What is an OSI network layer?
Network The third layer of the OSI model organizes and transmits data between multiple networks. The network layer is responsible for routing the data via the best physical path based on a range of factors including network characteristics, best available path, traffic controls, congestion of data packets, and priority of service, among others.
What is the 6th layer of the OSI model?
The sixth layer of the OSI model converts data formats between applications and the networks. Responsibilities of the presentation layer include: The presentation layer, also called the syntax layer, maps the semantics and syntax of the data such that the received information is consumable for every distinct network entity.
What is layer 4 transport in OSI model?
4. Transport. The fourth layer of the OSI model ensures complete and reliable delivery of data packets. The transport layer provides mechanisms such as error control, flow control, and congestion control to keep track of the data packets, check for errors and duplication, and resend the information that fails delivery.
Which OSI layers are combined into one application layer in TCP?
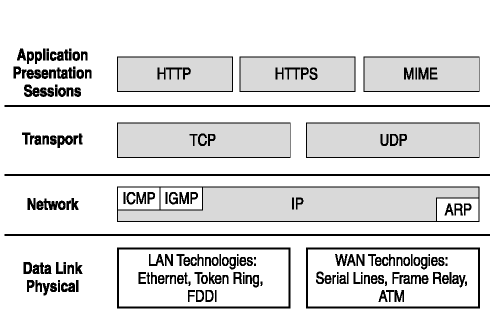
OSI layers 5, 6, 7 are combined into one Application Layer in TCP/IP OSI layers 1, 2 are combined into one Network Access Layer in TCP/IP – however TCP/IP does not take responsibility for sequencing and acknowledgement functions, leaving these to the underlying transport layer.

What layer of OSI is packet?
the network layerA packet is a data fraction transmitted over the network layer. The network layer encapsulates segments from the transport layer. Its primary aim is to forward packets to routers within interconnected, heterogeneous networks.
Where are packets in the OSI model?
the network layerIn the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, packet strictly refers to a protocol data unit at layer 3, the network layer.
Which layers are using packet?
Network-to-network connections are what make the Internet possible. The "network layer" is the part of the Internet communications process where these connections occur, by sending packets of data back and forth between different networks. In the 7-layer OSI model (see below), the network layer is layer 3.
Which layer of OSI model are responsible for routing of data packets and encryption of data?
Presentation- The sixth layer of the OSI model, responsible for translation, encryption, authentication, and data compression.
Which layer of the OSI model is used to forward packets on the network quizlet?
Layer three of the OSI model is the network layer. The network layer creates and sends packets from source network to destination network. It provides consistent end-to-end packet delivery services and control information. It creates and uses layer 3 addresses for use in path determination and to forward packets.
What is layer 3 of the OSI model?
Layer 3 of the OSI Model: Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from a source host on one network to a destination host on a different network, while maintaining the quality of service requested by the transport layer (in contrast to the data link ...
Which layer of the OSI model is responsible for converting the packet to an electrical signal that will be placed on the wire?
Within the semantics of the OSI model, the physical layer translates logical communications requests from the data link layer into hardware-specific operations to cause transmission or reception of electronic (or other) signals.
Which of the following OSI layers is responsible for node to node routing of packets?
The data link layerThe data link layer is responsible for the node-to-node delivery of the message. The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error-free from one node to another, over the physical layer.
What does OSI stands for?
OSI stands for Open Sytems Interconnection.
What is OSI Model?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model is a conceptual framework that describes functions of the networking or telecommunication sy...
What are the 7 layers of OSI model?
PhysicalData LinkNetworkTransportSession PresentationApplication
What is the physical layer of OSI?
The physical layer is the first and bottom-most layer of the OSI Reference Model. It mainly provides the bitstream transmission. It also characterizes the media type, connector type and signal type to be used for communication.
Which layer of the network is responsible for routing data packets from the source to destination host?
The network layer is the third layer from the bottom. This layer has the accountability to accomplish the routing of data packets from the source to destination host between the inter and intra networks operating on the same or different protocols.
What is UDP protocol?
It also supports client/server model for communication. UDP is a connectionless and unreliable protocol. Once data is transmitted between two hosts, the receiver host doesn’t send any acknowledgment of receiving the data packets. Thus the sender will keep on sending data without waiting for an acknowledgment.
What is the subnet mask for 192.168.1.0?
For the above Example, by using a subnet mask 255.255.255.0, we get to know that the network ID is 192.168.1.0 and the host address is 0.0.0.64. When a packet arrives from 192.168.1.0 subnet and has a destination address as 192.168.1.64, then the PC will receive it from the network and process it further to the next level.
What is the presentation layer?
As suggested by the name itself, the presentation layer will present the data to its end users in the form in which it can easily be understood. Hence, this layer takes care of the syntax, as the mode of communication used by the sender and receiver may be different.
What is the easiest way out between the sender and the receiver?
The answer is very simple that it finds out the easy, shortest, and time-efficient way out between the sender and the receiver to exchange data using routing protocols, switching, error detection and addressing techniques.
Which layer of OSI model is responsible for routing data between multiple networks?
Network. The third layer of the OSI model organizes and transmits data between multiple networks. The network layer is responsible for routing the data via the best physical path based on a range of factors including network characteristics, best available path, traffic controls, congestion of data packets, and priority of service, among others.
What is the second layer of OSI?
Hardware including networking devices, antennas, cables, modem, and intermediate devices such as repeaters and hubs. 2. Data Link. The second layer of the OSI model concerns data transmission between the nodes within a network and manages the connections between physically connected devices ...
Why is the OSI model so criticized?
The OSI model is widely criticized for an inherent implementation complexity that renders networking operations inefficient and slow. The academic approach to developing the OSI protocol suite relied on replacing existing protocols across all communication layers with better alternatives.
Why was the OSI model developed?
The OSI model was originally developed to facilitate interoperability between vendors and to define clear standards for network communication. However, the older TCP/IP model remains the ubiquitous reference framework for Internet communications today.
What is the application layer?
The application layer concerns the networking processes at the application level. This layer interacts directly with end-users to provide support for email, network data sharing, file transfers, and directory services, among other distributed information services. The upper most layer of the OSI model identifies networking entities to facilitate networking requests by end-user requests, determines resource availability, synchronizes communication, and manages application-specific networking requirements. The application layer also identifies constraints at the application level such as those associated with authentication, privacy, quality of service, networking devices, and data syntax.
What is the OSI reference model?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model is a conceptual framework that describes functions of the networking or telecommunication system independently from the underlying technology infrastructure. It divides data communication into seven abstraction layers and standardizes protocols into appropriate groups of networking functionality to ensure interoperability within the communication system regardless of the technology type, vendor, and model.
Which layer of OSI is responsible for the transmission of unstructured raw data streams over a physical medium?
The physical layer is responsible for the communication of unstructured raw data streams over a physical medium.
Which layer of OSI is responsible for the physical connection between devices?
Physical Layer (Layer 1) : The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer. It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. The physical layer contains information in the form of bits. It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the next.
What is the application layer in OSI?
At the very top of the OSI Reference Model stack of layers, we find Application layer which is implemented by the network applications. These applications produce the data, which has to be transferred over the network. This layer also serves as a window for the application services to access the network and for displaying the received information to the user.
What is the transport layer?
Transport layer provides services to application layer and takes services from network layer. The data in the transport layer is referred to as Segments. It is responsible for the End to End Delivery of the complete message. The transport layer also provides the acknowledgement of the successful data transmission and re-transmits the data if an error is found.#N#• At sender’s side:#N#Transport layer receives the formatted data from the upper layers, performs Segmentation and also implements Flow & Error control to ensure proper data transmission. It also adds Source and Destination port number in its header and forwards the segmented data to the Network Layer.#N#Note: The sender need to know the port number associated with the receiver’s application.#N#Generally, this destination port number is configured, either by default or manually. For example, when a web application makes a request to a web server, it typically uses port number 80, because this is the default port assigned to web applications. Many applications have default port assigned.#N#• At receiver’s side:#N#Transport Layer reads the port number from its header and forwards the Data which it has received to the respective application. It also performs sequencing and reassembling of the segmented data.
What does OSI stand for?
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It has been developed by ISO – ‘ International Organization of Standardization ‘, in the year 1984. It is a 7 layer architecture with each layer having specific functionality to perform. All these 7 layers work collaboratively to transmit the data from one person to another across the globe.
What is the function of the data link layer?
The functions of the data Link layer are : Framing: Framing is a function of the data link layer. It provides a way for a sender to transmit a set of bits that are meaningful to the receiver. This can be accomplished by attaching special bit patterns to the beginning and end of the frame.
What is the presentation layer?
Presentation layer is also called the Translation layer .The data from the application layer is extracted here and manipulated as per the required format to transmit over the network.#N#The functions of the presentation layer are :
What are the functions of the physical layer?
The functions of the physical layer are : Bit synchronization: The physical layer provides the synchronization of the bits by providing a clock. This clock controls both sender and receiver thus providing synchronization at bit level.