Major Events in the Middle Ages
- The Fall of Western Roman Empire (476 AD) The fall of Western Roman Empire is considered as the beginning of the Middle Ages. ...
- Charles the Hammer and the Battle of Tours (732 AD) Charles Martel, also known as Charles the Hammer was a Frankish political and military leader who worked under the Merovingian ...
- Charlemagne, the Emperor of Romans (800 AD) Charlemagne or Charles the Great was a Frankish king who expanded the Frankish kingdom and covered almost all of the Western and Central ...
What was daily life like in medieval times?
Narrator: Most people in medieval England were farming peasants who lived in villages in the countryside. They had a hard life working all day on farms owned by nobles. By the 12th century this was changing. New towns developed around religious buildings, castles or trade routes. These towns were crowded, noisy and smelly.
What weapons were used in medieval times?
What was the most deadly weapon in medieval times?
- Swords. Swords are most commonly a double-edged weapon (although you may see single-sided, “saber” style blades in the middle east during this period).
- Arrows.
- Poll weapons (including, pikes, halberds, poll axes, glaves, etc.)
- Knives and daggers.
- Axes (short-handled)
What was life like for women in medieval times?
Medieval women invariably had a hard time in an era when many men lived harsh lives. A few women lived comfortable lives but Medieval society was completely dominated by men and women had to know ‘their place’ in such a society. Medieval society would have been very traditional.
What did kings do during the midevile times?
Kings and Queens were the major power in the medieval times besides the pope. Kings led armies to battles everywhere at this time because wars were occuring everywhere. Nobles and lords helped kings, but kings had more power than both of them.

What was the major event of the High Middle Ages?
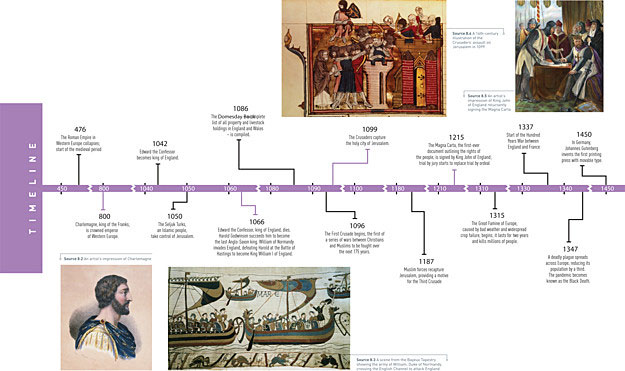
Even limiting it to a mere 300 years, the High Middle Ages saw such significant events as Norman conquests in Britain and Sicily, the earlier Crusades, the Investiture Controversy and the signing of the Magna Carta.
What were three major events that brought the Middle Ages to an end?
what events began to create something new in history.I. The Failure of Holy War. ... II. The Rediscovery of Aristotle. ... III. The Black Death, 1338-1353. ... IV. Power to the People. ... V. The Fall of Constantinople, 1415-1453.
What is the importance of medieval history?
Medieval period is an important period in the history of India because of the developments in the field of art and languages, culture and religion. Also the period has witnessed the impact of other religions on the Indian culture. Beginning of Medieval period is marked by the rise of the Rajput clan.
Why is medieval called Dark Ages?
Dark Past of the Middle Ages Some scholars perceive Europe as having been plunged into darkness when the Roman Empire fell in around 500 AD. The Middle Ages are often said to be dark because of a supposed lack of scientific and cultural advancement. During this time, feudalism was the dominant political system.
Why did the Middle Ages come to an end?
There were many reasons for the downfall of the Middle Ages, but the most crucial ones were the decline of the feudal system and the declination of the Church's power over the nation-states.
What are the 4 events that led to the Renaissance?
In conclusion, historians have identified several causes of the Renaissance in Europe, including: increased interaction between different cultures, the rediscovery of ancient Greek and Roman texts, the emergence of humanism, different artistic and technological innovations, and the impacts of conflict and death.
What was the main event that made the Renaissance possible?
Along with the revival of Roman and Greek literature, the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg of Germany was one of the major events that made Renaissance possible. Gutenberg printed bibles on his press and soon, his press became the symbol of the European Renaissance. Learn more about the medieval timeline at Wikipedia.
What was the medieval period?
Medieval Timeline 476 AD – 1453 – Important Events. The Medieval Period in Europe started around the time of the fall of Ancient Rome and ended with the European Renaissance, historians believe these dates to be from 476 AD – 1453. During this period, a number of major upheavals reshaped Europe permanently, established Christianity as its major ...
What did the Pope do after the Crusades?
After Muslims had captured the Holy Land, the Pope issued a decree asking the European powers to partake in Crusades against the Muslims and to repel them from the Holy Land , including the portions of Byzantine Empire that were under Muslim control.
What was the significance of the Hundred Years War?
1337: Hundred Years War Begins. 1337 marked a major moment in the history of the rivalry between England and France. In 1337, Edward III of England declared war on France, making a claim to the French throne.
What religion did Europe convert to?
By 732, most of the Europe had already converted to Christianity. Islam, another significant religion, had taken birth in Arabia in the 6th century. Muslims conquered vast territories and knocked on the doors of Europe during the 8th century. Franks, one of the only major powers in Europe at the time, confronted Muslims and defeated them.
What was the significance of the Magna Carta?
King John of England signed the Magna Carta in 1215. This document was decisive in laying the foundations for democracy in later centuries. The most significant part of the document stated that the King was not above the law .
What was the impact of the fall of Western Rome?
Eastern Rome, centered on Constantinople and continued to exist for many more centuries. But the fall of Western Rome led to fissures in Europe and a power vacuum was created.
What happened in the Middle Ages?
This period of the middle ages saw several significant events occur between England and France, including the death of Richard I, the ascension of King John as his successor and the loss of French territories to Arthur.
What was the most important event of the Middle Ages?
One of the great tragedies of the middle ages was the rise of The Black Death, otherwise known as the Plague. Between 1346 to 1353, this disease spread throughout Europe. This period was long before the discovery of the germ theory of disease, and therefore most efforts to stop its spread were unsuccessful.
Why were the Crusades important?
One of the reasons given for the crusades is to retake Jerusalem, which had fallen under the Islamic expansion. The crusades of Christianity are often seen as ...
Why did the Crusade take place?
The first took -place after Pope Urban II requested western troops to aid in the retaking of lost ground from the Muslim (Turkish) empire. The Pope’s request for military might was successful, and with this new military power, the first crusade was launched, leading to the recapturing of Jerusalem in 1099.
How long did the Vikings rule?
The Viking age is agreed on by historians as lasting around 150 years.
What was the first major event of the Roman Empire?
The first significant event that can be pointed at during this period is the fall of the Roman Empire, which was the largest empire seen up to that point in history, the fall of which is dated officially as being in AD 476.
What was Edward I's legacy?
Edward I’s legacy is his attempt to form a form of government more solid than that decreed by the Magna Carta. The high middle ages also saw the huge influence of Monastic Orders – religious communities with their own exclusive practices and beliefs, each following their own version of Christianity.
What were the major events of the Middle Ages?
Other important events of the Middle Ages included the success of Charles Martel against Islamic invaders and the establishment of Charlemagne’s empire. The agricultural revolution and establishment of Ottonian Empire was also ...
What was the most threatening epidemic of the Middle Ages?
The Black Death or the Black Plague proved to be the most threatening epidemic of the European Middle Ages that significantly weakened the feudal system and the Church of Europe. Huge masses of people met untimely death because of this plague and it significantly reduced the economic and political power of the kingdoms of Europe.
Why did the Carolingian Empire go into war?
However, after his death, the Carolingian empire faced a Civil War because of the internal tussle between the three surviving sons of Louis the Pious who struggled for the emperorship. At last, the Carolingian empire was divided in three parts in August 843 AD through the Treaty of Verdun which ended the three years long Civil War.
What did the papacy of Italy invite to the Ottonian Empire?
In 962 AD, the papacy of Italy invited him and declared him as the Emperor of Italy and he established his Holy Roman Empire.
How many contestants were there in the 1378-1417 papacy?
The Western Christendom suffered much bigger jolt during 1378 to 1417, when there were three contestants for the Papacy. This internal tussle for ultimate power of papacy significantly reduced the influence and power of the Church over common people.
What was the commercial revolution of Europe after the last crusade?
Commercial revolution of Europe after the last crusade changed the economical conditions of Europe. During the Great Famine of Europe in 13th century, a big mass of medieval people lost their life. One of the aftermaths of Great Famine was the increasing rivalry and bloodthirstiness of the members of nobility that was expressed by the event of the Hundred Years’ War between England and France.
What was the importance of the Battle of Hastings?
The Battle of Hastings had a very important incidence of European Middle Ages as it established the feudal system in England and gave way for feudalism in other parts of the Continent. Declaration of Magna Carta was also a very important event. Commercial revolution of Europe after the last crusade changed the economical conditions of Europe.
What was the name of the event that Muhammad and his followers escaped from?
622 Muhammad and his followers escape the city of Mecca. This event, known as the hegira , marks the beginning of the Muslim calendar.
What happened in 180?
180 The death of Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius marks the end of the "Pax Romana," or Roman peace. Years of instability follow, and although Rome recovers numerous times, this is the beginning of Rome's three-century decline.
What was the name of the region that Justinian captured?
534–563 Belisarius and other generals under orders from Justinian recapture much of the Western Roman Empire, including parts of Italy, Spain, and North Africa. The victories are costly, however, and soon after Justinian's death these lands will fall back into the hands of barbarian tribes such as the Vandals and Lombards.
What did the Greek Orthodox Church reject?
Though the Greek Orthodox Church ultimately rejects iconoclasm, the controversy helps widen a growing division between Eastern and Western Christianity.
What was the name of the dynasty that took over Western Europe in 481?
481 The Merovingian Age , named for the only powerful dynasty in Western Europe during the period, begins when Clovis takes the throne in France.
How long did Pope Gregory I reign?
590 Pope Gregory I begins his fourteen-year reign. Also known as Gregory the Great, he ensures the survival of the church, and becomes one of its greatest medieval leaders. Late 500s The first Turks begin moving westward, toward the Middle East, from their homeland to the north and west of China.
When did Tamerlane sack Delhi?
1398 Tamerlane sacks the Indian city of Delhi, hastening the end of the Delhi Sultanate, which comes in 1413.
How did the Middle Ages show devotion to the Church?
The Middle Ages: Art and Architecture. Another way to show devotion to the Church was to build grand cathedrals and other ecclesiastical structures such as monasteries. Cathedrals were the largest buildings in medieval Europe, and they could be found at the center of towns and cities across the continent.
What is the Middle Ages?
People use the phrase “Middle Ages” to describe Europe between the fall of Rome in 476 CE and the beginning of the Renaissance in the 14th century. Many scholars call the era the “medieval period” instead; “Middle Ages,” they say, incorrectly implies that the period is an insignificant blip sandwiched between two much more important epochs.
What caused the plague?
Today, scientists know the plague was caused by a bacillus called Yersina pestis, which travels through the air and can also be contracted through the bite of an infected flea or rat, both of which were common in the Middle Ages, especially on ships.
Why did people become flagellants in the Middle Ages?
Understandably terrified about the mysterious disease, some people of the Middle Ages believed the plague was a divine punishment for sin. To obtain forgiveness, some people became “flagellants,” traveling Europe to put on public displays of penance that could include whipping and beating one another.
How did feudal life change?
During the 11th century, however, feudal life began to change. Agricultural innovations such as the heavy plow and three-field crop rotation made farming more efficient and productive, so fewer farm workers were needed–but thanks to the expanded and improved food supply, the population grew. As a result, more and more people were drawn to towns and cities. Meanwhile, the Crusades had expanded trade routes to the East and given Europeans a taste for imported goods such as wine, olive oil and luxurious textiles. As the commercial economy developed, port cities in particular thrived. By 1300, there were some 15 cities in Europe with a population of more than 50,000.
What was the most powerful institution in the medieval period?
After the fall of Rome, no single state or government united the people who lived on the European continent. Instead, the Catholic Church became the most powerful institution of the medieval period. Kings, queens and other leaders derived much of their power from their alliances with and protection of the Church.
Why did the Catholic Church send soldiers to the Holy Land?
Toward the end of the 11th century, the Catholic Church began to authorize military expeditions, or Crusades, to expel Muslim “infidels” from the Holy Land . Crusaders, who wore red crosses on their coats to advertise their status, believed that their service would guarantee the remission of their sins and ensure that they could spend all eternity in Heaven. (They also received more worldly rewards, such as papal protection of their property and forgiveness of some kinds of loan payments.)

Beginning The of The Medieval Period
Middle Ages and The Formation of Europe
- Charlemagne’s successor was Louis I, who led various conquests, and was sole ruler of the Franks from the year 814. He appointed members of the church into his government, as well as implementing an important method of succession from this period onwards, known as the Ordinatio Imperii. 829 to 840 saw 3 uprisings resulting from feuds between Loui’s appointed suc…
The Infamous Crusades
- This period is one of the most famous in Medieval history, and involved an incredible display of battling, and the spread of religion by the sword. One of the reasons given for the crusades is to retake Jerusalem, which had fallen under the Islamic expansion. The crusades of Christianity are often seen as a direct response to Muslim expansion into the west and led to the inflation of Chr…
The High Middle Ages
- This period of the middle ages saw several significant events occur between England and France, including the death of Richard I, the ascension of King John as his successor and the loss of French territories to Arthur. The establishment of the “Magna Carta” also decreed that monarchs were forced to acknowledge that their power over their territori...
The End of The Medieval Period
- Although England and France had already had a history marred with conflict and battle for power, this period is also famous for the so-called 100-years war between the two countries. Though the two countries had battled for territory before, this war was the first indication of continued conflict between the two countries over a very long period of time, leading to nationalistic tendencies in t…