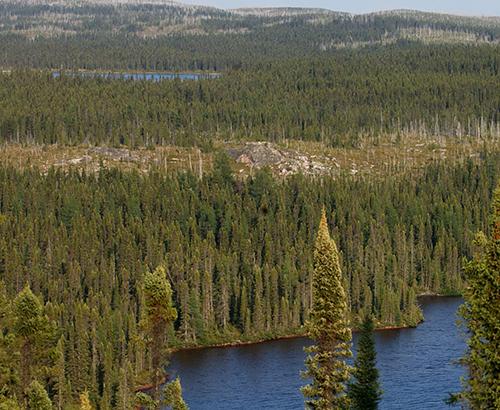
The taiga has several characteristics that distinguish it from the other forest biomes:
- Evergreen trees - This forest is covered with evergreen, or coniferous, trees.
- Cold weather - The taiga has the coldest weather of the forest biomes.
- Dry - The precipitation is only slightly more than the desert or the tundra.
Is a coniferous forest the same as a taiga?
The taiga has several characteristics that distinguish it from the other forest biomes: Evergreen trees - This forest is covered with evergreen, or coniferous, trees. Cold weather - The taiga has the coldest weather of the forest biomes. Dry - The precipitation …
Can a taiga be found in a temperate forest?
What makes a taiga forest? Taiga, also called boreal forest, biome (major life zone) of vegetation composed primarily of cone-bearing needle-leaved or scale-leaved evergreen trees, found in northern circumpolar forested regions characterized …
How does the taiga compare to the temperate forest?
The taiga is a forest of the cold, subarctic region. The subarctic is an area of the Northern Hemisphere that lies just south of the Arctic Circle . The taiga lies between the tundra to the north and temperate forests to the south.
Are taiga and the boreal forest the same thing?
Dec 31, 2019 · What makes a forest a taiga forest? Evergreen trees – This forest is covered with evergreen, or coniferous, trees. Cold weather – The taiga has the coldest weather of the forest biomes. Dry – The precipitation is only slightly more than the desert or the tundra. Where is the taiga forest located? The taiga is a forest of the cold, subarctic region.
What makes a taiga forest?
What are 2 characteristics of a taiga forest?
- Evergreen trees - This forest is covered with evergreen, or coniferous, trees. ...
- Cold weather - The taiga has the coldest weather of the forest biomes. ...
- Dry - The precipitation is only slightly more than the desert or the tundra.
What are 3 characteristics of the taiga biome?
What is the difference between a forest and a taiga forest?
What are 5 facts about taiga?
- In Taiga Biome, wildfires are very common. ...
- The average annual rainfall in the boreal forest biome is approximately 33 inches.
- The dominant plant in the taiga is the coniferous evergreen tree. ...
- These trees produce their seeds in cones.
What is the taiga known for?
Which forest is also known as taiga?
What are the characteristics of the boreal forest?
What defines a boreal forest?
How are a taiga and a temperate forest alike?
Is a taiga a coniferous forest?
Is taiga a tropical rainforest?
Where are the Taiga forests located?
These forests are located in the far north typically between the temperate forest biome and the tundra biome. On the globe this is between 50 degrees latitude north and the Arctic Circle. The largest taiga forest covers much of northern Russia and Siberia. Other major taiga forests include North America (Canada and Alaska) and Scandinavia (Finland, ...
What is the taiga biome?
The Taiga is one of the three main forest biomes. The other two are the temperate forest and the tropical rainforest. The taiga is the driest and coldest of the three. The taiga is sometimes called the boreal forest or the coniferous forest. It is the largest of all the land biomes. What makes a forest a taiga forest?
What is the largest biome in the world?
Taiga Forest. The Taiga is one of the three main forest biomes. The other two are the temperate forest and the tropical rainforest. The taiga is the driest and coldest of the three. The taiga is sometimes called the boreal forest or the coniferous forest. It is the largest of all the land biomes.
What are the characteristics of a taiga?
The taiga has several characteristics that distinguish it from the other forest biomes: Evergreen trees - This forest is covered with evergreen, or coniferous, trees. These are trees that don't drop their leaves, or needles, in the winter. They keep their leaves so they can soak up as much sunlight for as long as possible.
What are the plants in the Taiga?
Plants of the Taiga. The dominant plant in the taiga is the coniferous evergreen tree. These trees include spruce, pine, cedar, and fir trees. They grow close together forming a canopy over the land, like an umbrella. This canopy soaks up the sun and only lets a little bit of sunlight through to the ground.
What trees grow in the Taiga?
These trees include spruce, pine, cedar, and fir trees. They grow close together forming a canopy over the land, like an umbrella. This canopy soaks up the sun and only lets a little bit of sunlight through to the ground. The conifers of the taiga produce their seeds in cones. They also have needles for leaves.
Do conifers have needles?
This canopy soaks up the sun and only lets a little bit of sunlight through to the ground. The conifers of the taiga produce their seeds in cones. They also have needles for leaves. Needles are good at holding in water and surviving the harsh cold winds each winter. The trees also grow in a cone shape.
What is the Taiga?
The Taiga, an area of coniferous forests in the northern temperate zones, is created by boreal species of spruce, fir, larch, pine, cedar with a small mixture of hardwoods. The Taiga comprises open woodlands with trees spaced widely apart, as well as dense, shaded forests. Russian for "marshy pine forest," the Taiga covers about 50 million acres ...
What type of trees are in the Taiga?
Image credit: Elena Fox/Shutterstock. Dark coniferous is the most common type of forest found in the Taiga. This includes spruce, fir, pine and Siberian cedar trees. Light coniferous Taiga includes forest pine, larch, and some American species of pine.
How cold is the Taiga?
The area gets very short, mild and humid summers of about 50 to 100 days, with the average temperature in July being about 10 to 13 degrees Celsius (50-55 Fahrenheit). Winters are quite cold with steady snow cover and average temperatures below freezing. Some locations in Russia have even experienced temperatures of -67 degrees Celsius (-90 Fahrenheit)!
What is the Taiga zone?
In Russia, almost one-third of the territory belongs to the Taiga zone. Large Taiga areas in the mountains are concentrated in Siberia and the Far East in a predominantly continental climate. On each of the Northern Hemisphere's continents, the Taiga forms the northern border of the forest line.
What are the animals that live in the Taiga?
The widespread species of the Taiga that we know and see in other climatic areas include the wolf, fox, otter, weasel, ermine, European hedgehog, hare, the forest and field mouse, mink, deer, and roe deer. The largest predator is the brown bear.
Is the Taiga unpopulated?
Most of the Taiga is pretty unpopulated, and many of the Taiga's largest animals are sensitive to human presence, pollution, and changes to their habitat. However, a few large cities exist in the southern Taiga, like Toronto and Moscow, and there are 18 Indigenous communities throughout the Taiga with populations exceeding 200,000.
Why is the Taiga important?
Despite the various threats to the Taiga, there is some good news. Because of the biodiversity and ability of the area's flora and fauna to live and grow in cold temperatures , the Taiga plays a crucial role in confronting the threat of global warming.
What is the Taiga?
Much of the taiga is a dark, dense forest. Image by Orcaborealis. A cold wind whips through a huge coniferous forest. In its wake, falling snow swirls and evergreen branches sway. Sunlight filters through the dark green canopy, but it is too weak to warm your hands. Snow slides down from the peaks of cone-shaped trees and clumps on ...
What is the difference between a conifer and an evergreen?
Conifer: a type of tree or bush that makes cones and evergreen leaves , some of which we call needles. Decomposition: when dead plants, animals, or other living matter rot and break down into nutrients that can be used by other plants and living things. Evergreen: a plant that has leaves throughout the year.
What is an evergreen plant?
Evergreen: a plant that has leaves throughout the year. Hence, this plant is for"ever" green. Lichen: a living organism that is not a plant or an animal. Lichens usually have two living organisms, fungus and algae that work together in a beneficial manner... more (link is external)
What is the meaning of "evergreen"?
Evergreen: a plant that has leaves throughout the year. Hence, this plant is for"ever" green. Hibernate: the act of sleeping through the cold winter months, like some animals do to survive the winter... more (link is external) Lichen: a living organism that is not a plant or an animal.
What is a lichen?
Lichen: a living organism that is not a plant or an animal. Lichens usually have two living organisms, fungus and algae that work together in a beneficial manner... more (link is external) Migratory: moving from place to place. Birds often migrate to avoid cold and hot temperatures.
What is the largest biome in the world?
You are standing in the largest land biome in the world: the taiga. In Russian, “taiga” translates to “forest.”. This biome is also known as the snow forest or Boreal Forest, named after the Greek Goddess of the North wind. Coniferous trees dominate most of this biome, but occasional lakes and bogs punctuate the evergreen landscape.
What do animals eat in the winter?
Many animals eat whatever plants they can find, munching on the seeds of pine cones or green shoots buried beneath the snow. Some snack on other animals. For others that won't find enough food over the winter, hibernation is another option. Yet others leave the taiga and migrate south to warmer biomes for the winter.
Where are the Taiga forests located?
The taiga regions of North America and Eurasia are broad belts of vegetation that span their respective continents from Atlantic to Pacific coasts. In North America the taiga occupies much of Canada and Alaska. Although related transition forest types are present in the northern tier of the lower 48 United States, true taiga stops just north of the southern Canadian border. The vast taiga of Asia extends across Russia and southward into northeastern China and Mongolia. In Europe most of Finland, Sweden, and Norway are covered with taiga. A small, isolated area of boreal forest in the Scottish Highlands lacks some continental species but does contain the most widespread conifer of the Eurasian taiga, Scotch pine ( Pinus sylvestris ).
What is a taiga?
Taiga, also called boreal forest, biome (major life zone) of vegetation composed primarily of cone-bearing needle-leaved or scale-leaved evergreen trees, found in northern circumpolar forested regions characterized by long winters and moderate to high annual precipitation. The taiga, “land of the little sticks” in Russian, ...
What are the adaptations of the Taiga biome?
Plants and animals in the taiga are adapted to short growing seasons of long days that vary from cool to warm. Winters are long and very cold, the days are short, and a persistent snowpack is the norm. The taiga biomes of North America and Eurasia display a number of similarities, even sharing some plant and animal species.
When did the Taiga move northward?
As the glaciers began to retreat gradually about 18,000 years ago, species of the taiga began to move northward in Europe and North America. In eastern and central North America the northward movement of the forest was relatively steady and gradual.
Where is the tundra in the forest?
To the north of the lichen woodland lies forest-tundra, which occurs along the northern edge of tree growth (tree line). Patches of trees consisting of only a few species dot restricted portions of the landscape, forming a complex mosaic with tundra.
Where is the biota located?
This biota exists today as part of the taiga in the Highlands of Scotland. The areas of lowland central Alaska, the central Yukon territory, and the Far East region of Russia, which had climates too arid to permit the formation of ice sheets, were connected by the Bering Land Bridge, across which many species migrated.
As nouns the difference between forest and taiga
is that forest is a dense collection of trees covering a relatively large area larger than woods while taiga is a subarctic zone of evergreen coniferous forests situated south of the tundras and north of the steppes in the northern hemisphere.
English
A dense collection of trees covering a relatively large area. Larger than woods.
