What are the fibrous tissue?
Any tissue in plants and animals composed of bundles of densely woven, tiny fibres is known as fibrous tissue. Collagen fibres are arranged in parallel bundles to make fibrous (connective) tissue. It is also known as dense connective tissue and is present in the tendons, dermis, and ligaments.
What cells are in fibrous tissue?
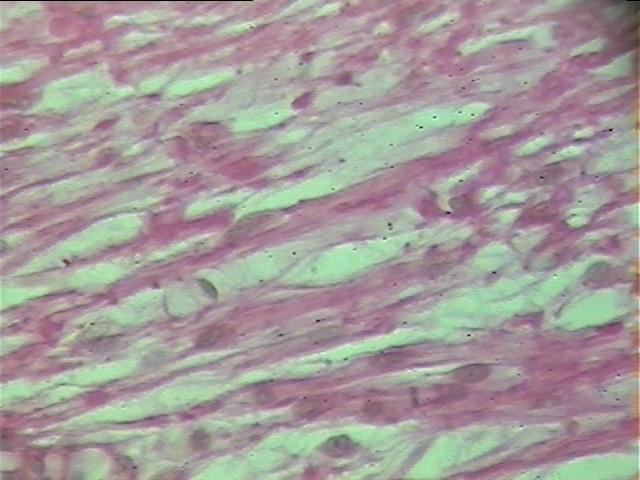
This tissue contains closely packed, parallel, often wavy bundles of collagen fibres, with scanty ground substance (figure 6). The only cells in this tissue are fibroblasts which are squeezed between the bundles of collagen fibres. It is found especially in tendons and ligaments.
What is the main component of fibrous connective tissue?
A type of tissue that is mostly made up of tough protein fibers called collagen and cells called fibroblasts. Fibrous connective tissue supports, protects, and holds bones, muscles, and other tissues and organs in place.
What are the 2 forms of fibrous connective tissue?
Three types of fibrous connective tissue include the ligaments, tendons, and fasciae.
What is an example of a fibrous?
Skull is the best example of a fibrous joint. In this type of immovable joint, the bones are fused together in such a way that they are fixed to that part and frame a structure.
What are the 3 fibers that make up the connective tissue?
Loose and dense connective tissue are made up of the following three fibers: collagen fibers, reticular fibers, and elastin fibers.
What are the three fibrous components of connective tissue?
Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells.
What layer is a fibrous connective tissue?
The perichondrium is a dense layer of fibrous connective tissue that covers the surface of most of the cartilage in the body. The perichondrium consists of an outer fibrous layer that contains fibroblasts and an inner chondrogenic layer that contains chondroblasts.
How fibrous connective tissue is formed?
It may be synthesized by fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells (around blood vessels) and osteoblasts (bone-forming cells). Type II collagen fibers are less than 80 nm in diameter and occur in hyaline cartilage and in intervertebral discs. It is synthesized by chondrocytes (cartilage-forming cells).
What fibrous means?
Definition of fibrous 1a : containing, consisting of, or resembling fibers. b : characterized by fibrosis. c : capable of being separated into fibers a fibrous mineral.
Where is fibrous tissue found in the body?
Fibrous connective tissue, which is composed of parallel bundles of collagen fibers, is found in the dermis, tendons, and ligaments.
What is the most common cell type found in fibrous connective tissue?
FibroblastsFibroblasts are the most common cell type of connective tissue. They produce both fibers and amorphous ground substance.
Where are fibrous cells found?
Irregularly arranged fibrous connective tissues are found in areas of the body where stress occurs from all directions, such as the dermis of the skin. Regular fibrous connective tissue, shown in Figure 2, is found in tendons (which connect muscles to bones) and ligaments (which connect bones to bones).
What type of cell produces a fibrous protein?
Fibroblasts are cells found commonly in the body of humans and other animals, which regulate and maintain connective tissue through the production of fibrous proteins and ground substance.
What are the 3 types of fibers in connective tissue?
Loose and dense connective tissue are made up of the following three fibers: collagen fibers, reticular fibers, and elastin fibers.
What are 3 types of fibrous connective tissue?
There are different types of fibrous connective tissue. Three types of fibrous connective tissue include the ligaments, tendons, and fasciae.
What is an example of fibrous connective tissue?
There are many examples of fibrous connective tissue in the body. One example of fibrous connective tissue is the Achilles tendon found in the heel...
What is the main function of fibrous connective tissue?
There are a few functions of fibrous connective tissue in the body. One of the main functions is to allow for movement while preventing twisting an...
Who was addressing the issue of fibrous tissue formation?
Really, it was primarily the PEEK-based companies who were addressing the issue of the fibrous tissue formation.
What is the common connective tissue of the body?
fatty tissue connective tissue made of fat cells in a meshwork of areolar tissue. fibrous tissue the common connective tissue of the body, composed of yellow or white parallel elastic and collagen fibers. gelatinous tissue mucous tissue.
What is cicatricial tissue?
cicatricial tissue the dense fibrous tissue forming a cicatrix, derived directly from granulation tissue; called also scar tissue.
What is adipose tissue?
adipose tissue connective tissue made of fat cells in a meshwork of areolar tissue.
What is the specialized tissue forming the bones?
osseous tissue the specialized tissue forming the bones.
What is subcutaneous tissue?
subcutaneous tissue the layer of loose connective tissue directly under the skin. tissue typing identification of tissue types for purposes of predicting acceptance or rejection of grafts and transplants. The process and purposes of tissue typing are essentially the same as for blood typing. The major difference lies in the kinds ...
What is a sclerous T?
sclerous t's the cartilaginous, fibrous, and osseous tissues. skeletal tissue the bony, ligamentous, fibrous, and cartilaginous tissue forming the skeleton and its attachments. splenic tissue red pulp. subcutaneous tissue the layer of loose connective tissue directly under the skin. tissue typing identification of tissue types for purposes ...
What are fibrous connective tissues made of?
Remember that fibrous connective tissues are primarily made up of collagen; now you can see why structure and support are such crucial jobs for this tissue! There are three specialized types of fibrous connective tissue. Ligaments connect bones to other bones, tendons (or sinew) connect muscle to bones and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles.
What are the four main types of tissue?
Connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue are the four main types of tissue in humans. Learn about connective tissue, the function of fibrous connective tissue, and the types of specialized fibrous connective tissues, including the ligaments, tendons, and fasciae. Updated: 08/26/2021
What is the purpose of connective tissue?
Connective tissue includes tissues such as cartilage, bone, blood and fat. In this lesson, we'll be specifically looking at fibrous connective tissue. The primary purpose of connective tissue is to hold our organs and other tissues together, as well as provide support for our body as a whole.
What are the two main components of FCT?
The two other main components of FCT are water and polysaccharides, which are complex strands of carbohydrates, which also provide support. The primary purpose of fibrous connective tissue is to provide support and shock absorption to our bones and organs. The slide below is a histological section of fibrous connective tissue.
What is collagen tissue?
This high-strength, slightly stretchy tissue consists mainly of collagen, a protein which is known for providing strength and stability. We find collagen just about everywhere that provides support for our body - our muscles, bones and skin are great examples.
Where are ligaments found?
Ligaments connect bone to bone and can be found in places such as the knee. There are three types of specialized fibrous tissue in our body which serve a specific purpose. The first is ligaments. Ligaments are fibrous tissues that connect bones to other bones.
What is the function of the fascia in the back?
Fasciae in your back allows all the muscles to work together.
What causes fibrocystic breasts?
The exact cause of fibrocystic breast changes isn't known, but experts suspect that reproductive hormones — especially estrogen — play a role.
Why are fibrocystic breasts considered normal?
In fact, medical professionals have stopped using the term "fibrocystic breast disease" and now simply refer to "fibrocystic breasts" or "fibrocystic breast changes" because having fibrocystic breasts isn't a disease. Breast changes that fluctuate with the menstrual cycle and have a ropelike texture are considered normal.
What is lumpy breast?
Breast lumps or areas of thickening that tend to blend into the surrounding breast tissue. Generalized breast pain or tenderness or discomfort that involves the upper outer part of the breast. Breast nodules or lumpy tissue change in size with the menstrual cycle.
What is the term for a round sac in the breast?
Fluid-filled round or oval sacs (cysts) A prominence of scar-like fibrous tissue (fibrosis) Overgrowth of cells (hyperplasia) lining the milk ducts or milk-producing tissues (lobules) of the breast. Enlarged breast lobules (adenosis)
How many lobes are there in breast?
Breast anatomy. Each breast contains 15 to 20 lobes of glandular tissue, arranged like the petals of a daisy. The lobes are further divided into smaller lobules that produce milk for breastfeeding. Small tubes (ducts) conduct the milk to a reservoir that lies just beneath your nipple.
Is fibrocystic breast normal?
Most fibrocystic breast changes are normal. However, make an appointment with your doctor if:
Is fibrocystic breast tissue more bothersome?
Fibrocystic breast changes tend to be more bothersome before your menstrual period and ease up after your period begins. When examined under a microscope, fibrocystic breast tissue includes distinct components such as: Fluid-filled round or oval sacs (cysts) A prominence of scar-like fibrous tissue (fibrosis)
Where do fibroids come from?
Doctors believe that uterine fibroids develop from a stem cell in the smooth muscular tissue of the uterus (myometrium). A single cell divides repeatedly, eventually creating a firm, rubbery mass distinct from nearby tissue.
What are the three types of fibroids?
There are three major types of uterine fibroids. Intramural fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall. Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity. Subserosal fibro ids project to the outside of the uterus. Some submucosal or subserosal fibroids may be pedunculated — hanging from a stalk inside or outside the uterus.
What are the changes in fibroids?
Genetic changes. Many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in typical uterine muscle cells.
What are the risk factors for uterine fibroids?
Factors that can have an impact on fibroid development include: Race. Although any woman of reproductive age can develop fibroids, black women are more likely to have fibroids than are women of other racial groups.
Why do fibroid cells shrink?
Fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than normal uterine muscle cells do. Fibroids tend to shrink after menopause due to a decrease in hormone production. Other growth factors. Substances that help the body maintain tissues, such as insulin-like growth factor, may affect fibroid growth.
What is the material that makes cells stick together like mortar between bricks?
ECM is the material that makes cells stick together, like mortar between bricks. ECM is increased in fibroids and makes them fibrous. ECM also stores growth factors and causes biologic changes in the cells themselves. Doctors believe that uterine fibroids develop from a stem cell in the smooth muscular tissue of the uterus (myometrium).
How to reduce fibroid risk?
But, by making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a normal weight and eating fruits and vegetables, you may be able to decrease your fibroid risk. Also, some research suggests that using hormonal contraceptives may be associated with a lower risk of fibroids. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What is the term for the formation of fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue?
Now we are going to discuss Wiki’s entry for Fibrosis. “ Fibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue ” Although FIBROSIS can be caused by things other than injury, when injury is the cause, “ it is called scarring.
What is the role of fibrosis in the body?
Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can obliterate the architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing.
How does a clot work?
To begin to patch the damage, a clot is created; the clot is the beginning process that results in a provisional matrix. Over time, the wounded body tissue then overexpresses collagen inside the provisional matrix to create a collagen matrix.
What is striae scar?
As a side note to this, the Scar Tissue entry also mentioned STRETCH MARKS . “ Stretch marks (technically called striae) are also a form of scarring. These are caused when the skin is stretched rapidly (for instance during pregnancy, significant weight gain, or adolescent growth spurts), or when skin is put under tension during the healing process, (usually near joints). ”
What is tissue insult?
Sometimes in the practice of medicine, a tissue that is exposed to injury, surgery, or disease processes, is referred to in a strange-sounding manner. Said tissue is said to have experienced an “ insult ” or been “ embarrassed “.
What are the mediators of fibrosis?
Other soluble mediators of fibrosis include CTGF, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and Interleukin 4 (IL-4) [Inflammation]. These ultimately lead to the proliferation and activation of fibroblasts, which deposit extracellular matrix into the surrounding connective tissue.”.
What is the fourth stage of soft tissue repair?
Via use and normal mechanical stresses, this tissue aligns itself in as an elastic manner as it can, going through a process known as the “Remodeling Phase”. This is the fourth and final stage of the soft tissue repair process, and not surprisingly, is not only the least talked about but the longest lasting (see previous link).
What fills the spaces between glandular and fibrous tissue?
fatty tissue fills in the spaces between glandular and fibrous tissue and largely determines your breast size
What type of tissue is in the breast?
Female breasts contain different types of fatty, fibrous, and glandular tissue: fatty tissue fills in the spaces between glandular and fibrous tissue and largely determines your breast size. Doctors refer to all non-fatty tissue as fibroglandular tissue. There are also bands of supportive, flexible connective tissue called ligaments, ...
What are lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that help fight infection and are found throughout the body. They produce and filter a colorless fluid called lymph, which contains white blood cells known as lymphocytes (immune cells involved in defending against infections and such diseases as cancer).
What are dense breasts?
It is very common for women to be told that they have dense breasts after a mammogram. Dense breasts are completely normal and tend to be more common in younger women and in women with smaller breasts. But anyone — regardless of age or breast size — can have dense breasts.
What is the muscle that holds breast tissue in place?
There are also bands of supportive, flexible connective tissue called ligaments, which stretch from the skin to the chest wall to hold the breast tissue in place. Muscle plays an important role too. The pectoral muscle lies against the chest wall underneath both breasts, giving them support.
How many glands are there in the breast?
Embedded in the breast’s fatty and fibrous tissue are 15 to 20 glands called lobes, each of which has many smaller lobules, or sacs, that produce milk. Lobules are arranged in clusters, like bunches of grapes. Ducts are thin tubes that carry milk to the nipple.
What does it mean when your breasts are dense?
A doctor will tell you that your breasts are dense if most of the tissue seen on your mammogram is fibrous or glandular breast tissue. These tissue types appear thicker and denser than fatty tissue and will show up white on a mammogram.