Lewis acids and bases
Lewis acid is a chemical species that reacts with a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that donates a pair of electrons to a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, OH and NH3 are Lewis bases, because they can donate a lone pair of electrons…
What is a Lewis base?
A Lewis base can be defined as a chemical species in which the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) is highly localized, giving it the ability to donate pairs of electrons. Does Hydrochloric Acid Qualify as a Lewis Acid?
What are some examples of Lewis acids and bases?
An example of such a Lewis acid would be BR 3 (where R can be a halide or an organic substituent). Water and some other compounds are considered as both Lewis acids and bases since they can accept and donate electron pairs based on the reaction. Some common examples of Lewis acids which can accept electron pairs include:
How do you determine the strength of a Lewis base?
The strength of Lewis basicity correlates with the pK a of the parent acid: acids with high pK a 's give good Lewis bases. As usual, a weaker acid has a stronger conjugate base . The strength of Lewis bases have been evaluated for various Lewis acids, such as I 2, SbCl 5, and BF 3.
Do Lewis acids have stronger conjugate bases?
As usual, a weaker acid has a stronger conjugate base . The strength of Lewis bases have been evaluated for various Lewis acids, such as I 2, SbCl 5, and BF 3. Nearly all electron pair donors that form compounds by binding transition elements can be viewed as a collections of the Lewis bases—or ligands.
What makes a stronger Lewis base?
The strength of Lewis basicity correlates with the pKa of the parent acid: acids with high pKa 's give good Lewis bases. As usual, a weaker acid has a stronger conjugate base. Examples of Lewis bases based on the general definition of electron pair donor include: simple anions, such as H− and F.
What are the requirements for a Lewis base?
Lewis Bases donate an electron pair. Lewis Bases are Nucleophilic meaning that they “attack” a positive charge with their lone pair. They utilize the highest occupied molecular orbital or HOMO (Figure 2). An atom, ion, or molecule with a lone-pair of electrons can thus be a Lewis base.
What is a characteristic of Lewis base?
A Lewis base is any substance, such as the OH- ion, that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis base is therefore an electron-pair donor. One advantage of the Lewis theory is the way it complements the model of oxidation-reduction reactions.
What is weak Lewis base?
Lewis base is a compound that should donate electrons easily. The weakest Lewis base is Cl⊝, because it has octet rule. Cl⊝ won't donate electrons easily.
How do you identify a Lewis acid and base?
Identify the acid and the base in each Lewis acid–base reaction. Strategy: In each equation, identify the reactant that is electron deficient and the reactant that is an electron-pair donor. The electron-deficient compound is the Lewis acid, whereas the other is the Lewis base.
What is required to happen in Lewis acid-base reactions?
A Lewis base is a substance that donates a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. So, a Lewis acid-base reaction is represented by the transfer of a pair of electrons from a base to an acid. A hydrogen ion, which lacks any electrons, accepts a pair of electrons.
Which is a characteristic of a Lewis base quizlet?
Which is a characteristic of a Lewis base? It behaves as the electron donor.
Why is H2O a Lewis base?
Water shows Amphoterism. By donating its proton to a base to become its conjugate acid, water acts as an acid. By accepting a proton from acid and thus becoming its conjugate base, water acts as a base. Therefore water can act as a Lewis acid as well as a Lewis base.
What is a Lewis base explain with example?
Water (H2O) has two nonbonding pairs of electrons, so it donates one pair to the carbocation. As a result, one bond is formed and shared between carbon and oxygen. Water acts as a Lewis base because it is the electron pair donor in this reaction. Water acts as a Lewis base.
Which is the strongest Lewis acid?
BBr3Hence, BBr3 has the highest acidic character and is the strongest lewis acid.
Is HCl a Lewis base?
Cl in HCl has three lone pairs of electrons, so it can donate a lone pair and thus becomes a Lewis base. Just like water is called a Lewis base because oxygen has two lone pairs and can donate a lone pair.
Which is weakest Lewis acid?
Lewis acid strength depends upon the ease with which it can accept a pair of electrons from the donor. BF3 is the weakest Lewis acid due to back bonding.
Which is a Lewis base?
A Lewis base is a chemical compound that can donate a pair of electrons to a suitable electron-pair acceptor (Lewis acid) to form a Lewis adduct.
Do all Lewis bases have a lone pair?
Lewis bases usually have non-bonding electrons or lone pairs this makes oxygen and nitrogen compounds common Lewis bases. Lewis bases may be anionic or neutral. The basic requirement is that they have a pair of electrons to donate. Figure 2.11.
Which of the following is a Lewis base?
Carbon molecules which have pie electrons i.e multiple bonds of a carbon have more electron density in that bond which can be easily donated to other species so they generally act as lewis base.
Can Fe3+ act as a Lewis base?
In this reaction the ferric ion (Fe3+) is acting as a Lewis Acid and the oxalate anion (C2O42-) as a Lewis Base. A Lewis Acid is an electron pair acceptor and a Lewis Base is an electron pair donor.
What is the Lewis definition of an acid or a base?
In this theory an acid is defined as an electron acceptor and a base is defined as an electron donor.
Which acids are Lewis acids?
Examples of Lewis Acids according to its ability to accept an electron pair: H+, K+, Mg2+, Fe3+, BF3, CO2, SO3, RMgX, AlCl3, Br2.
How do you identify a Lewis acid?
A Lewis acid can be identified as any molecule with an empty orbital that can be filled with an electron pair from another molecule.
How do you identify Lewis acids and bases?
You can identify Lewis Acids and Bases by looking at the configuration of the molecules and counting the electrons. If the molecule has space to ac...
What is the difference between acid and Lewis acid?
An acid can be any liquid with a pH less than 7, whereas a Lewis acid specifically is a molecule that has the ability to accept an electron pair.
Why is Trimethylamine a Lewis base?
Trimethylamine, which is classified as an amine, is the Lewis base because it donates its nonbonding pair of electrons to boron trifluoride. Water (H2O) has two nonbonding pairs of electrons, so it donates one pair to the carbocation. As a result, one bond is formed and shared between carbon and oxygen.
Why do amines act as Lewis bases?
Phosphine, or phosphorus containing organic compounds, and amines typically act as Lewis bases because they also have nonbonding pairs. Amines are organic compounds with a lone pair of electrons, so they contain carbon (C). We can think of them as relatives of ammonia (NH3), so they also contain nitrogen (N).
Why is water a Lewis base?
As a result, one bond is formed and shared between carbon and oxygen. Water acts as a Lewis base because it is the electron pair donor in this reaction.
Which ion donates one of its nonbonding pairs to the proton (H+)?
In the example below, the hydroxide ion (OH-) donates one of its nonbonding pairs to the proton (H+). The hydroxide ion acts as a Lewis base.
What are negatively charged particles?
Electrons are negatively-charged particles. If an atom, ion, or molecule has an excess number of electrons , then they can be negatively charged. So, negatively-charged ions, or anions, typically act as Lewis bases. Acid-Base Reactions.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What does the bond between A and B mean?
The bond formed between A and B indicates that A and B are now sharing a pair of electrons, because the single line between A and B is equivalent to two electrons.
What are Lewis acids?
Most compounds considered to be Lewis acids require an activation step prior to formation of the adduct with the Lewis base. Well known cases are the aluminium trihalides, which are widely viewed as Lewis acids. Aluminium trihalides, unlike the boron trihalides, do not exist in the form AlX 3, but as aggregates and polymers that must be degraded by the Lewis base. A simpler case is the formation of adducts of borane. Monomeric BH 3 does not exist appreciably, so the adducts of borane are generated by degradation of diborane:
What does a center dot represent?
A center dot may also be used to represent a Lewis adduct, such as Me3B•NH3. Another example is boron trifluoride diethyl etherate, BF 3 •Et 2 O. (In a slightly different usage, the center dot is also used to represent hydrate coordination in various crystals, as in MgSO 4 •7H 2 O for hydrated magnesium sulfate, irrespective of whether the water forms a dative bond with the metal.)
What are the different types of hard bases?
typical hard bases: ammonia and amines, water, carboxylates, fluoride and chloride. typical soft bases: organophosphines, thioethers, carbon monoxide, iodide. For example, an amine will displace phosphine from the adduct with the acid BF 3. In the same way, bases could be classified.
How are two atoms held together?
Lewis had suggested in 1916 that two atoms are held together in a chemical bond by sharing a pair of electrons. When each atom contributed one electron to the bond, it was called a covalent bond. When both electrons come from one of the atoms, it was called a dative covalent bond or coordinate bond.
What is a Lewis base called?
Many Lewis bases are "multidentate," that is they can form several bonds to the Lewis acid. These multidentate Lewis bases are called chelating agents .
What is the ECW model?
The ECW model is a quantitative model that describes and predicts the strength of Lewis acid base interactions, −Δ H. The model assigned E and C parameters to many Lewis acids and bases. Each acid is characterized by an E A and a C A. Each base is likewise characterized by its own E B and C B. The E and C parameters refer, respectively, to the electrostatic and covalent contributions to the strength of the bonds that the acid and base will form. The equation is
What are the methods used to determine Lewis acidity?
Many are based on spectroscopic signatures such as shifts NMR signals or IR bands e.g. the Gutmann-Beckett method and the Childs method.
Definition of Lewis and Acid Base
In science liquids are either an acid, a base, or neutral, according to a pH scale. A pH scale has a range of 0-14 numbers and will place a liquid on the scale 0-6 being acid, 7 is neutral, and 8-14 is a base. Generally sour or bitter liquids are acids, and slimy cleaning liquids are bases.
Background
Gilbert Lewis (1875-1946) was an American chemist who discovered the bonding electron pairs, and who the acid and base concepts are named after. He attended Harvard University and taught at Berkley college for 34 years. He helped mold the chemistry program and teachings into one of the best in the nation, still to this day.
Identifying Lewis Acid and Base
Liquids can either be described as an acid or a base, also known as, an electron acceptor (acid) or an electron donor (base). They often react with each other to form a covalent bond, this is a bond where electron pairs are shared.
Lewis Acid and Base Reactions
The general equation for acid and base reactions is: Lewis acid + Lewis base ? acid-base product. This means that there is an acid and a base present, an electron acceptor and an electron donor in order for a reaction to occur.
Why is hydrogen an acid?
For example, in Brønsted acid base reactions the hydrogen ion is an acid because it accepts an electron pair from the Brønsted base. Consequently under the Lewis acid-base concept in Brønsted acid base reactions involve the formation of an adduct between H + and a base.
How do Lewis acids and bases work?
The Lewis acid base concept generalizes the Brønsted and solvent system acid base concepts by describing acid-base reactions in terms of the donation and acceptance of an electron pair. 1 Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors 2 Lewis bases are electron pair donors
Why are substances considered amphoteric?
2. Substances are sometimes considered amphoteric because they exhibit Lewis acidity and basicity at different types of atomic centers. The classic example is aluminum hydroxide, A l ( O H) 3. In water A l ( O H) 3 can act as a Lewis acid towards OH - ion. The reaction occurs by formation of an adduct at A l ( O H) 3 's Al 3+ center:
What is the arrow in a covalent bond?
Such coordinate covalent bonds are often represented by an arrow that indicates the direction of electron donation from the base to the acid.
What are the two factors that govern the course of chemical reactions?
Two factors govern the course of chemical reactions - thermodynamics and kinetics . Thermodyamics determines what possible fates of the reaction can take place while kinetics determines which among those possible fates will take place quickly under a particular reaction conditions. Because of this, it can be helpful to distinguish Lewis acids and bases that tend to undergo reaction quickly with one another from those which do so more slowly. For this reason, synthetic chemists use the terms electrophile and nucleophile to refer to Lewis acids and bases that react quickly:
Why are Lewis acid base reactions displacement reactions?
1. Many Lewis-Acid base reactions are displacement reactions. This is because the hydrogen ion is usually bound to something at the start of the reaction. In such cases the Lewis acid H + unit is transferred from one Lewis base and another :
Which class of Lewis acids reacts with a given Lewis base?
electrophile - Lewis acids that rapidly react with a given Lewis base or class of Lewis bases are said to be good electrophiles
Lewis Acid
Lewis acid is a substance that is always an electron pair acceptor. Classically, It is described by trigonal planar structure and an empty p or d-orbital.
Lewis Base
Lewis bases are electron-rich species that also act as nucleophiles. These are the chemical species that have the most localized highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO. These species can donate their electron pairs to Lewis acids for the formation of coordinate covalent bonds or complexes.
Lewis adduct
When a Lewis base donates its electrons from the highest occupied molecular orbital, HOMO (high energy) to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, LUMO (low energy) of Lewis acid, a coordinate covalent bond or complex is formed called Lewis adduct. It is represented with dots in the center of the complex as a gesture of showing electrons.
Common reactions between Lewis acids and Lewis bases
In this reaction, fluoride anion is an electron donor, and boron from boron trifluoride is an electron acceptor. This means that the fluoride ions act as a Lewis base and boron trifluoride as a Lewis acid. An adduct is formed when Lewis base (F –) attacks the Lewis acid (BF 3 ).
Applications of Lewis acids and Lewis base
They are used in the Friedel-Crafts reactions (acylation and alkylation).
Concepts Berg
Metal ions such as sodium (Na 1+ ), magnesium (Mg 2+ ), and cerium (Ce 3+ ), etc act as Lewis acids because they have empty orbitals. They can coordinate with bases to form adducts. This means all metal ions that have one or more empty orbital can be Lewis acid.
Which is the strongest inorganic base?
The hydroxide ion (OH-) is the strongest inorganic base because it strongly attracts a proton (H+) to become water. In this sense, any inorganic compound like NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH and FrOH (group 1 hydroxides or alkali metal hydroxides) which ionises completely in water to give free OH- ions can be considered as very strong bases. Note that it is not a particular compound, but the OH- ion which is the strong base.
Which is more basic, NH3 or BH3?
Greater the tendency to donate the electrons more is the basic character and hence NH3 is more basic than BH3
What is a base?
A base is defined as an “electron-pair donor” or as a “proton acceptor”.
Why is the size of N so small?
Size of N is very small. It can not accommodate the two lone pairs of electrons on it, so that it has greater tendency to lose these electrons.
Is AlF3 stronger than AlCl3?
AlF3 is the stronger acid between AlF3 and AlCl3. This is because fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine, which means that fluorine has a greater affinity for electrons than chlorine and thus will tend to pull the electrons away from the Al atom. (Fluorine is a stronger 'electron withdrawing' element than chlorine). The partial positive charge on Al in AlF3 will be greater than in AlCl3, so electrons will more easily be accepted by AlF3 than AlCL3.
Which Lewis base is stronger, F- or carbon?
F- is the strongest Lewis base as Flourine is more electronegative than Carbon,so it can stabilize the negative charge more….
Which Lewis base does not readily donate an electron pair?
So it’ll own the electron. Taking it away from F is too hard. So it does not readily donate an electron pair making it the weakest Lewis base.
Lewis Acid
Examples of Lewis Acids
- Some common examples of Lewis acids which can accept electron pairs include: 1. H+ ions (or protons) can be considered as Lewis acids along with onium ions like H3O+. 2. The cations of d block elements which display high oxidation states can act as electron pair acceptors. An example of such a cation is Fe3+. 3. Cations of metals such as Mg2+ and Li+can form coordinat…
Examples of Lewis Bases
- Examples of Lewis bases which have an ability to donate an electron pair are listed below. 1. Pyridine and the derivatives of pyridine have the ability to act as electron pair donors. Thus, these compounds can be classified as Lewis bases. 2. The compounds in which Oxygen, Sulphur, Selenium, and Tellurium (which belong to group 16 of the Periodic Table) exhibit an oxidation st…
Chemical Reactions Between Lewis Acids and Bases
- Reactions with the H+ ion
The H+ ion acts as a Lewis acid and H2O acts as a Lewis base. The reaction between the water molecule and the proton yields a hydronium ion (H3O+), as illustrated below. Here, the oxygen atom donates an electron pair to the proton, forming a coordinate covalent bond in the process. … - Reaction Between Ag+ and Ammonia
In this reaction, two Lewis bases form an adduct with one Lewis acid, as illustrated below. Here, ammonia acts as a Lewis base and the silver ion acts as a Lewis acid. Each nitrogen atom donates an electron pair to Ag+, resulting in two separate coordinate covalent bonds. The adduc…
Applications of Lewis Acids and Bases
- Some important applications of Lewis acids and bases are provided below. Lewis acids play a vital role as a catalyst in the Friedel-Crafts reaction – AlCl3 accepts a lone pair of electrons belonging to the chloride ion leading to the formation of AlCl4–in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation process. This also leads to the formation of the highly electrophilic carbonium ion which acts a…
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
- What is the Lewis Definition of Acids and Bases?
Gilbert N. Lewis put forward his definitions of acids and bases in the year 1923. According to this definition, an acid is an electron pair acceptor and a base is an electron pair donor. Therefore, a Lewis acid can be defined as a chemical entity that can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis … - Does Hydrochloric Acid Qualify as a Lewis Acid?
Hydrochloric acid cannot be classified as a Lewis acid since it cannot accept an electron pair. However, this compound dissociates into its constituent ions, liberating H+ions (which are considered as Lewis acids). Due to its inability to accept electron pairs, hydrochloric acid is ofte…
Overview
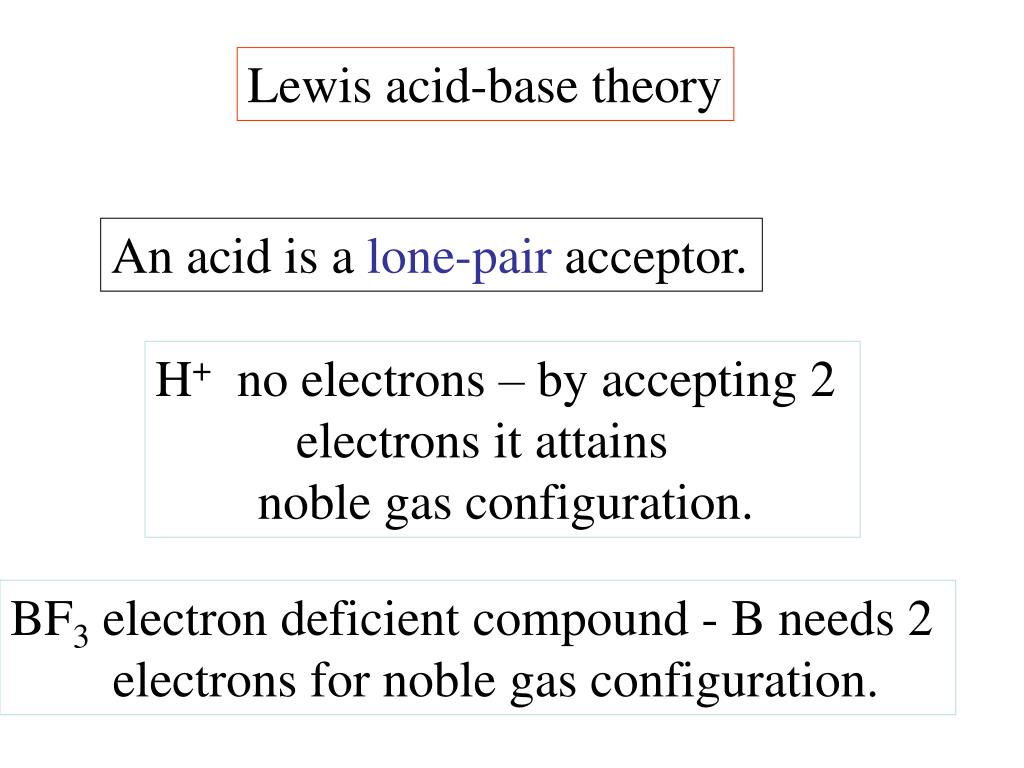
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct…
Lewis bases
A Lewis base is an atomic or molecular species where the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) is highly localized. Typical Lewis bases are conventional amines such as ammonia and alkyl amines. Other common Lewis bases include pyridine and its derivatives. Some of the main classes of Lewis bases are
• amines of the formula NH3−xRx where R = alkyl or aryl. Related to these are pyridine and its deri…
Depicting adducts
In many cases, the interaction between the Lewis base and Lewis acid in a complex is indicated by an arrow indicating the Lewis base donating electrons toward the Lewis acid using the notation of a dative bond — for example, Me3B←NH3. Some sources indicate the Lewis base with a pair of dots (the explicit electrons being donated), which allows consistent representation of the transition from the base itself to the complex with the acid:
Lewis acids
Lewis acids are diverse and the term is used loosely. Simplest are those that react directly with the Lewis base, such as boron trihalides and the pentahalides of phosphorus, arsenic, and antimony.
In the same vein, CH3 can be considered to be the Lewis acid in methylation reactions. However, the methyl cation never occurs as a free species in the co…
Hard and soft classification
Lewis acids and bases are commonly classified according to their hardness or softness. In this context hard implies small and nonpolarizable and soft indicates larger atoms that are more polarizable.
• typical hard acids: H , alkali/alkaline earth metal cations, boranes, Zn
• typical soft acids: Ag , Mo(0), Ni(0), Pt
Quantifying Lewis acidity
Many methods have been devised to evaluate and predict Lewis acidity. Many are based on spectroscopic signatures such as shifts NMR signals or IR bands e.g. the Gutmann-Beckett method and the Childs method.
The ECW model is a quantitative model that describes and predicts the strength of Lewis acid base interactions, −ΔH. The model assigned E and C parameters to many Lewis acids and bases. Eac…
History
The concept originated with Gilbert N. Lewis who studied chemical bonding. In 1923, Lewis wrote An acid substance is one which can employ an electron lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. The Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory was published in the same year. The two theories are distinct but complementary. A Lewis base is also a Brøns…
See also
• Acid
• Base (chemistry)
• Acid–base reaction
• Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory
• Chiral Lewis acid