union has not granted the employer an overly broad management rights clause that allowed the employer to make such unilateral changes.
What are permissive subjects?
A frequently encountered permissive topic is the scope of who is in the bargaining unit and the work encompassed in the bargaining unit. Determining the inclusion or exclusion of employees covered by the contract is a permissive topic of bargaining regardless of whether the unit was certified by the National Labor Relations Board (“NLRB”) or whether the employer voluntarily agreed to recognize the unit. The rationale behind finding this topic a permissive subject of bargaining is really to protect the union. For example, in one case where the company was found to violate the law when it insisted on changes that limited the scope of employees who were covered by the agreement, a court stated that if an employer could require bargaining over the scope of the unit, “an employer could use its bargaining power to restrict (or extend) the scope of union representation in derogation of employees’ guaranteed right to representatives of their own choosing.” Sometimes it is not clear on the face of a proposal that it is really affecting unit composition because the employer claims, for example, that it really addresses work assignments. However, if the sole effect of the proposal is to exclude a group of employees from the bargaining unit, it is a permissive subject of bargaining and neither party can bargain to impasse on it.
What is the NLRA?
Under the National Labor Relations Act (“NLRA” or “ Act”), an employer must bargain collectively with the representative of its employees over matters affecting “wages, hours, and other terms and conditions of employment.”. Generally, once the parties reach a good-faith impasse, the employer may implement any change in a mandatory subject reasonably ...
Can a party make a permissive subject a condition to a mandatory subject?
The bargaining parties also cannot make agreement on a permissive subject a condition to agreement on a mandatory subject. It is an unfair labor practice for either party to insist to impasse on a permissive subject of bargaining. Under certain circumstances, the insistence to impasse on bargaining demands about permissive bargaining subjects ...
Can unions agree on permissive topics of bargaining?
It is fine for either party to make proposals on permissive topics of bargaining. However, insisting on those proposals to the point of impasse or making them part and parcel of a package deal is not permitted.
Can a union waive its right to bargain?
A union can waive its right to bargain over mandatory subjects during the term of a contract, but only if the waiver is “clear and unmistakable.”. In contrast, the law prohibits both the employer and the union from conditioning a collective bargaining agreement on the other party’s acceptance of a proposal on a permissive subject of bargaining. ...
What are the mandatory subjects of bargaining?
These terms are called “mandatory subjects of bargaining”, and generally include provisions relating to “wages, hours, and other conditions of employment”.
What is mid term bargaining?
Mid-term Bargaining. If either the employer or the union wishes to alter a mandatory subject of bargaining during the effective term of the collective bargaining agreement (“CBA”), neither may do so unilaterally. If both parties agree, they may enter into a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) containing the new negotiated term, which would be effective until the adoption of a new CBA. However, if it’s agreed to reopen portions of the contract for negotiations, the parties must bargain as you would when there is no contract in place. This means that you may implement your proposals if the parties have reached impasse or impose a lockout, and the union can strike. For issues that may be expected to change significantly during the term of a CBA, such as health insurance contributions, the parties may wish to negotiate a “reopener” clause with respect to those specific issues, which would automatically impose a bargaining obligation upon the occurrence of certain pre-defined events, such as the passage of two years, or the employer’s health care premium increase in excess of a predetermined percentage from one year to the next.
What is management rights clause?
Most CBAs contain a “management rights clause”, the purpose of which is to leave matters not specified in the contract to be determined by the employer. Thus, if you’re contemplating a change to your business operations that is not susceptible to effects bargaining and not counter to any specific language in the CBA, you’ll want to check to see if it is a right that has been allotted to management in your CBA’s management rights clause. For example, even though implementation of a drug testing program would ordinarily be viewed as a mandatory subject of bargaining, if a management rights clause specifies circumstances under which the employer may insist on drug testing, the employer is free to act unilaterally within the scope defined by that management rights provision.
What are the three categories of collective bargaining?
There are three main classification of bargaining topics: mandatory, permissive, and illegal. Wages, health and safety, management rights, work conditions, and benefits fall into the mandatory category. Permissive topics are those that are not required but may be brought up during the process. An example might include the requirement of drug testing for candidates or the required tools that must be provided to the employee to perform the job, such as a cellular phone or computer. It is important to note that while management is not required by labor laws to bargain on these issues, refusing to do so could affect employee morale. We can also classify bargaining issues as illegal topics, which obviously cannot be discussed. These types of illegal issues may be of a discriminatory nature or anything that would be considered illegal outside the agreement.
How does collective bargaining work?
The collective bargaining process can take time. Both parties prepare for the process by gathering information and reviewing the old contract. They then set time lines for the bargaining and reveal their wants and negotiate those wants. A bargaining impasse occurs when members cannot come to an agreement.
What is the importance of collective bargaining?
Another important point in the collective bargaining process is the aspect of union security. Obviously, it is in the union’s best interest to collect dues from members and recruit as many new members as possible. In the contract, a checkoff provision may be negotiated.
What are the three main categories of bargaining topics?
There are three main classification of bargaining topics: mandatory, permissive, and illegal. Wages, health and safety, management rights, work conditions, and benefits fall into the mandatory category. Permissive topics are those that are not required but may be brought up during the process.
How many steps are involved in collective bargaining?
The collective bargaining process has five main steps; we will discuss each of these steps next. The first step is the preparation of both parties. The negotiation team should consist of individuals with knowledge of the organization and the skills to be an effective negotiator. An understanding of the working conditions and dissatisfaction with working conditions is an important part of this preparation step. Establishing objectives for the negotiation and reviewing the old contract are key components to this step. The management team should also prepare and anticipate union demands, to better prepare for compromises.
When does a strike occur?
When a bargaining impasse occurs, a strike or lockout of workers can occur. An economic strike occurs during negotiations, while an unfair labor practices strike can occur anytime, and during negotiations. A sick-out can also be used, when workers call in sick for the day. These strategies can be used to encourage the other side to agree to collective bargaining terms.
Why is it important to have a positive relationship with a union?
Because as managers and HR professionals we will be working with members of the union on a daily basis, a positive relationship can not only assist the day-to-day operations but also create an easier bargaining process. Solicitation of input from the union before decisions are made can be one step to creating this positive relationship. Transparent communication is another way to achieve this goal.
