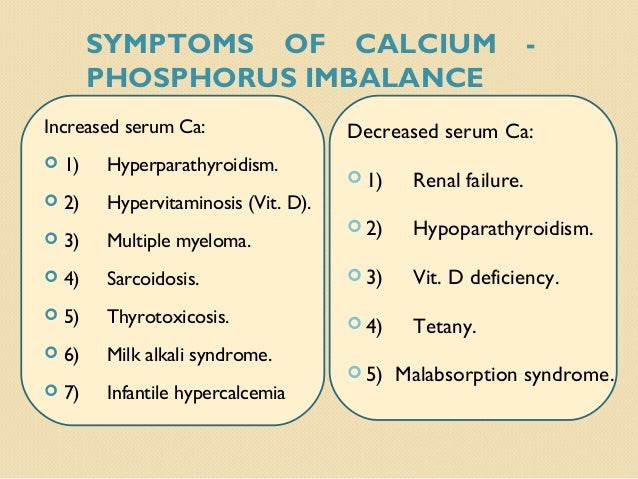
What are the dangers of high phosphorus levels?
Other possible causes of hyperphosphatemia include:
- low parathyroid hormone levels (hypoparathyroidism)
- damage to cells
- high vitamin D levels
- diabetic ketoacidosis — high levels of acids called ketones in the blood of people with diabetes
- injuries — including those that cause muscle damage
- serious body-wide infections
What foods have the highest phosphorus?
Foods high in phosphorus include fish, pork, tofu, milk, chicken, scallops, lentils, squash seeds, beef, and whole grains. The daily value (%DV) for phosphorus is 1250mg. Below is a list of high phosphorus foods by common serving size, use the complete nutrient ranking of phosphorus foods to sort by 100 gram or 200 calorie serving sizes.
What causes elevated phosphorus levels?
- Pseudohyperphosphatemia: It may be due to paraproteinemia caused by Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance.
- Vitamin D intoxication
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Tumor lysis syndrome
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
What are the symptoms of elevated phosphorus?
- Decreased intake or intestinal absorption of phosphorus. ...
- Increased renal excretion of phosphorus. ...
- Shift of phosphorus into cells. ...
- Genetic disorders causing renal phosphate wasting are a rare cause of hypophosphatemia. ...
What is a critical phosphorus level?
Soft tissue calcification is also an important long-term effect of high phosphorus levels. Phosphorus levels below 1.0 mg/dL are potentially life-threatening and are considered a critical value in the Mayo Health System.
How much is too much phosphorus?
Health Risks from Excessive PhosphorusAgeMaleFemale14–18 years4,000 mg4,000 mg19–50 years4,000 mg4,000 mg51–70 years4,000 mg4,000 mg71+ years3,000 mg3,000 mg5 more rows•Mar 26, 2021
How many mg of phosphorus is considered high?
Checking nutrition labels for hidden phosphorusLow phosphorus:0-50 mg or less than 5 percent Daily ValueMedium phosphorus:51-150 mg or 5-15 percent Daily ValueHigh phosphorus:150 mg or higher or greater than15 percent Daily Value
What happens when phosphorus levels are too high?
Extra phosphorus causes body changes that pull calcium out of your bones, making them weak. High phosphorus and calcium levels also lead to dangerous calcium deposits in blood vessels, lungs, eyes, and heart. Over time this can lead to increased risk of heart attack, stroke or death.
What is the normal range for phosphorus?
Normal Results Normal values range from: Adults: 2.8 to 4.5 mg/dL. Children: 4.0 to 7.0 mg/dL.
How do I bring my phosphorus levels down?
Here are seven methods to help control high levels of phosphorus:Reduce the amount of phosphorus you eat. ... Take phosphorus binders. ... Take vitamin D. ... Take a calcimimetic medicine. ... Stay on dialysis the entire time. ... Start an exercise program approved by a doctor. ... Get an operation to remove some of the parathyroid glands.
Is 4.9 phosphorus high?
Serum phosphorus is measured in milligrams of phosphorus per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). According to Mayo Medical Laboratories, a normal range for adults is generally 2.5 to 4.5 mg/dL. The normal range varies slightly depending on your age.
How much phosphorus is OK for kidney disease?
Healthy adults with normal kidney function, under 70 years of age, should consume less than 4,000 mg/day of phosphorus. Those over 70 years should consume no more than 3,000 mg/day.
What is the creatinine level for stage 3 kidney disease?
The ideal cutoff values for serum creatinine as a diagnostic test for stage 3 CKD varied by gender (Table 3). Among men ≥65 years, a serum creatinine value of ≥1.3 mg/dl indicated stage 3 CKD. Among women ≥65 years, a serum creatinine of ≥1.0 mg/dl indicated stage 3 CKD.
Does vitamin D lower phosphorus?
With vitamin D deficiency, serum phosphorus values usually decrease because of the associated hyperparathyroidism, but hyperphosphatemia has been reported to occur when vitamin D deficiency is severe [1, 6].
What causes increased phosphorus?
Hyperphosphatemia is a condition that means you have high levels of phosphorus in your body. It can happen due to your diet or a change in your kidneys' function. Often, hyperphosphatemia has no symptoms.
What medications cause high phosphorus levels?
With three of the top five medications, amlodipine, lisinopril, or omeprazole, the phosphate binder pill burden could increase significantly, particularly with sevelamer or calcium-based binders.
What are the risks of high phosphate levels?
Conversely, the risk of breast, endometrial, and other endocrine cancers dropped with higher phosphate levels in both sexes [ 61 ].
What are the effects of phosphorus?
Decreasing Blood Phosphorus. Further Reading. Phosphorus is the second most abundant mineral in the body, essential for energy, bone, heart, lung, and brain health. Imbalances may disrupt your metabolism and raise your risk of chronic diseases.
How much phosphorus does the kidney absorb?
In adults, kidneys will normally get rid of a fairly constant amount of phosphorus (> 90% ). But when the supply is low, kidneys can reabsorb phosphate very efficiently, reducing urine levels down to virtually zero. Also, when there’s phosphate overload, healthy kidneys can rid the body of any excess amounts [ 1, 2 ].
What is the sixth most abundant element in the human body?
Phosphorus is the sixth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and calcium. It is the second most abundant mineral and makes up about 1% of our body weight [ 1, 2 ]. Phosphorus is mainly found as phosphate in the body.
How does phosphorus affect the body?
Phosphate in the bones acts as a buffer that responds to specific imbalances. It moves in and out of bones as needed. Bone breakdown releases phosphorus, raising its blood levels. Increased bone mineralization, on the other hand, attracts phosphorus into the bones and lowers its blood levels [ 7, 2 ].
Which hormones affect phosphate levels?
Hormones that affect blood phosphate levels are [ 2, 1, 16, 12 ]: Calcitriol, or active vitamin D: promotes phosphorus absorption in the gut and increases blood phosphate levels.
Why do manufacturers add phosphates to their products?
Manufacturers add phosphates to their products to enhance appearance and shelf life. Phosphorus-based additives are used as pH stabilizers, leavening, and anti-bacterial agents. They account for about 10 – 50% of total daily phosphorus intake in the typical Westernized diet [ 8, 9 ].
What is it called when you have a high phosphate level?
Having a high level of phosphate — or phosphorus — in your blood is known as hyperphosphatemia. Phosphate is an electrolyte, which is an electrically charged substance that contains the mineral phosphorus.
Why does my phosphate level rise?
Your blood phosphate level can also rise abruptly if you receive a phosphorus-containing laxative as preparation for a colonoscopy. Other possible causes of hyperphosphatemia include: low parathyroid hormone levels (hypoparathyroidism) damage to cells. high vitamin D levels.
How to reduce risk of kidney disease?
Hyperphosphatemia is often a complication of chronic kidney disease. One way to reduce your risk is by slowing kidney damage. Protect your kidneys by treating the cause of your kidney disease. High blood pressure can weaken the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to your kidneys.
How to lower phosphate levels in kidneys?
If your kidneys are damaged, you can lower high blood phosphate levels in three ways: reduce the amount of phosphate in your diet. remove extra phosphate with dialysis. lower the amount of phosphate your intestines absorb using medication. First, limit foods that are high in phosphorus, such as: milk. red meat.
Why do kidneys remove phosphate from blood?
Your kidneys help remove extra phosphate from your body to keep the levels in balance. When your kidneys are damaged , your body can’t remove phosphate from your blood quickly enough. This can lead to chronically elevated levels of phosphate.
What are the symptoms of low calcium levels in the kidneys?
Symptoms of low calcium include: muscle cramps or spasms. numbness and tingling around the mouth. bone and joint pain. weak bones.
What happens if you have low calcium in your blood?
Low calcium in the blood increases your risks for: high parathyroid hormone levels (secondary hyperparathyroidism) seizures. bone disease called renal osteodystrophy. Because of these complications, people with severe kidney disease who have high phosphate levels in their blood face an increased risk. Trusted Source.
What causes high phosphate levels?
There are other conditions linked with high levels of phosphate in the blood, however, including the following: 1 Uncontrolled diabetes: This causes high levels of blood sugar that can lead to serious medical problems, such as organ damage. 2 Diabetic ketoacidosis: A complication of diabetes that can happen if the body begins to run out of insulin. Harmful ketones build up in the body and blood sugar levels rise. 3 Hypoparathyroidism: A rare hormone disorder in which the body does not produce enough parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH helps control the levels of phosphorus in the blood and bones. 4 Hypocalcemia: Low levels of calcium in the blood.
What is too much phosphate in the blood called?
Treatment. Prevention. Outlook. Too much phosphate in the blood is known as hyperphosphatemia. The most common cause is kidney disease, but other conditions can lead to phosphate levels being out of balance. Phosphate is a chemical found in the body. It contains a mineral called phosphorus that occurs naturally in many foods.
How to prevent hyperphosphatemia?
The main way to prevent hyperphosphatemia is to control the levels of phosphate and calcium in the body. This is usually done by eating certain foods and avoiding others. Processed foods often contain phosphorus as a preservative, shown by ingredients that have the letters PHOS together.
What is the effect of phosphates on the kidneys?
The kidneys naturally control levels of phosphates. However, if the kidneys are not working efficiently, they may not be able to remove enough phosphate, leading to high levels in the body. Treatment for hyperphosphatemia will depend on the underlying condition.
What is the best treatment for hyperphosphatemia?
Medication or supplements containing calcium may be recommended for treating and preventing hyperphosphatemia. Treatment for hyperphosphatemia will depend on the underlying cause: If a person has uncontrolled diabetes, it is essential to bring this under control with diet, exercise, and a medicine called insulin.
Why do kidneys have a bad balance?
Because kidneys control the balance of minerals and other chemicals, chronic kidney disease can cause mineral and bone disorders. Those who have had kidney failure and are having dialysis are most at risk. This deterioration can take place over many years, often without symptoms.
What is the chemical that makes up phosphate?
Phosphate is a chemical found in the body. It contains a mineral called phosphorus that occurs naturally in many foods. Phosphorus supports bones and teeth to develop and helps turn food into energy for the body to use. The kidneys naturally control levels of phosphates.
What does it mean when your phosphorus level is too high?
Marked hyperphosphatemia (> 6.5 mg/dL in adults): Your phosphorus blood level is too high and you must visit your doctor because it is necessary to reduce these values. Marked hyperphosphatemia is usually a sign of kidney failure, a situation where the kidneys progressively lose the ability to filtrate and excrete phosphorus.
Why is phosphorus in the blood?
Hyperphosphatemia or high phosphorus level in the blood may be a consequence of a high phosphorus intake or because the body cannot remove excess phosphorus from your blood due to a kidney problem. Phosphorus blood values are usually given in mg/dl but sometimes you can see those values in mmol/l following the International System of Units (SI).
What are the symptoms of hyperphosphatemia?
The symptoms of marked hyperphosphatemia are those of acute hypocalcemia and include tetany, muscle fasciculation and dysrhythmias. Calcification in tissue, such as cornea and lungs, is a serious complication that may occur as a response to diseases causing hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia.
What drugs raise phosphorus levels?
Excess intake of vitamin D. Blood transfusion. Drugs. Androgen. Antibiotics. Tetracycline. Antiepileptic drugs.
Is phosphorus level higher than normal?
Mild hyperphosphatemia (4.5 - 5 mg/dL in adults): Phosphorus levels in the blood are higher than normal but there is no need to worry without any other symptom. You must take care of your phosphorus intake trying to reduce it. Take a new blood test in the following months and these levels will probably be within the normal range.
Is phosphorus high in adults?
Moderate hyperphosphatemia (5 - 6.5 mg/dl in adults): Your phosphorus blood level is moderately high. Talk to your doctor because it is necessary to study the possible causes. There are chances that you are suffering a kidney disease as kidneys lose the ability to remove the excess of phosphorus in the blood by urinary excretion.
What happens if you have hyperphosphatemia?
If your hyperphosphatemia is left untreated, you may be at risk of developing other life-threatening conditions. These include the following: 1 Secondary hyperparathyroidism 2 Renal osteodystrophy, a bone disease caused by kidney failure 3 Metastatic calcification, or deposition of calcium, in blood vessels and soft tissue
Can CKD cause high phosphorus levels?
Properly functioning kidneys remove extra phosphorus that ends up in your body. But with CKD, your kidneys can’t remove the phosphorus, causing it to build up in your body. High levels of phosphorus can damage your body.#N#
What happens if your phosphorus level is too high?
Or, you might not feel any different. But, in the long run, phosphorus levels that are too high can lead to bone and other health problems if your calcium level is high, too. If you are taking active vitamin D, your doctor may lower your dose.
Where is phosphorus stored?
Like calcium, it is very common in the earth—and in your own cells. Phosphorus is stored in your bones and teeth, and is part of each cell membrane. In your blood, phosphorus plays a vital role in your use of energy. And, it is an electrolyte, which helps carry nerve signals. It is found in most foods.
Is calcium phosphorus good for you?
Less than 55: Good for you! Your calcium phosphorus product is in the range that can help prevent blood vessel calcification. Bone is vital to have—in your skeleton. But when bone forms in your blood vessels, it can cut off the blood supply to your limbs. You could get gangrene or even lose a limb.
Why is phosphorus high in the blood?
Because CKD is the number one reason for high phosphorus levels in the blood, also known as hyperphosphatemia. Other causes include diabetic ketoacidosis, injuries (specifically to muscles), hypoparathyroidism, high vitamin D levels and phosphorus-containing laxatives.
How to lower phosphorus levels in blood?
They help lower blood phosphorus levels by binding to the phosphorus in food so that it is excreted in the gastrointestinal tract instead of absorbed into the blood.
Why is phosphorus important for kidneys?
This decreases blood flow in the body, which can cause poor wound healing and tissue or organ death. Maintaining blood phosphorus levels within the recommended range is particularly important for anyone with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
When to take phosphorus binders?
Phosphorus binders work best if they are taken right before eating or with the first few bites of food. Your nephrologist or dietitian will tell you the number of binders you should take with your meals and snacks based on your diet and blood phosphorus levels.
What is the role of phosphorus in the body?
Phosphorus is a mineral in the body that helps build strong bones, aids in metabolism, and helps muscles and nerves function properly. The kidneys and digestive tract regulate phosphorus levels in the blood so that it does not get too high or low. Chronically elevated blood phosphorus levels can weaken the bones and cause calcium ...
Can phosphorus binders cause constipation?
People with CKD are prone to constipation due to fluid and dietary restrictions that limit intake of high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables and legumes. If you are constipated, ask your nephrologist or dietitian about starting a stool softener, laxative or fiber supplement. Other tips that can help with constipation are eating more low-potassium fruits and vegetables, and walking or exercising daily (if approved by your doctor).
