
How to determine correct spinal level?
What does SP mean in spinal?
What factors influence the correct spinal level?
About this website
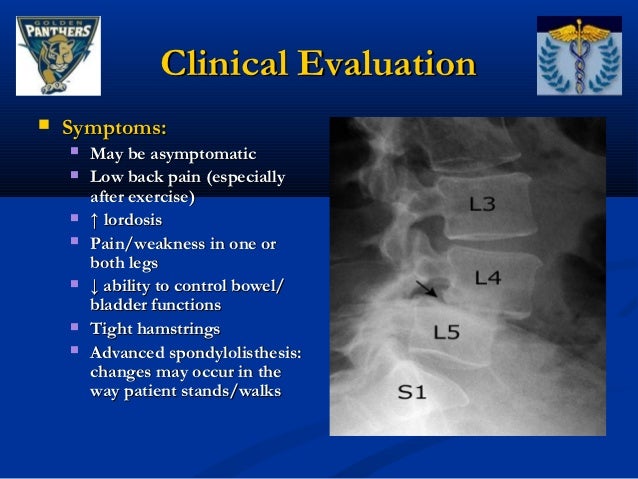
What sacral level is PSIS?
second sacral vertebraThe PSIS is approximately level with the second sacral vertebra in the coronal plane and is from 1.7 to 2.2 cm dorsal to the SIJ. The thickness of the ilium overlying the SIJ ranges from 0.8 to 2.2 cm medial to lateral and is generally thicker dorsally [ 15 ] (Fig. 3.6).
Where is the PSIS located?
The posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) is located on the back, just above the buttock. It can usually be seen and felt under the indents just above the buttock.
How do I know if I have L4 or L5?
Count up one level and find the spinous process of L4. The L4 spinous process is typically larger than the L5 process. To double check place your hands on the iliac crests with your thumbs pointing towards one another which will put you in the region of L4.
How do you find L3 and L4?
Wearing nonsterile gloves, locate the L3-L4 interspace by palpating the right and left posterior superior iliac crests and moving the fingers medially toward the spine (see the image below). Palpate that interspace (L3-L4), the interspace above (L2-L3), and the interspace below (L4-L5) to find the widest space.
What is PSIS anatomy?
The PSIS, or Posterior Superior Iliac Spine, is one of the three major components of the hip bone. Unlike most other major bones, it is not palpable and is instead recognized by a small dimple directly above the buttock.
What is PSIS pain?
Abstract. Objective: Pain at or around the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) is characteristic of sacroiliac joint (SIJ) -related pain. This pain can be treated by either a peri- or intra-articular injection into the joint, with the former being much easier to perform.
What are the symptoms of L4-L5 nerve damage?
Tingling, numbness (pins and needles), and an aching or burning sensation in the leg and on top of the foot are widespread. In severe cases, an L4-L5 slipped disc leads to weakness in the legs or feet. Some may even have an inability to walk, leading to an inability to stand.
What nerves do L4 and L5 affect?
The sciatic nerve consists of the L4 and L5 nerves plus other sacral nerves. Your sciatic nerve starts in your rear pelvis and runs down the back of your leg, ending in your foot.
What are the symptoms of L4-L5 stenosis?
Symptoms may include:Pain in the back.Burning pain going into the buttocks and down into the legs (sciatica)Numbness, tingling, cramping, or weakness in the legs.Loss of sensation in the feet.A weakness in a foot that causes the foot to slap down when walking ("foot drop")Loss of sexual ability.
Where is L3 L4 and L5 on the spine?
The lumbar region of the spine, more commonly known as the lower back, consists of five vertebrae labeled L1 through L5. The lumbar region is situated between the thoracic, or chest, region of the spine, and the sacrum. The lumbar spine typically has a slight inward curve known as lordosis.
What muscles are affected by L3 L4?
L3-L4 Pinched Nerve: The L3 nerve root is responsible for the quadriceps femoris muscles, located on the front of the thigh and helps extend, or straighten, the knee.
How do you get rid of L3 L4 pain?
Nonsurgical Treatments for L3-L4Medication. Both over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications are used to treat pain stemming from L3-L4, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, tramadol, and/or corticosteroids. ... Immobilization. ... Physical therapy. ... Chiropractic manipulation. ... Injection.
Where is the posterior superior iliac spine?
In most persons, the posterior superior iliac spine can be easily palpated as a bony prominence at the posterior end of the iliac crest.
What is the posterior superior iliac spine?
The posterior superior iliac spine is the lower part of the spine above the tailbone. The sacrum is the triangular region at the back of the pelvis that is situated between the lumbar spine and the coccyx, or tailbone.
What is the full form of PSIS?
PSIS may refer to: Posterior superior iliac spine, part of the human hip bone.
What is the PSIS and ASIS?
Pelvic tilt is often quantified using the angle between the horizontal and a line connecting the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS).
Which spinal levels are identified by palpation of the iliac crests and ...
J. Anat. (2007) 210, pp232–236 doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00686.x © 2007 The Authors Journal compilation © 2007 Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland
Landmark identification - University of Oxford
PROVE: February 2013 REC Number: 12/SC/0411 ISRCTN Number: 49117867 Physiotherapy Rehabilitation of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture 4. To locate L1.
Elsevier: Ludwig Ombregt: A System of Orthopaedic Medicine · Welcome
Elsevier: Ludwig Ombregt: A System of Orthopaedic Medicine · Welcome
Definition
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction or sacroiliitis are common terms used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. hyper- or hypo-mobile) or malalignment of the sacroiliac joint. Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a significant source of pain in 15% to 30% of people with mechanical low back pain.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
The sacroiliac joints are located on each side of the spine between the two pelvic bones, which attach to the sacrum.
Etiology
It is often hard to determine exactly what caused the wear and tear to the joints.
Epidemiology
Approximately 90% of the population will at some experience or present to the clinic with some form of low back pain/pathology. About 10% to 25% of these patients are thought to be experiencing pain from the SI joint. The majority of SI joint pathologies affect the adult patient population.
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms of sacroiliac joint syndrome are often difficult to distinguish from other types of low back pain. This is why making a diagnosis of sacroiliac joint syndrome is very difficult.
Differential Diagnosis
Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a controversial diagnosis, therefore pain and injury to the sacroiliac joint are commonly overlooked. This condition is often listed under the general term dysfunction, a term that serves as a collective term for different conditions. The differential diagnosis should include:
Diagnostic Procedures
A comprehensive physical examination for evaluating SI joint dysfunction.
How to determine correct spinal level?
Identification of the correct spinal level through examination is a necessary part of spinal medicine but its importance is most clearly evident when performing lumbar injections without fluoroscopy. The main hazard would be selecting too high a level, thus injecting a level more cephalad than the conus medullaris, which can extend as low as to the upper aspect of the L3 vertebral segment ( Kim et al. 2003a ). Various methods of identifying the correct spinal level by examination have been described, including dropping a vertical line downwards from the uppermost iliac crest with the patient in a side-lying position (half-Tuffier's line) ( Ievins, 1991 ), construction of a line between the two PSISs ( Borley, 1997) and constructing a line between the lowermost margins of the tenth ribs ( Jung et al. 2004 ). However, construction of the ICL through palpation of the iliac crests, first described by Jacoby and Tuffier ( Tuffier, 1900; Kubota et al. 1992) in the late 19th century, has proven to be the most popular method, with several authoritative textbooks referring to it as crossing the L4 or L4–5 spinal level ( Cunningham & Ramenes, 1979; Atkinson et al. 1987; Ellis & Feldman, 1993; Ombregt et al. 1998 ).
What does SP mean in spinal?
Table 2. A cross-tabulation showing the frequency of spinal levels identified by palpation and imaging of the intercristal line (SP = spinous process, IS = interspinous space)
What factors influence the correct spinal level?
Factors that have been shown to influence poor identification of the correct spinal level include selection of a high lumbar spinal level and obesity ( Broadbent et al. 2000; Furness et al. 2002 ). Positioning of the patient in a sitting or lateral position does not affect the accuracy even though in nearly half the patients, the spinal level intersected by the ICL on imaging moves downward by one level on full lumbar flexion ( Kim et al. 2003b ).
What is the difference between level 1 and level 2?
Level 1 corresponds OSPF intra-area routing whereas Level 2 corresponds with the OSPF backbone Area 0 routing. Level 2 areas join all the areas with the backbone area. Every Cisco router comes by default as Level 1-2 (L1/L2) router to allow for easy configuration and deployment.
Can ISIS authenticate LSP?
ISIS can be configured separately authenticate hellos and Link State Protocol Data Units (LSP). If hellos are authenticated correctly and LSP authentication fails, the adjacency will come up but updates will not be exchange. Therefore if authentication is configured for ISIS hellos or PDUs (Protocol Data Unit) must match on both the ends.
How to determine correct spinal level?
Identification of the correct spinal level through examination is a necessary part of spinal medicine but its importance is most clearly evident when performing lumbar injections without fluoroscopy. The main hazard would be selecting too high a level, thus injecting a level more cephalad than the conus medullaris, which can extend as low as to the upper aspect of the L3 vertebral segment ( Kim et al. 2003a ). Various methods of identifying the correct spinal level by examination have been described, including dropping a vertical line downwards from the uppermost iliac crest with the patient in a side-lying position (half-Tuffier's line) ( Ievins, 1991 ), construction of a line between the two PSISs ( Borley, 1997) and constructing a line between the lowermost margins of the tenth ribs ( Jung et al. 2004 ). However, construction of the ICL through palpation of the iliac crests, first described by Jacoby and Tuffier ( Tuffier, 1900; Kubota et al. 1992) in the late 19th century, has proven to be the most popular method, with several authoritative textbooks referring to it as crossing the L4 or L4–5 spinal level ( Cunningham & Ramenes, 1979; Atkinson et al. 1987; Ellis & Feldman, 1993; Ombregt et al. 1998 ).
What does SP mean in spinal?
Table 2. A cross-tabulation showing the frequency of spinal levels identified by palpation and imaging of the intercristal line (SP = spinous process, IS = interspinous space)
What factors influence the correct spinal level?
Factors that have been shown to influence poor identification of the correct spinal level include selection of a high lumbar spinal level and obesity ( Broadbent et al. 2000; Furness et al. 2002 ). Positioning of the patient in a sitting or lateral position does not affect the accuracy even though in nearly half the patients, the spinal level intersected by the ICL on imaging moves downward by one level on full lumbar flexion ( Kim et al. 2003b ).
