
Hydroxyl groups are a functional group found in sugars and alcohols. A hydroxyl group consists of one hydrogen and one oxygen atom An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers (1×10⁻¹⁰ m, a ten-millionth of a millim…Atom
What is the function of a hydroxyl group?
A hydroxyl group is a functional group that attaches to some molecules containing an oxygen and hydrogen atom, bonded together. Also spelled hydroxy, this functional group provides important functions to both alcohols and carboxylic acids. Alcohols are chains of carbon molecules with a functional hydroxyl group side chain.
What is a hydroxyl group in a carboxylic acid?
Carboxylic acids contain a hydroxyl group within their functional carboxyl group. A carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group. A carbonyl group is simply a carbon double bonded to an oxygen. These two functional groups together create an extremely reactive molecule, which is prone to forming new carbon-carbon bonds.
What is a general alcohol with a hydroxyl group?
Below is a general alcohol which contains a hydroxyl group. The oxygen is the red atom, while the hydrogen is represented by the grey atom. The R represent any generic carbon chain. Carboxylic acids contain a hydroxyl group within their functional carboxyl group. A carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group.
What happens when hydrogen atoms are added to the hydroxyl group?
The hydroxyl group expelled consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom. When you add another hydrogen atom to that, what do you get? H 2 O! Both the hydroxyl group and the hydrogen proton are very reactive when they leave their respective molecule.
What macromolecule is carboxyl found on?
Carboxyl groups are commonly found in amino acids, fatty acids, and other biomolecules. An example of a less hydrophilic group is the carbonyl group (C=O), an uncharged but polar (contains partial positive and partial negative charges) functional group.
Where is the hydroxyl group found?
Hydroxyl groups are very common in biological molecules. Hydroxyl groups appear on carbohydrates (A), on the R-groups of some amino acids (B), and on nucleic acids (C).
Are hydroxyl groups found in lipids?
Lipids contain the same elements as carbohydrates: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (C, H, and O). However, lipids are mainly made of hydrocarbon chains (or rings) and contain fewer polar hydroxyl groups (-OH). This makes most lipids nonpolar hydrophobic molecules (they do not dissolve well in water).
Are hydroxyl groups found in all carbohydrates?
Answer and Explanation: Regardless of their structure, all carbohydrates contain hydroxyl (-OH) groups.
What has a hydroxyl group?
alcoholsHydroxyl groups are a functional group found in sugars and alcohols. A hydroxyl group consists of one hydrogen and one oxygen atom and can be written as either -OH or HO-. Hydroxyl groups are polar, and the oxygen side is always negative, while the hydrogen side is always positive.
What is a hydroxyl group quizlet?
hydroxyl group: structure. —OH : A hyrdrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom, bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
What functional groups are in lipids?
Lipids contain proteins, oils, waxes, vitamins (such as A, D, E, and K), hormones, and the majority of the cell membrane that is not composed of protein. Although the compositions of lipids vary, the most common functional groups are ester (both carboxylate and phosphate) and alcohol groups.
What is a hydroxyl functional group?
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula −OH and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups.
What elements are found in lipids?
Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, and in some cases contain phosphorus, nitrogen, sulfur and other elements.
What is hydroxyl group carbohydrates?
The hydroxyl group that is attached to the anomeric carbon atom (i.e., the carbon containing the aldehyde or keto group) of carbohydrates in solution has unusual reactivity, and derivatives, called glycosides, can be formed; glycosides formed from glucose are called glucosides.
What functional groups are found in each macromolecule?
Functional groups in biological molecules play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Functional groups include: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl.
What functional group is found in carbohydrates?
Naming the Major Functional Group in a Carbohydrate Sugars, or carbohydrates, have two major functional groups: an aldehyde or a ketone (both are collectively called carbonyls), and an alcohol functional group.
Which amino acids contain a hydroxyl group?
Two amino acids, serine and threonine, contain aliphatic hydroxyl groups (that is, an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, represented as ―OH). Tyrosine possesses a hydroxyl group in the aromatic ring, making it a phenol derivative.
What is the hydroxyl functional group?
A hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula -OH and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups.
Does water contain a hydroxyl group?
alcohols. …properties because water molecules contain hydroxyl groups that can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules and with alcohol molecules, and likewise alcohol molecules can form hydrogen bonds with other alcohol molecules as well as with water.
Is a hydroxyl group an alcohol?
The functional group of the alcohols is the hydroxyl group, –OH. Unlike the alkyl halides, this group has two reactive covalent bonds, the C–O bond and the O–H bond.
What is the function of hydroxyl group?
A hydroxyl group is a functional group that attaches to some molecules containing an oxygen and hydrogen atom, bonded together. Also spelled hydroxy, this functional group provides important functions to both alcohols and carboxylic acids. Alcohols are chains of carbon molecules with a functional hydroxyl group side chain.
Why do hydroxyl groups have a strong attraction?
As mentioned, a large part of the action caused by the hydroxyl group is due to the electronegativity of the oxygen. Because oxygen has a stronger attraction with the electrons bonding hydrogen to the molecule, the hydroxyl group can easily lose the hydrogen to an atom that will share electrons more equally. When this happens, the oxygen takes on a much more negative electrical energy, and can donate the extra electrons it has to a number of reactions. Biological organisms use this property of oxygen to help connect and disconnect chains of carbon molecules, which hold energy the organism can use to power cellular functions.
What happens when the carboxyl group loses the hydroxyl group attached to it?
When the protein is formed, the carboxyl group loses the hydroxyl group attached to it, while the amino group loses a hydrogen. With the loss of these molecules, the amino group binds to the carbonyl group, forming a peptide bond. What else is produced during this reaction? A. Water.
What is a carboxyl group?
A carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group. A carbonyl group is simply a carbon double bonded to an oxygen. These two functional groups together create an extremely reactive molecule, which is prone to forming new carbon-carbon bonds. Along with alcohols, carboxylic acids are commonly seen in nature.
What is the difference between oxygen and hydrogen?
The oxygen is the red atom, while the hydrogen is represented by the grey atom. The R represent any generic carbon chain. Carboxylic acids contain a hydroxyl group within their functional carboxyl group. A carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group. A carbonyl group is simply a carbon double bonded to an oxygen.
Why does oxygen have a stronger attraction with the electrons bonding hydrogen to the molecule?
Because oxygen has a stronger attraction with the electrons bonding hydrogen to the molecule, the hydroxyl group can easily lose the hydrogen to an atom that will share electrons more equally. When this happens, the oxygen takes on a much more negative electrical energy, and can donate the extra electrons it has to a number of reactions.
What happens when you add another hydrogen atom to a molecule?
The hydroxyl group expelled consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom. When you add another hydrogen atom to that, what do you get? H 2 O! Both the hydroxyl group and the hydrogen proton are very reactive when they leave their respective molecule. In fact, it takes heat or energy input to cause this to happen, and is one reason animals need a source of energy to continue to make new proteins. Because of this formation of water, the reaction is known as a condensation or dehydration reaction. This reaction takes place constantly in your body as your cells repair and replace their components.
What are macromolecules similar to?
All of the major macromolecule classes are similar, in that, they are large polymers that are assembled from small repeating monomer subunits. In Chapter 6, you were introduced to the polymers of life and their building block structures, as shown below in Figure 11.1.
What are the four macromolecules?
These are the carbohydrates, lipids (or fats), proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the chemistry of carbohydrates?
The chemistry of carbohydrates most closely resembles that of alcohol, aldehyde, and ketone functional groups. As a result, the modern definition of a CARBOHYDRATE is that the compounds are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones. The chemistry of carbohydrates is complicated by the fact that there is a functional group (alcohol) on almost every carbon. In addition, the carbohydrate may exist in either a straight chain or a ring structure. Ring structures incorporate two additional functional groups: the hemiacetal and acetal.
How many amino acids are in a protein?
Proteins range in size from 50 amino acids in length to the largest known protein containing 33,423 amino acids.
How are amino acids linked to proteins?
Within cellular systems, proteins are linked together by a complex system of RNA and proteins called the ribosome. Thus, as the amino acids are linked together to form a specific protein, they are placed within a very specific order that is dictated by the genetic information contained within the RNA. This specific ordering of amino acids is known as the protein’s primary sequence. The primary sequence of a protein is linked together using dehydration synthesis that combine the carboxylic acid of the upstream amino acid with the amine functional group of the downstream amino acid to form an amide linkage. Within protein structures, this amide linkage is known as the peptide bond. Subsequent amino acids will be added onto the carboxylic acid terminal of the growing protein. Thus, proteins are always synthesized in a directional manner starting with the amine and ending with the carboxylic acid tail. New amino acids are always added onto the carboxylic acid tail, never onto the amine of the first amino acid in the chain. In addition, because the R-groups can be quite bulky, they usually alternate on either side of the growing protein chain in the trans conformation. The cis conformation is only preferred with one specific amino acid known as proline.
Where are hydrophobic amino acids found?
For proteins found inside the watery environments of the cell, hydrophobic amino acids will often be found on the inside of the protein structure , whereas water-loving hydrophilic amino acids will be on the surface where they can hydrogen bond and interact with the water molecules.
Which macromolecule carries the genetic information of a cell and carries instructions for the functioning of the cell?
nucleic acid : a biological macromolecule that carries the genetic information of a cell and carries instructions for the functioning of the cell
How many different types of macromolecules are there in a cell?
Each cell has thousands of different kinds of macromolecules. These molecules vary among cells of the same individual. They vary more among unrelated individuals of a species, and even more between species. This diversity comes from various combinations of the 40–50 common monomers and some others that occur rarely.
What are the four major classes of macromolecules?
The four major classes of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
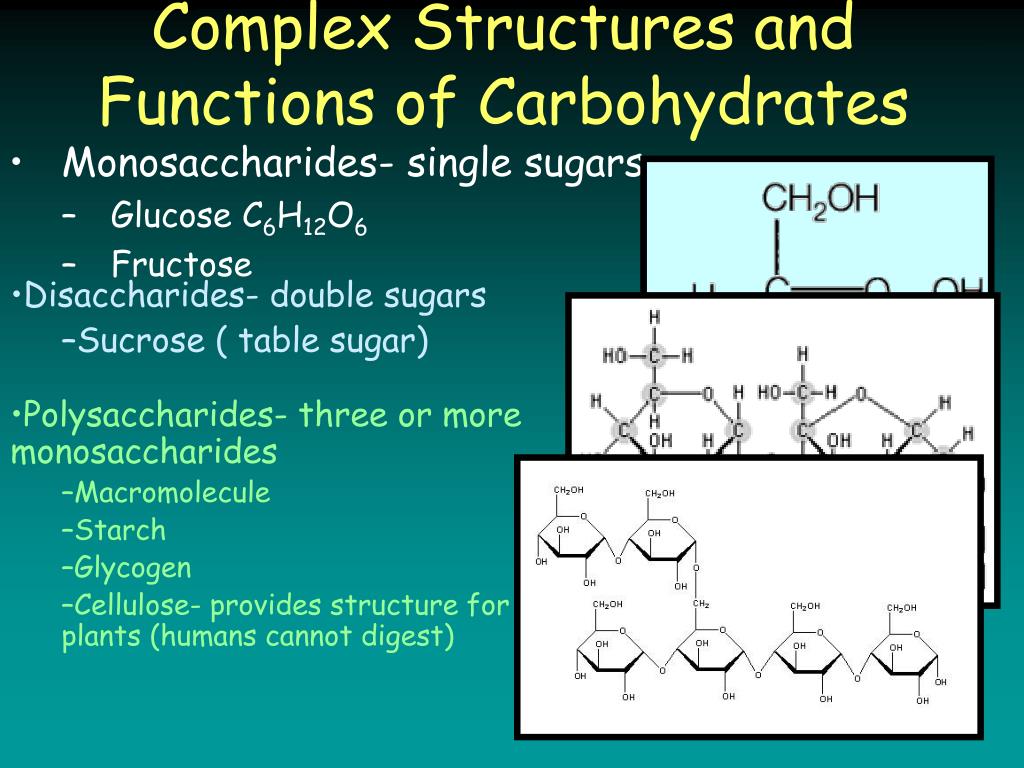
How are two monosaccharides formed?
Two monosaccharides can join with a glycosidic linkage to form a disaccharide via dehydration. Maltose, malt sugar, is formed by joining two glucose molecules. Sucrose, table sugar, is formed by joining glucose and fructose. Sucrose is the major transport form of sugars in plants.
What is the role of monosaccharides in cellular work?
Monosaccharides, particularly glucose, are a major fuel for cellular work. They also function as the raw material for the synthesis of other monomers, such as amino acids and fatty acids. While often drawn as a linear skeleton, monosaccharides in aqueous solutions form rings.
What are the functions of monomers?
The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. Monomers are connected by covalent bonds that form through the loss of a water molecule .
What are the simplest carbohydrates?
The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides, or simple sugars. Disaccharides, or double sugars, consist of two monosaccharides joined by a condensation reaction. Polysaccharides are polymers of many monosaccharides. Sugars, the smallest carbohydrates, serve as fuel and a source of carbon.
How do cells perform dehydration?
Cells invest energy to carry out dehydration reactions. The process is aided by enzymes. The covalent bonds connecting monomers in a polymer are disassembled by hydrolysis, a reaction that is effectively the reverse of dehydration. In hydrolysis, bonds are broken by the addition of water molecules.
What are Macromolecules?
The term molecule refers to very large molecules and something that consists of more than one atom. Herman Staudinger coined it in 1920. Macromolecules are so huge that these are made up of more than 10,000 or more atoms.
How many types of macromolecules are there in the human body?
There are three main types of biological macromolecules, according to mammalian systems:
What are the three major groups of macromolecules that are essential in the industry?
There are three major groups of macromolecules that are essential in the industry, apart from biological macromolecules. These include plastics, fibres, and elastomers . Elastomers are macromolecules that are flexible and stretchy.
What are the polymers of nucleotides?
The nucleic acids include DNA and RNA that are the polymers of nucleotides. Nucleotides comprise a pentose group, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base group. All the hereditary information is stored in the DNA. The DNA synthesised into RNA and proteins.
What are the polymers of amino acids?
Proteins are the polymers of amino acids. These include the carboxylic and the amino group. There would be no lipids or carbohydrates without proteins because the enzymes used for their synthesis are proteins themselves.
What are the three types of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are polymers of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen . They can be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides . Carbohydrates are found in starch, fruits, vegetables, milk and sugars. They are an important source of a healthy diet.
Do lipids dissolve in water?
Lipids are a hydrophobic set of macromolecules, i.e., they do not dissolve in water. These involve triglycerides, carotenoids, phospholipids, and steroids. They help in the formation of the cell membrane, formation of hormones and in the and as stored fuel.
How are D. molecules synthesized?
D.) are synthesized from monomers by hydrolysis reactions.
Which two hormones have different functional groups attached to the same carbon skeleton?
Testosterone and estradiol have different functional groups attached to the same carbon skeleton.
What is the primary ingredient in margarine?
Hydrogenated vegetable oil is the primary ingredient in margarine. How does hydrogenated vegetable oil differ from nonhydro genated vegetable oil?
What is a C. s polymer?
C.) s a polymer composed of enantiomers of glucose.
Does hydrogen bond with water?
A.) It will form hydrogen bonds with water.
Can amylase break down glycosidic linkages?
The enzyme amylase can break glycosidic linkages between glucose monomers only if the monomers are the α form. Which of the following could amylase break down?
Hydrolysis
Polymers are broken down into monomers in a process known as hydrolysis, which means to split water. Basically, hydrolysis is a reaction in which a water molecule is used during the breakdown ( see image below ). During these reactions, the polymer is broken into two components.
Video Summarizing Hydrolysis and Dehydration Synthesis
The video below by Ricochet Science is a quick and easy overview of hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis.
