
- Significance. The true ankle joint is made up of the tibia, which is on the inside, the fibula on the outside and the talus, which is the underneath part of ...
- Features. The ankle mortise features three articulations or "movable joints between bones." They are the fibular latural malleolar, on one side, and the tibial medial malleolar on the other side.
- Function. Two tough ligaments support the mortise. The cylindrical shape of the ankle bone rolls within the mortise.
- Benefits. The mortise is beneficial to the range of motion of the ankle. The ankle goes up and down in the mortise, forming a pivot.
- Warning. Ankle injuries happen when the foot rolls onto the outside of the ankle. ...
What does mortise joint mean?
mortise joint, mortise-and-tenon joint noun. a joint made by inserting tenon on one piece into mortise holes in the other
How tight should a mortise and tenon joint be?
Here’s how I did it:
- Cut mortise
- Mark for tenon off mortise
- Cut tenon using dado set or box joint blade on the tablesaw
- Final fitting with shoulder and rabbet planes
How to make mortise and tenon joints with hand tools?
Tenon is the male, mortise is the female. to make tenon joint we only need a saw and some rulers and markers. hand saw are slow so we use table saw. make a mark, set the side bar and cut it in both sides. do this process to cut loose the exces wood until you only have one in the middle. you might have to clean the excess wooden cut with sharp ...
What is mortise view of ankle?
- laterally to the skin margins
- superiorly to examine the distal third of the tibia and fibula
- inferior to the proximal aspect of the metatarsals
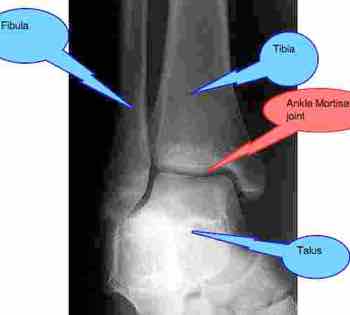
What makes up the mortise of the ankle?
The ankle joint is made up of two joints: the true ankle joint, which moves the foot up and down, and the subtalar joint, which moves the foot from side to side. The ankle mortise is the "hinge" that connects the ends of the tibia and fibula to the talus.
What joints make up the mortise joint?
It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations. It is often described as a tenon and mortise joint, as the tibia and fibula act as a mortise and form a notch in which the body of the talus fits, acting as the tenon....Ankle joint.TypeSynovial hinge joint; uniaxialMovementsDorsiflexion, plantar flexion4 more rows
What are the 3 joints of the ankle?
The true ankle joint is composed of three bones, seen above from a front, or anterior, view: the tibia which forms the inside, or medial, portion of the ankle; the fibula which forms the lateral, or outside portion of the ankle; and the talus underneath.
What is mortise joint in anatomy?
1. mortise joint - a gliding joint between the distal ends of the tibia and fibula and the proximal end of the talus. ankle, ankle joint, articulatio talocruralis. anklebone, astragal, astragalus, talus - the bone in the ankle that articulates with the leg bones to form the ankle joint.
What type of joint is in the ankle?
hinged synovial jointThe ankle joint is a hinged synovial joint with primarily up-and-down movement (plantarflexion and dorsiflexion).
What is another name for the ankle mortise?
The ankle AP mortise (mortice is equally correct) view is part of a three view series of the distal tibia, distal fibula, talus and proximal 5th metatarsal.
What type of joint is primarily found in the ankle and wrist?
(1) Gliding joints move against each other on a single plane. Major gliding joints include the intervertebral joints and the bones of the wrists and ankles. (2) Hinge joints move on just one axis.
Is the ankle joint a saddle joint?
A saddle joint (sellar joint, articulation by reciprocal reception) is a type of synovial joint in which the opposing surfaces are reciprocally concave and convex. It is found in the thumb, the thorax, the middle ear, and the heel....Saddle JointLatinarticulatio sellarisTA98A03.0.00.048TA21560FMA752985 more rows
Is the ankle a pivot joint?
So, the correct answer is 'hinge joint'.
What type of joint is the subtalar joint?
synovial jointThe subtalar (ST) joint is an articulation between two of the tarsal bones in the foot, the talus and calcaneus. The joint is classed structurally as a synovial joint, and functionally as a plane synovial joint.
What type of joint is Talocrural joint?
The talocrural joint is a synovial hinge joint that connects the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus.
What are the different mortises?
There are 4 stages: Pallor Mortis, Algor Mortis, Rigor Mortis and Livor Mortis. Death is one of the most fundamental facts of life.
What are mortise joints used for?
A mortise and tenon is one of the most well-known and useful means to join wood together. Primarily used in solid wood woodworking to join end grain to edge grain. A mortise and tenon joint is, at its most basic, a peg fit into a hole.
How are mortise and tenon joints made?
It is a locked (pegged) mortise and tenon technique that consists of cutting two mortises into the edges of two planks; a separate rectangular tenon is then inserted in the two mortises. The assembly is then locked in place by driving a dowel through one or more holes drilled through mortise side wall and tenon.
What do you need to make a mortise and tenon joint?
C. Woodworking Hand Tools Required for Making a Mortise and Tenon JointBrass wheel marking gauge (update: my new favorite)6-Inch Combination Square.Dovetail Saw.Carcass Back Saw.Joiner's Mallet.Pig Sticker Mortise Chisel.Marking Knife.Woodworking Clamps.More items...
What are the three articulations of the ankle mortise?
The ankle mortise features three articulations or "movable joints between bones." They are the fibular latural malleolar, on one side, and the tibial medial malleolar on the other side. The tibial dome is above the mortise.
What flexes the hips and extends the knees?
What Flexes the Hips & Extends the Knees? The ankle joint is made up of two joints: the true ankle joint, which moves the foot up and down, and the subtalar joint, which moves the foot from side to side. The ankle mortise is the "hinge" that connects the ends of the tibia and fibula to the talus.
What is the tibia on the inside of the ankle?
The true ankle joint is made up of the tibia, which is on the inside, the fibula on the outside and the talus, which is the underneath part of the joint. The subtalar joint consists of the talus on the top and the calcaneus on the bottom.
Why do ankles hurt when walking?
Ankles are prone to this type of injury because of the small size of the joint in comparison to the leg and foot. You should pay attention to the surface of which you are walking, running or jumping.
Who is Angela Robinson?
Center for Holistic Instruction: The Ankle. Writer Bio. Angela Robinson is a work at home mom who is currently pursuing a career in freelance writing. She enjoys the challenge of researching and writing on topics such as home and garden, travel, education and health issues.
What muscle is used to eversion of the ankle joint?
The peroneus longus and Peroneus Brevis muscles, found in the lateral compartment of the leg, function to facilitate eversion of the ankle joint.
What ligaments are responsible for lateral motion?
The lateral ligaments stabilize the ankle, and serve as a guide to direct ankle motion by attaching the lateral malleolus to the bones below the ankle joint. They are responsible for resistance against inversion and internal rotation stress.
Which muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle joint?
The tibialis anteriormuscle, found in the anterior compartment of the leg, is the primary muscle that facilitates dorsiflexion of the ankle joint. The peroneus longusand Peroneus Brevismuscles, found in the lateral compartment of the leg, function to facilitate eversion of the ankle joint. [1]
Which part of the ankle joint forms the lateral border of the ankle joint?
The articular facet of the lateral malleolus (bony prominence on the lower fibula) forms the lateral border of the ankle joint
What joint is formed by the articulation of the talus, tibia, and fibula?
The ankle joint is a hinged synovial jointthat is formed by the articulation of the talus, tibia, and fibulabones. Together, the three borders (listed below) form the ankle mortise. The articular facet of the lateral malleolus (bony prominence on the lower fibula) forms the lateral border of the ankle joint.
What is the medial malleolus?
The articular facet of the medial malleolus (bony prominence on the lower tibia) forms the medial border of the joint. The superior portion of the ankle joint forms from the inferior articular surface of the tibia and the superior margin of the talus.
How long does it take for an ankle fracture to heal?
Patients typically present with pain, swelling, and inability to bear weight on the ankle joint. Management of stable fractures includes a short leg cast for 4 to 6 weeks. Unstable fractures require an open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) to restore a congruent mortise and fibular length.
What are the different types of talus?
The body of the talus fits snugly into the mortise formed by the bones of the leg. The articulating part of the talus is wedge shaped – it is broad anteriorly, and narrow posteriorly: 1 Dorsiflexion – the anterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is more stable. 2 Plantarflexion – the posterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is less stable.
What is the socket of the talus called?
This socket is known as a mortise. The body of the talus fits snugly into the mortise formed by the bones of the leg. The articulating part of the talus is wedge shaped – it is broad anteriorly, and narrow posteriorly: Dorsiflexion – the anterior part of the talus is held in the mortise , and the joint is more stable.
What is the anterior talofibular?
Anterior talofibular – spans between the lateral malleolus and lateral aspect of the talus.
Which part of the talus is held in the mortise?
Dorsiflexion – the anterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is more stable. Plantarflexion – the posterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is less stable. By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 2 – X-ray of a normal ankle joint.
What type of joint is the shin joint?
Functionally, it is a hinge type joint, permitting dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot.
What is a pott's fracture?
A Pott’s fracture is a term used to describe a bimalleolar (medial and lateral malleoli) or trimalleolar (medial and lateral malleoli, and distal tibia) fracture.
Where are inversion and eversion produced?
Eversion and inversion are produced at the other joints of the foot, such as the subtalar joint. Plantarflexion – produced by the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and posterior tibialis).
What is the mortise view?
In Australia, the mortise view is part of a three-part ankle series, yet in other countries, including the United Kingdom, the mortise view is the primary 'AP projection' of the ankle alongside the lateral projection.
What is the AP mortice?
The ankle AP mortise ( mortice is equally correct) view is part of a three view series of the distal tibia, distal fibula, talus and proximal 5 th metatarsal.
How to align the 5th toe?
Aligning the 5 th toe to the center of the calcaneus is a practical way to gauge optimal internal rotation needed to demonstrate the mortise joint. Another way to ensure correct positioning is by rotating the leg internally until the central line of the collimation field is in line with the 5 th metatarsal.
What happens if your foot is not in dorsiflexion?
Often if the foot is not in dorsiflexion, the mortise joint will not be in full profile. In trauma, it is important to obtain a diagnostic mortise view for the proper assessment of the mortise joint.
Where does internal rotation occur?
internal rotation must be from the hip; isolated rotation of the ankle will result in a non-diagnostic image
How do you know if you have a syndesmosis sprain?
Mild to moderate syndesmosis sprains may at first feel like a routine sprained ankle. Symptoms include pain and swelling on the outside of the ankle. If the problem has been ongoing, patients may have pain due to an unstable ankle joint. They may feel vague pain around the ankle.
What is the surgery for syndesmosis?
Surgery for a syndesmosis injury is designed to reduce the separation between the tibia and fibula. If there are no barriers keeping the tibia and fibula apart, the surgeon may simply need to place screws through the two bones to hold them together while the ligaments heal.
What does it mean when your fibula is enlarged?
An enlarged gap between the tibia and fibula indicates a diastasis (mentioned earlier). X-rays are also used to check for other problems, such as a fracture in the leg or ankle. Doctors usually suspect a syndesmosis injury when patients have severe pain that lingers after what was thought to be a routine ankle sprain.
What is the X-ray used to determine if a syndesmosis is severe?
X-rays are used to determine the severity of the syndesmosis injury. Stress X-rays are done to see if the tibia and fibula splay apart.
What is syndesmosis injury?
An ankle syndesmosis injury involves a sprain of one or more of the ligaments that support the ankle syndesmosis. A ligament is made up of multiple strands of connective tissue, similar to a nylon rope. A sprain stretches or tears the ligaments. Minor sprains only stretch the ligament. A tear may be either a complete tear of all the strands of the ligament or a partial tear of only some of the strands. The ligament is weakened by the injury. How much it is weakened depends on the degree of the sprain.
What is the injury of the ankle called?
Introduction. An ankle injury common to athletes is the ankle syndesmosis injury. This type of injury is sometimes called a high ankle sprain because it involves the ligaments above the ankle joint. In an ankle syndesmosis injury, at least one of the ligaments connecting the bottom ends of the tibia and fibula bones (the lower leg bones) ...
What is the connection between the tibia and fibula?
The connection of the lower leg bones, the tibia and fibula, is a syndesmosis. The tibia is the main bone of the lower leg. The fibula is the small, thin bone that runs down the outer edge of the tibia. Only a few joints in the body are syndesmosis joints.

Description
Clinical Significance
- Ankle Fracture -Ankle fractures are common in all ages with the involvement of one or both malleoli. The fracture pattern determines the stability of the fracture. Patients typically present with pain, swelling, and inability to bear weight on the ankle joint. Management of stable fractures includes a short leg cast for 4 to 6 weeks. Unstable fractures require an open reduction and inter…
Motions Available
- Talocrural Joint is a uniaxial hinge joint that has just 1° of Motion
- The reported normal available range for dorsiflexion varies in the literature between 0-16.5o and 0-25o.This changes in weight-bearing.
- The normal range of Plantarflexion has been reported to be around 0°- 50°
Clinical Examination
- Assessment
1. Ankle Joint Assessment Video - Special Tests
1. Kaltenborn Ankle & Foot Examination 2. Anterior Drawer of the Ankle 3. Squeeze Test 4. Talar Tilt Test 5. Kleiger Test
Pathology/Injury
Physiotherapeutic Techniques
- Rehabilitation of ankle injuries should be structured and individualized. 1. In the acute phase, the focus should be on controlling inflammation, reestablishing full range of motion, and gaining strength. 2. Once a pain-free range of motion and weight-bearing has been established, balance-training exercises should be incorporated to normalize neuromuscular control. 3. Advanced-pha…
Return to Activity Specific Training
- For sports persons an example is given below: When pain-free walking is achieved, progress to a regimen of 50% walking and 50% jogging. Using the same criteria, jogging eventually progresses to running, backward running, and pattern running. Circles and figures of 8 are commonly employed patterns. The final phase of the rehabilitation process is the athlete can perform spor…
Resources
- Anatomy of the Ankle Ligaments: A Pictorial Essay- In this pictorial essay, the ligaments around the ankle are grouped, depending on their anatomic orientation, and each of the ankle ligaments is d...