Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Electron pairs shared between atoms of equal or very similar electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside fro…
What happens to the electrons in a completely covalent bond?
When covalent bonding happens, atoms share their valence electrons with other atoms. A type of chemical bond where a pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are not equally shared because one atom spends more time with the electrons than the other atom.
What are 5 examples of covalent bonds?
What are 5 examples of covalent bonds? Examples of Covalent Bonds Hydrogen (H 2 ) Hydrogen (H) is the simplest of all elements. Oxygen (O 2 ) The valency of oxygen (O) is two, which means that it requires two electrons to complete its outermost (valence) shell. Nitrogen (N 2 ) Water (H 2 O) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Methane (CH 4 ) Ammonia (NH 3 ...
What elements make a covalent bond?
Terms in this set (12)
- Nonmetals can bond to other nonmetals by sharing electrons.
- Atoms of some nonmetals can bond with each other.
- Atoms can form single, double, & triple covalent bonds by sharing 1 or more pairs of electron.
How pairs of electrons are involved in a covalent single bond?
In chemistry, a single bond is a chemical bond between two atoms involving two valence electrons. That is, the atoms share one pair of electrons where the bond forms. Therefore, a single bond is a type of covalent bond. When shared, each of the two electrons involved is no longer in the sole possession of the orbital in which it originated.
What type of electrons form covalent bonds?
In a covalent bond, the atoms bond by sharing electrons. Covalent bonds usually occur between nonmetals. For example, in water (H2O) each hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) share a pair of electrons to make a molecule of two hydrogen atoms single bonded to a single oxygen atom.
What molecules form covalent bonds?
Molecules that have covalent linkages include the inorganic substances hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine, water, and ammonia (H2, N2, Cl2, H2O, NH3) together with all organic compounds.
What types of covalent bonds can form between all atoms?
One carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (H) atom....Properties of polar covalent bond:Number of electron pairs sharedType of covalent bond formed1Single2Double3Triple
What are 3 types of covalent bonds?
Types of Covalent BondsSingle Covalent Bond.Double Covalent Bond.Triple Covalent Bond.
How is the covalent bond formed answer?
As pairs of electrons are exchanged between atoms, covalent bonding happens. In order to achieve further stability, which is gained by forming a complete electron shell, atoms can covalently bond with other atoms.
How many types of covalent bonds are there?
There are two basic types of covalent bonds: polar and nonpolar. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are unequally shared by the atoms and spend more time close to one atom than the other.
What causes atoms to form covalent bonds?
Covalent bonding occurs when pairs of electrons are shared by atoms. Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms in order to gain more stability, which is gained by forming a full electron shell. By sharing their outer most (valence) electrons, atoms can fill up their outer electron shell and gain stability.
Which of the following is a covalent molecule?
The Correct Answer is Carbon tetrachloride.
What is a covalent bond?
Covalent bonds are directional where the atoms that are bonded showcase specific orientations relative to one another. Most compounds having covalent bonds exhibit relatively low melting points and boiling points. Compounds with covalent bonds usually have lower enthalpies of vaporization and fusion.
What type of bond is formed by equal sharing of electrons from both the participating atoms?
Covalent Bond. A covalent bond is formed by equal sharing of electrons from both the participating atoms. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called shared pair or bonding pair. The covalent bonds are also termed as molecular bonds. Sharing of bonding pairs will ensure that the atoms achieve stability in their outer shell ...
How is covalent bonding achieved?
Covalent Bonding can be Achieved in two Ways: Sharing of electrons between atoms of the same kind E .g. Formation of H 2 , Cl 2, O 2, etc. Sharing of electrons between atoms of different kind E.g. Formation of CH 4, H 2 O, NH 3, etc.
What are the properties of covalent bonds?
Some of the properties of covalent bonds are: Covalent bonding does not result in the formation of new electrons. The bond only pairs them. They are very powerful chemical bonds that exist between atoms. A covalent bond normally contains the energy of about ~80 kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol).
What type of bond is formed between two metals?
A covalent bond is formed between two similar electronegative non-metals. This type of bond is formed between a metal and non-metal. Bonds formed from covalent bonding have a Definite shape. Ionic Bonds have No definite shape. Low Melting Point and Boiling Point.
What type of bond is between oxygen and carbon?
Since two electron pairs are shared there is a double bond between the two oxygen atoms. Ethylene Molecule: In ethylene, each carbon atom shares two of its valence electron with two hydrogen atoms and remaining two electrons with the other carbon atom. So there is a double bond between the carbon atoms.
Why do covalent bonds have unequal electrons?
This type of covalent bond exists where the unequal sharing of electrons occurs due to the difference in the electronegativity of combining atoms. More electronegative atom will have a stronger pull for electrons. The electronegative difference between the atoms is greater than zero and less than 2.0. As a result, the shared pair of electrons will be closer to that atom.
What is the name of the group of electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond?
The electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called the bonding pair of electrons. These bonding pair of electrons results in the formation of a discrete group of atoms called a molecule —the smallest part of a compound that retains the chemical identity of that compound.
When electrons are equally shared between the combining atoms, a nonpolar covalent bond is formed?
When electrons are equally shared between the combining atoms, a nonpolar covalent bond is formed. This phenomenon happens when there is no difference in the electro negativities of the two combining atoms. That is, to say, identical pairs of atoms form a nonpolar covalent bond. The bond is nonpolar If the electronegativity difference is less than Although oxygen is very electronegative, is not Polar. This is because both atoms have the same electronegativity, and electrons are shared equally between them.
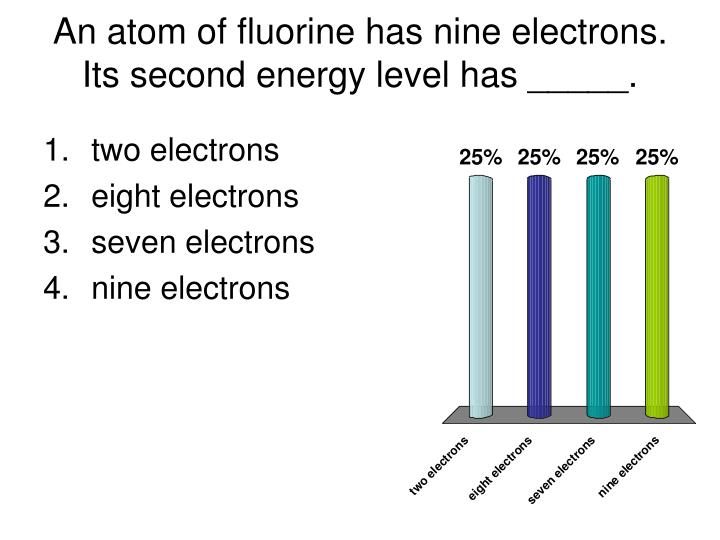
How many electrons does fluorine have?
Like hydrogen, the fluorine molecule is also represented with a dash as shown below-. Each fluorine atom has three pairs of electrons or six electrons, which do not participate in the covalent bonding. These electrons are not shared; hence they are considered to belong to a single atom.
How does each fluorine atom complete its valence shell?
Each fluorine atom completes its valence shell by contributing one valence electron. This leads to the formation of a single bond and giving each atom a complete valence shell. The image above shows that each fluorine atom completes its valence shell and fulfils the octet rule.
What is the purpose of covalent bonding?
Covalent bonding, in simple words, is the sharing of electrons between atoms to attain the noble gas configuration of the participating individual atoms. The atoms in a covalent bond are held together by the electrostatic force of attraction.
How do covalent bonds work?
What is Covalent Bond? 1 Covalent bonding, in simple words, is the sharing of electrons between atoms to attain the noble gas configuration of the participating individual atoms. 2 The atoms in a covalent bond are held together by the electrostatic force of attraction. This force is in between the positively charged nuclei of the bonded atoms and the negatively charged electrons they share. 3 The electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called the bonding pair of electrons. These bonding pair of electrons results in the formation of a discrete group of atoms called a molecule —the smallest part of a compound that retains the chemical identity of that compound. 4 This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements close to each other in the periodic table. This bonding occurs primarily between non-metals; however, it can also be observed between non-metals and metals.
Which compound has a triple bond?
Some molecules in which three pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms contain triple bonds. A simple compound that has a triple bond is nitrogen. Nitrogen is non-metal. Nitrogen belongs to group of the periodic table and has electrons in its outermost shell. In order to attain the noble gas configuration, one nitrogen atom will share three electrons present in its valence shell with another nitrogen atom. This results in the formation of a nitrogen molecule with three covalent bonds.
What type of bond is formed when two atoms share three electrons?
When three pairs of electrons are shared by two participating atoms, a triple bond is formed. Triple covalent bonds are the least stable type of covalent bond and are represented by three dashes.
How are covalent bonds formed?
A covalent bond is formed when electrons from both participating atoms are shared equally. The pair of electrons involved in this type of bonding is known as a shared pair or bonding pair. Molecular bonds are another name for covalent bonds. The sharing of bonding pairs will ensure that the atoms achieve stability in their outer shell, similar to noble gas atoms.
What is the difference between covalent and ionization bonds?
A covalent Bond refers to such an association formed by the sharing of electron pairs among different or similar kinds.
What type of bond is a dative covalent bond?
Coordinated or Dative Covalent Bond: This type of bond occurs when one of the atoms in the bond provides electrons for sharing. This is accomplished through the reaction of ammonia and boron trifluoride. Nitrogen has two free electrons, whereas boron lacks electrons. They complete their last shell with eight electrons by combining nitrogen and boron.
What type of bond exists when the electronegativity of combining atoms differs, resulting in une?
This type of covalent bond exists when the electronegativity of combining atoms differs, resulting in unequal electron sharing. Electrons will be drawn to more electronegative atoms. The atoms’ electronegative difference is greater than zero but less than 2.
How many electrons does nitrogen have?
This is accomplished through the reaction of ammonia and boron trifluoride. Nitrogen has two free electro ns, whereas boron lacks electrons. They complete their last shell with eight electrons by combining nitrogen and boron.
How many electron pairs can an atom share?
If sharing a single electron pair between atoms does not satisfy an atom’s normal valence, the atoms may share more than one electron pair between them. Covalent bonds have the following properties:
What are some examples of covalent bonds?
Covalent compounds also are known as molecular compounds. Organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, are all examples of molecular compounds. You can recognize these compounds because they consist of nonmetals bonded to each other.
How do covalent bonds form?
Covalent bonds form when two nonmetallic atoms have the same or similar electronegativity values. So, if two identical nonmetals (e.g., two hydrogen atoms) bond together, they will form a pure covalent bond. When two dissimilar nonmetals form bonds (e.g., hydrogen and oxygen), they will form a covalent bond, but the electrons will spend more time closer to one type of atom than the other, producing a polar covalent bond.
Why can you recognize covalent bonds?
You can recognize these compounds because they consist of nonmetals bonded to each other. So, for example, you would not expect to find covalent bonds in a metal or alloy, such as silver, steel, or brass. You would find ionic rather than covalent bonds in a salt, such as sodium chloride.
Is silver ionic or covalent?
So, for example, you would not expect to find covalent bonds in a metal or alloy, such as silver, steel, or brass. You would find ionic rather than covalent bonds in a salt, such as sodium chloride.
How do covalent bonds form?
A covalent bond forms when two non-metal atoms share a pair of electrons. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. An atom that shares one or more of its electrons will complete its outer shell. Covalent bonds are strong – a lot of energy is needed to break them.
Which substances have strong covalent bonds?
Substances with covalent bonds often form molecules with low melting and boiling points, such as hydrogen and water. These substances have strong covalent bonds within the molecules (between the atoms), but weak intermolecular forces between the molecules.
What is the bond between a hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom?
The slideshow shows a covalent bond being formed between a hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom, to form hydrogen chloride.
How many covalent bonds does hydrogen form?
Hydrogen forms one covalent bond. The noble gases in Group 0 do not form any.
When a metal element reacts with a non-metal element, an ionic compound is formed?
When a metal element reacts with a non-metal element an ionic compound is formed. When a non-metal element reacts with a non-metal element a covalent bond is formed. An understanding of the way the elements are bonded allows us to explain their typical properties.
Is chlorine stable after bonding?
next. 2. The hydrogen atom has bonded with the chlorine atom, meaning there is now a shared pair of electrons. After bonding, the chlorine atom is now in contact with eight electrons in its outer shell, so it is stable. The hydrogen atom is now in contact with two electrons in its outer shell, so it is also stable.
Do covalent bonds require energy?
Both nuclei are strongly attracted to the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond, so covalent bonds are very strong and require a lot of energy to break.
How are covalent bonds formed?
Single covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of a single pair of electrons by the participating atoms. A single covalent bond is indicated by (-).
Which type of bond is formed between two atoms with similar electronegativities?
The two atoms involved in the formation of the covalent bond should be electronegative, and true covalent bonds are formed between atoms with similar electronegativities.
Why do covalent compounds not dissolve in polar solvents?
Some covalent compounds might dissolve in water due to the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water molecules. The insolubility of covalent compounds in polar solvents is due to the lack of polarity of the bond.
Why are covalent bonds directional?
4. Directional nature. Covalent bonds are directional in nature due to the overlapping of certain orbitals that are oriented towards a particular axis. The overlapping of the orbitals determine the strength of the bond and thus, effective overlapping result in stronger bonds.
What type of bond is between the same or different elements?
The covalent bond is a type of chemical bond between the atoms of the same or different elements by the mutual sharing of pairs of electrons.
Why do atoms share electrons?
Like in all forms of bonding, atoms involved in covalent bonding share electrons in order to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
How many states of matter can covalent compounds exist?
Covalent compounds can exist in all three states of matter depending on the type and number of covalent bonds present between atoms.
How to explain covalent bonds?
Covalent bonds can be understood using the simple example of a molecule, which consists of one electron in the electric field of two protons. This system can be modeled by an electron in a double square well ( (Figure) ). The electron is equally likely to be found in each well, so the wave function is either symmetric or antisymmetric about a point midway between the wells.
What type of bond is formed when electrons transfer from one atom to another?
Types of Bonds. Chemical units form by many different kinds of chemical bonds. An ionic bond forms when an electron transfers from one atom to another. A covalent bond occurs when two or more atoms share electrons.
How to determine the energy of a molecule?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 Distinguish between the different types of molecular bonds 2 Determine the dissociation energy of a molecule using the concepts ionization energy, electron affinity, and Coulomb force 3 Describe covalent bonding in terms of exchange symmetry 4 Explain the physical structure of a molecule in terms of the concept of hybridization
What happens to the electrons after the electron transfer from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom?
After the electron transfers from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom, the sodium atom becomes a positive ion and the chlorine atom becomes a negative ion. The total energy required for this transfer is given by. The positive sodium ion and negative chloride ion experience an attractive Coulomb force.
What type of bond is NaCl?
The ionic bond is perhaps the easiest type of bonding to understand. It explains the formation of salt compounds, such as sodium chloride, NaCl. The sodium atom (symbol Na) has the same electron arrangement as a neon atom plus one 3 s electron. Only 5.14 eV of energy is required to remove this one electron from the sodium atom. Therefore, Na can easily give up or donate this electron to an adjacent (nearby) atom, attaining a more stable arrangement of electrons. Chlorine (symbol Cl) requires just one electron to complete its valence shell, so it readily accepts this electron if it is near the sodium atom. We therefore say that chlorine has a large electron affinity, which is the energy associated with an accepted electron. The energy given up by the chlorine atom in this process is 3.62 eV. After the electron transfers from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom, the sodium atom becomes a positive ion and the chlorine atom becomes a negative ion. The total energy required for this transfer is given by
Why is van der Waals bond weaker than ionic bond?
A van der Waals bond occurs due to the attraction of charge-polarized molecules and is considerably weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. Many other types of bonding exist as well. Often, bonding occurs via more than one mechanism. The focus of this section is ionic and covalent bonding.
How does the energy of sodium and chloride move?
As the sodium and chloride ions move together (“descend the potential energy hill”), the force of attraction between the ions becomes stronger. However, if the ions become too close, core-electron wave functions in the two ions begin to overlap. Due to the exclusion principle, this action promotes the core electrons—and therefore the entire molecule—into a higher energy state. The equilibrium separation distance (or bond length) between the ions occurs when the molecule is in its lowest energy state. For diatomic NaCl, this distance is 0.236 nm. (Figure) shows the total energy of NaCl as a function of the distance of separation between ions.