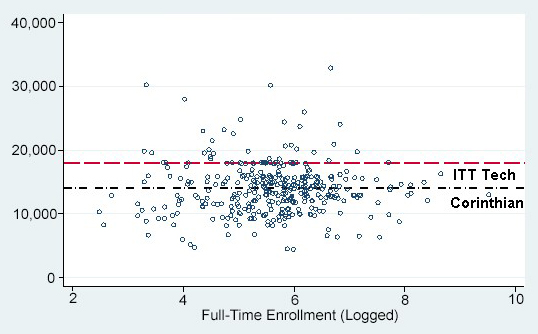
What Is a For-Profit College?
- Purpose and Business Goals For-profit colleges operate to make money. ...
- Funding Colleges often rely on multiple funding sources, including tuition, endowment funds, and government grants. ...
- Tuition and Affordability The posted tuition rates at for-profit colleges typically exceed public schools but are lower than those at private nonprofit institutions. ...
Why are for-profit colleges so expensive?
As a result, for-profit colleges generally cost more. For-profit colleges operate to make money. While educating students represents the primary purpose for a nonprofit or public college, for-profit schools attempt to limit costs, increase revenue, and report profits.
How do for-profit colleges operate?
For-profit colleges operate to make money. While educating students represents the primary purpose for a nonprofit or public college, for-profit schools attempt to limit costs, increase revenue, and report profits. The for-profit model can shape factors like admission standards, tuition rates, and financial aid opportunities.
Should you consider a for-profit college?
There is good news for students considering a for-profit school. They can almost always find the same program offered at a lower cost through a community college. This page introduces for-profit colleges so students know how to avoid predatory schools. What Is a For-Profit College?
How do non-profit schools make money?
Nonprofit schools still make money from tuition and donations, but those profits all go toward running the college rather than paying shareholders. Public or Private? Compared with nonprofits, for-profit colleges leave a much larger number of students in debt.

What does it mean if a college is for-profit?
For-Profit University: A for-profit institution is a college or university with shareholders who have an ultimate purpose to make money. For-profits are privately run. For-profit institutions charge tuition, and that tuition often goes back into the university for marketing and recruiting.
What is the difference between a for-profit and nonprofit college?
For-profit colleges distribute their profits among the institution's owners, investors, and shareholders. In contrast, nonprofit colleges reinvest their profits back into the institution. Public universities, which are nonprofit institutions, tend to have lower average tuition rates than private universities.
Why you shouldn't go to a for-profit college?
They're Often More Expensive. Considering that many for-profit schools don't hold regional accreditation — and that students pay nearly twice as much in tuition compared to public four-year colleges — for-profit college prices often don't match the education they provide.
Why do for-profit colleges exist?
The for-profits can offer class times that are convenient for students, rather than for professors. They can offer online classes, which many traditional universities have been reluctant — or unable — to dive into. They pay professors to teach, not conduct research.
Is Harvard for-profit or nonprofit?
Harvard University is a nonprofit, not a business. This is one of the central arguments that we hear professors, politicians, and students make when they advocate for Harvard to be more socially and morally responsible.
What are the cons of for-profit colleges?
Are for-profit schools bad? 6 issues to be aware ofThey often cost more than traditional colleges.They might spend less on your education.You could end up earning less.Their job placement statistics can sometimes be misleading.If your school closes, credit transfers might be difficult.More items...•
Are for-profit colleges worth it?
Because for-profit colleges prioritize revenue above all else, they won't hesitate to raise tuition costs and effectively force their students to take out loads of loans. Tuition at for-profit colleges is on average $8,000 a year more than that at public universities.
What percent of student debt is from for-profit colleges?
For-profit schools have been a central focus of the debate over the causes of these student debt and default trends. In 2016-2017, about 15% of Stafford loans went to for-profit students, even though they only comprise 5.6% of enrollments (Digest of Education Statistics 2019).
Is Penn State a for-profit school?
Public universities such as Penn State are a type of nonprofit university that receives some funding from the state. As Pennsylvania's only land-grant university, Penn State was founded in 1855 with a focus on research and public service, a tradition that has continued to this day.
Is DeVry a for-profit school?
DeVry University (formerly known as DeVry Education Group) is an American for-profit college. The school was founded in 1931 as DeForest Training School, and officially became DeVry University in 2002.
How many for-profit colleges are there in the US?
The federal government reports that there are currently 998 degree-granting for-profit colleges and another 1,723 non-degree granting for-profit institutions (U.S. Department of Education 2019).
How do nonprofit colleges make money?
These colleges receive funding from a variety of sources such as the government, tuition fees, and donations. A leading body of trustees oversees them. There are no proprietors or investors in a nonprofit school, leaving the administration to concentrate on giving quality education to their students.
Is Stanford a for profit university?
Stanford University is a non-profit public charity that receives its funds from sponsors, donors, parents/students and others in furtherance of our educational, research and patient care missions.
Is University of Phoenix for profit or nonprofit?
University of Phoenix, for-profit institution of higher learning based in Phoenix, Arizona, that offers classes primarily online. One of the largest universities of its kind in the United States, it spurred the rise of for-profit postsecondary schools in the late 1990s.
What is the hardest school to get into?
Harvard University — 3.19% With a record-low admission rate of just 3.19% for the class of 2026, Harvard currently ranks as the most difficult school to get into. This rate reflects admission into Harvard College, the Ivy League university's undergraduate school.
What Is a For-Profit College?
A for-profit college confers certificates, diplomas, and degrees at the postsecondary level. However, unlike nonprofit colleges, for-profit schools primarily aim to make a profit. Investors and shareholders expect to earn money from the school. As a result, for-profit colleges generally cost more.
Why do colleges offer for profit programs?
You have low grades or test scores. If there is something about your college application profile that is likely keep you from being accepted by more competitive schools, a for-profit college might have a program that could help you achieve your education and career goals, regardless of your past scores and grades.
What Are Examples of For-Profit Colleges?
Many for-profit colleges advertise heavily. They also often choose names that sound like legitimate, not- for-profit colleges. As a result, students might face confusion when researching colleges. Below are some well-known for-profit colleges.
What is a non profit school?
Not-for-profit schools, including public colleges and private nonprofit colleges, make educating students their primary mission. For-profit schools exist to make money.
How much debt do for-profit graduates have?
However, 88% of for-profit college graduates had loans with an average debt of nearly $40,000.
What is a degree mill?
Disreputable for-profit colleges are sometimes labeled “degree mills” or “diploma mills,” implying that these schools churn out one-size-fits-all degrees with little concern for individual students. This critique also suggests that for-profit colleges are, above all, concerned with profit, even to the detriment of their students. This may be true in some cases. In fact, more than a few for-profit schools have been shut down for unethical behavior. Still, there are for-profit schools that offer accessible, flexible degree programs that serve students and their best interests. Recognizing the differences between a for-profit college and a diploma mill is essential.
What is a college scorecard?
The College Scorecard lists whether a college operates on a for-profit or a nonprofit or public basis. The site, run by the Department of Education, also provides information on graduation rates, cost, and average salaries of graduates.
What is a for profit college?
For-profit colleges also cost more and offer degrees that are typically worth less than those earned from nonprofit institutions.
How are nonprofit schools funded?
Public nonprofits are funded by state governments, whereas private nonprofit colleges are funded privately through a combination of tuition, donations, and endowments.
Why are colleges closing?
Low graduation rates and high student debt have forced many for-profit colleges to close.
How many for profit credits fail to transfer to public colleges?
An average of 94% of for-profit credits fail to transfer to public colleges and universities. Despite their career promises and tuition discounts, for-profit schools should be a last resort. By and large, the for-profit industry fails to benefit students, who rarely graduate and often find themselves steeped in debt.
Why did the University of Phoenix get a fine?
The school was ordered to pay a $50 million fine and cancel $141 million in debts owed by students who'd been harmed by the deceptive ads.
Do for profit colleges leave students in debt?
Compared with nonprofits, for-profit colleges leave a much larger number of students in debt. Even worse, they produce a disproportionate share of indebted dropouts.
Do for profit credits transfer to nonprofit schools?
Not only do degrees from for-profit institutions carry little weight on the job market, but the credits themselves are also unlikely to transfer to nonprofit schools. Research indicates that an average of 94% of for-profit credits fail to transfer to public colleges and universities.
What is a For Profit College?
For-profit colleges are higher education institutions owned and run by private, profit-seeking corporations. A group of shareholders, or investors, are involved in all the decision-making processes of the college. They generally have a profit-seeking mindset. Essentially, for-profit colleges prioritize shareholders rather than students, in their attempts to make more money. Therefore, many for-profit colleges have programs that are highly “career-oriented” or “tech-oriented” because these study areas are in higher demand and typically result in better college revenues. Moreover, these For-profit colleges also try to cater to the needs of a specific student section by offering online and evening classes.
Why is college important?
Your college plays a very crucial role by imparting you the right education & guidance to shape your career in a specific direction. So, with so many college-options to choose from, it is a difficult job to figure out which college will be an ideal fit for you.
How long does it take to get a for profit degree?
Some of the courses at a for-profit college usually takes longer than four years to complete. This makes a degree from a for-profit college both costlier and more time-consuming than a degree from a non-profit college.
Is a for profit college better than a non profit?
While a non-profit college supports its students even if it has to suffer some losses in that academic year, a for-profit college will not hesitate to cut programs that aren’t making them money. Referring to data released by the National Center for Education Statistics, annual tuition fees of for-profit colleges is approximately $8,000 more than the tuition fees of a public non-profit college. So, if you are looking for an affordable option, a for-profit school may not be the right choice.
Is it smart to go to a for profit college?
So, if you take a well-researched decision to attend a particular course in a for-profit college or university, it can prove to be a smart step in your pursuit of a degree or a career shift.
Is for profit college good?
If you don’t care too much about having a well-rounded education and would rather want to leap straight into advanced training, for-profit college is a perfect blend for you. You can get started on a particular career, even while working.
Do for profit colleges give you a degree?
It is a widely accepted notion that these for-profit colleges will turn you up debt-laden and provide you a degree that places you far-behind in your career goals. However, this is not true in every ca?se. Some of the for-profit colleges offer a flexible degree program that equips you with the required marketable skills and supports your transition process towards a promising career.
What Is a For-Profit College?
A for-profit college is a school that is owned and operated by a private business or corporation. A group of shareholders, or investors, makes all of the decisions for the school, always with the aim of turning a profit.
Why are for profit colleges so popular?
Because for-profit colleges are revenue-driven and will cut classes and programs that don't make them money, you're more likely to find programs at these schools specializing in career-oriented degrees and vocational training.
What is the difference between a nonprofit and a for profit college?
By contrast, nonprofit colleges are publicly owned schools that place a strong emphasis on supporting and educating students, no matter the cost.
How long does it take to get a degree from a for profit college?
In addition, an undergraduate education at a for-profit college usually takes longer than four years, meaning that a degree from a for-profit college is often both costlier and more time-consuming than is a degree from ...
Why do for-profit colleges prioritize shareholders over students?
Essentially, for-profit colleges prioritize shareholders over students in their efforts to make money. Most for-profit colleges have programs that are heavily career- or tech-oriented as these areas of study are in higher demand and usually result in better revenue for the college.
What is the difference between a private for profit college and a private nonprofit college?
The main difference between a private for-profit college and a private nonprofit college is that the former focuses on making a profit, while the latter puts students' needs first.
Why do colleges offer online classes?
This is because many for-profit colleges offer online classes, allowing you to work at your own pace and earn more credits in a shorter amount of time. Remember that you will likely want to spend as little time as possible at a for-profit college considering these schools' high tuition costs!
What is a for-profit college?
For-profit colleges – it is higher education facilities that are founded and owned by private organizations.
What is the difference between for-profit and non-profit colleges?
Of course, there are numerous differences between for-profit and non-profit colleges.
What is a degree mill?
Most people think that a for-profit college – it is a “degree mill” or “diploma mill” as there are lots of such colleges that offer unified courses without paying attention to students’ needs.
Why is it important to have a professional attitude towards your school?
It is really important as the attitude of professionals in your field towards your school is really important and can significantly influence your career.
Do for profit colleges have flexibility?
Most for-profit colleges can provide with more flexibility.
Is a for profit college good?
In fact, for-profit colleges and schools can be a great opportunity to obtain the required training so you can start your career successfully.
Is it true that colleges are closed?
Unfortunately, it is 100% true in some cases and many for-profit colleges were shut because of it.
What Is a For-Profit College?
As opposed to nonprofit institutions, for-profit colleges prioritize financial dividends and the needs of stakeholders over student success and academic quality. Additionally, nonprofit schools can receive regional accreditation. Schools that earn regional accreditation meet rigorous standards related to areas like administration, academics, and student services.
Why do people attend for-profit schools?
Attending a for-profit school often leads to more academic flexibility for students. In addition to offering rolling or open admission, many for-profit institutions boast a deep catalog of online classes.
Why do we need online programs?
Especially enticing for working students anticipating a career change, online programs can allow learners to keep up with personal and professional obligations while simultaneously completing degree requirements. Many online programs deliver coursework asynchronously, enabling students to complete assignments largely at their own pace.
How much will college enrollment increase in 2020?
Coinciding with an increased demand for online learning, undergraduate enrollment at for-profit institutions rose 3% in 2020, while community colleges saw a 9% decline. Even in the face of substantial bad press, for-profit colleges are welcoming more and more students.
What to do before enrolling in a school?
Before enrolling, conduct serious research about your prospective schools. Define your academic and vocational needs and weigh them against online reviews, news, and professional opinions.
Do for-profit colleges have regional accreditation?
Considering that many for-profit schools don't hold regional accreditation — and that students pay nearly twice as much in tuition compared to public four-year colleges — for-profit college prices often don't match the education they provide. If vocational training is on your radar, community colleges offer similar educational resources at a fraction of the for-profit price.
Is a long list of general education requirements worth it?
In that case, completing a long list of general education requirements might not be worth your time or money.
Who bought Altierus Career College?
Altierus Career College is the remains of the Corinthian Colleges chain, purchased by a subsidiary the nonprofit student loan guaranty agency ECMC in 2015.
When did Wright Career College close?
Wright Career College, converted in 1995, closed in 2016.
Is a conversion from a for profit to a nonprofit legitimate?
Conversions from for-profit to nonprofit are legitimate when the assets and income are fully committed to the educational purpose, and control by private interests is eliminated. Some converted nonprofits may not be legitimate. A Government Accountability Office report about the problem is anticipated.
Is Southern New Hampshire University a for profit school?
The accreditor lists the school as for-profit as of December 2020. Southern New Hampshire University (converted in 1968) Stevens-Henager College and its affiliates Independence University, CollegeAmerica, and California College San Diego were purchased by a tax-exempt organization in 2012.