
The characteristics of positively charged particles are:
- The positive rays or anode rays travel in the opposite direction to the cathode rays.
- The deflection of anode rays in an electric and magnetic field is opposite to that of cathode rays.
- The anode rays are attracted towards the negative plate in the electric field and towards the north pole in a magnetic field. ...
Which particle has a negative charge?
What are examples of negative charges?
- bromide Br-
- chloride Cl-
- fluoride F-
- iodide I-
- nitride N3-
- oxide O2-
- sulfide S2-
What is a negatively charged particle called?
What Is a Negatively Charged Particle Called? A negatively charged particle within an atom is called an electron. Electrons were discovered in 1897 by a British scientist named J.J. Thomson. All of the electrons found in an atom balance out the protons of the atom.
What are positive and negative charged particles?
Positively charged things/particles are those which have more protons than electrons. Negatively charged things/particles have more electrons than protons. Think of it as label, implying a property. The property is that opposite charges attract, and the same would repel. Example : ++ and - - is repels , + - attracts
Which particle of an atom has a positive charge?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the three main subatomic particles found in an atom. Protons have a positive (+) charge. An easy way to remember this is to remember that both proton and positive start with the letter 'P.' Neutrons have no electrical charge.
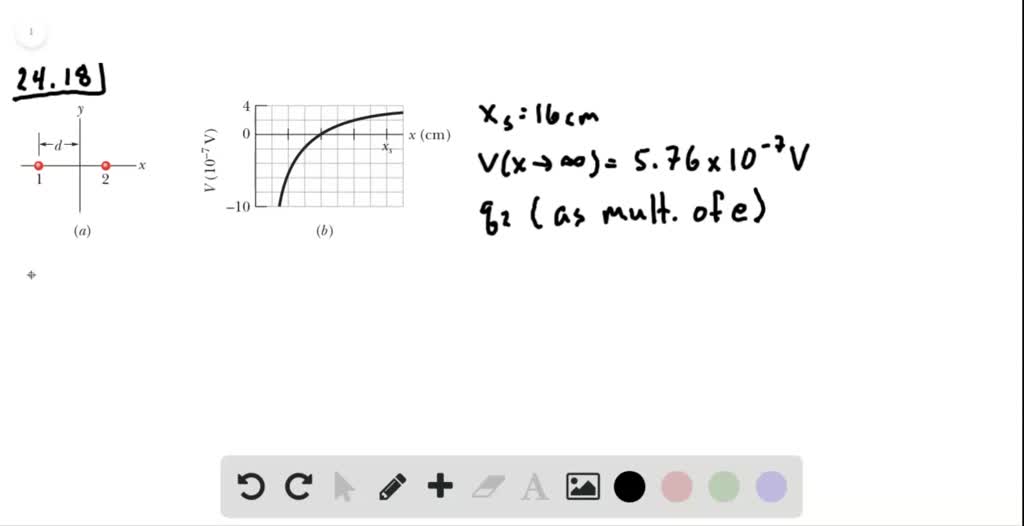
How does a particle become positively charged?
An electrical charge is created when electrons are transferred to or removed from an object. Because electrons have a negative charge, when they are added to an object, it becomes negatively charged. When electrons are removed from an object, it becomes positively charged.
What makes a particle positively or negatively charged?
Any particle, whether an atom, molecule or ion, that contains less electrons than protons is said to be positively charged. Conversely, any particle that contains more electrons than protons is said to be negatively charged.
What causes a positive charge in an atom?
The atom that has lost an electron becomes a positively charged ion (called a cation), while the atom that picks up the extra electron becomes a negatively charged ion (called an anion).
What particle has positively charged?
protonsThere are three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Two of the subatomic particles have electrical charges: protons have a positive charge while electrons have a negative charge.
What does it mean to be positively charged?
If an object has a positive charge, that means it has lost some electrons and now has more protons than electrons.
What is a positive particle?
positron, also called positive electron, positively charged subatomic particle having the same mass and magnitude of charge as the electron and constituting the antiparticle of a negative electron.
What is a positive charge called?
Positively charged ions are called cations; negatively charged ions, anions.
How is the charge of the particle determined?
An atom is called neutral if the number of protons equals the number of electrons. Thus, an atom can be positive, negative, or neutral. The charged particle is negative when it gains electron from another atom. It is positively charged if it loses electron from it.
What particle has either a positive or negative charge?
Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge. Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge. Protons are bound together in an atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. Neutrons are a type of subatomic particle with no charge (they're neutral).
How do you differentiate between positive and negative charge?
If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a negative charge, if there are fewer it will have a positive charge, and if there are equal numbers it will be neutral.
Which describe a negatively charged particle?
Electron: A negatively charged particle found circling or orbiting an atomic nucleus. An electron, like a proton is a charged particle, although opposite in sign, but unlike a proton, an electron has negligible atomic mass.
Which particle is a negatively charged ion?
ElectronsElectrons have a negative charge, whereas protons have a positive charge. When an atom gains electrons, this results in a negative charge. This type of ion is called an anion.
What are the particles that stick together?
Protons and neutrons are sticky and stick together into atomic nuclei. This is called the strong nuclear force or the strong interaction. Some matter does not feel the strong force; these particles are called "leptons.". Some matter does, and they are called "quarks" (and combinations of them are called "hadrons").
Which experiment found that electrons have a definite charge?
Starting with the Millikan oil drop experiments the electron was found to have a definite charge and the microcosm of elementary particles made mathematical sense , from nuclear physics to quark physic s with assigned charges and masses and a number of quantum numbers.
Why does the Higgs field have a weak coupling to all of the "matter" particles?
In short, the Higgs explains why everything which is not a proton or a neutron doesn't zip off at the speed of light.
Why do protons and neutrons have a mass so much higher than electrons?
We've secretly also answered why protons and neutrons have a mass so much higher than the electron: the electron is a single particle which does not feel the strong force; the protons and neutrons are made up of three quarks which are bound together by the strong force.
What is the term for the phenomenon where electrons attract and repel protons?
To particle physics, this is all known as "electromagnetism."
How do weak interactions play nice together?
named Sheldon Glashow discovered that you could make relativistic quantum theory and the weak interaction play nice together if you "bundle in" the electromagnetic force and describe them both together, mediated by four types of 'virtual' particles: two of those particles, the Z boson of the weak interaction and the photon of electromagnetism, at very high energies can phase into each other.
Why can't we explain why Nature hasn't chosen fewer interactions or more interactions?
We cannot give you a great explanation why Nature hasn't chosen fewer interactions or more interactions; in particular we cannot tell you a deep reason why Nature chose for there to be an electromagnetic interaction at all. We can give you details but you can always persist asking "why" until we find ourselves in ignorance.
What is a positive charge?
Positively charged things/particles are those which have more protons than electrons. Negatively charged things/particles have more electrons than protons. Think of it as label, implying a property. The property is that opposite charges attract, and the same would repel. Example : ++ and - - is repels , + - attracts
Which molecule has a positive or negative charge?
Larger molecules such as proteins may have individual parts of the molecule be ionic, but in general, an ion is an atom (or molecule) that has a positive or negative charge.
What are the quarks in a proton?
Quarks come in 6 flavors, but only two of these flavors are found in protons and neutrons: the Up quark and the Down quarks. The Up quark has charge +2/3 and the Down quark has charge -1/3. A little math will let you guess that a proton consists of 2 Up quarks and 1 Down quark and the neutron consists of 2 Down quarks and 1 Up quark. [1]
What is the charge of the universe?
The first thing is that there is more than electric charge to describe the contents of the Universe. Most importantly, there are protons and electrons (in addition to neutrons and neutrinos). Protons have charge +1 and electrons have charge -1 (neutrons and neutrinos are neutral with charge 0). Relativistic quantum field theory tells us that there is an anti-particle for every particle and we have discovered antiprotons and anti-electrons (usually called positrons).
How much energy does a protons have?
It depends a lot on energies of interacting particles. In the LHC positively charged protons have so much energy ( 7 TeV) that they interact mainly via the short range strong interaction between quarks which results in production of many (up to few hundreds) new particles and antiparticles
What is the charge of a protons and electron?
Protons have charge +1 and electrons have charge -1 (neutrons and neutrinos are neutral with charge 0). Relativistic quantum field theory tells us that there is an anti-particle for every particle and we have discovered antiprotons and anti-electrons (usually called positrons).
What are the elements that make up atoms?
Particles in this sense are the building block used to form atoms: neutrons, protons and electrons. As previously stated bringing a single electron and a single proton together would form a hydrogen atom, but since you mentioned ions I don't think this is what you meant.
What does it mean when a protons are positively charged?
Protons are positively charged, they define the element that the atom is part of. Changing the number of protons in an atom changes the element.
Which subatomic particle has a positive charge?
It is the nucleus of the atom that has a positive charge this charge is due to protons which are the subatomic particle that have a positive charge
What forces hold quarks together?
The gluons hold the quarks together into protons and neutrons. “Residual” forces from these gluons then in turn hold the protons and neutrons together into a nucleus.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The nucleus is a group of positive protons and (sometimes) neutral neutrons. The strong force holds the protons and neutrons together to form the nucleus. The nucleus serves as a source of attraction for all the negative electrons that orbit the center of the atom.
What is a positive charge atom called?
Positively charged constituent of an atom is called a proton. But when an atom has a positive charge it is called cation.
What are the particles that make up the nucleus called?
The particles that make up a nucleus - up and down - are called “quarks”, and the other ones - electrons and neutrinos, which, like quarks, have two heavier variants - are “leptons”.
What is the weak interaction between Z and W?
The Z and W Bosons mediate the “weak interaction”, depicted below. In the weak interaction, a down is turned into an up, an electron, and an (anti-)neutrino. This is called “beta decay”. It is a form of (harmless) radioactive decay. By changing a down into an up, it is changing a neutron into a proton. Since it causes an atom’s proton number to change, it’s effectively turning one element to another.

The Basic interactions.
- The world as we know it today consists of five fundamental things that happen; they are all called "fields" and the first four are called "forces" or "interactions". In rough order from strongest to weakest, these 4 are as follows. 1. Protons and neutrons are sticky and stick together into atomic nuclei. This is called the strong nuclear force or t...
and Then There Was Unity.
- We can tell you some other things about electric charge though. A full classical theory was available per James Clerk Maxwell, and a full quantum theory became available due to the works of Schwinger, Tomonaga, and Feynman. This became a template for understanding the strong force, with photons replaced by "gluons" and electric charge replaced with three "color charges" (…
What The Electroweak Theory Tells Us About charge.
- Okay, now that you know that the electromagnetic force is a low-temperature part of this electroweak theory, what does that tell us about electric charge? It says that electric charge comes about as part of two conserved quantities, called "weak isospin" or T3 and "weak hypercharge" or YW.The quarks, for some reason, have a weak hypercharge of +1/3. The leptons…
Mass discrepancies.
- We've secretly also answered why protons and neutrons have a mass so much higher than the electron: the electron is a single particle which does not feel the strong force; the protons and neutrons are made up of three quarks which are bound together by the strong force. (In general that is a property of the strong force: it is caused by a powerful three-way charge that we call a "…