Capillary Exchange
- Internal respiration: Process by which gases are exchanged between capillary blood and tissues.
- Oxygen is carried from the lungs to the tissues in the form of oxyhemoglobin.
- Exchange occurs between blood at the arterial end of the capillaries and tissue fluid and then between tissue fluid and cells.
What is capillary exchange?
Capillary exchange includes all exchanges that happen at the microcirculatory or capillary level. When capillaries penetrate the tissues, they branch or arborize out to maximize the surface area for the exchange of material that includes gases, nutrients, ions, and waste products.
What substances are exchanged through the thin walls of capillaries?
Oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged through the thin walls of the capillaries. Capillaries play an important role in microcirculation.
What type of tissue are capillaries made of?
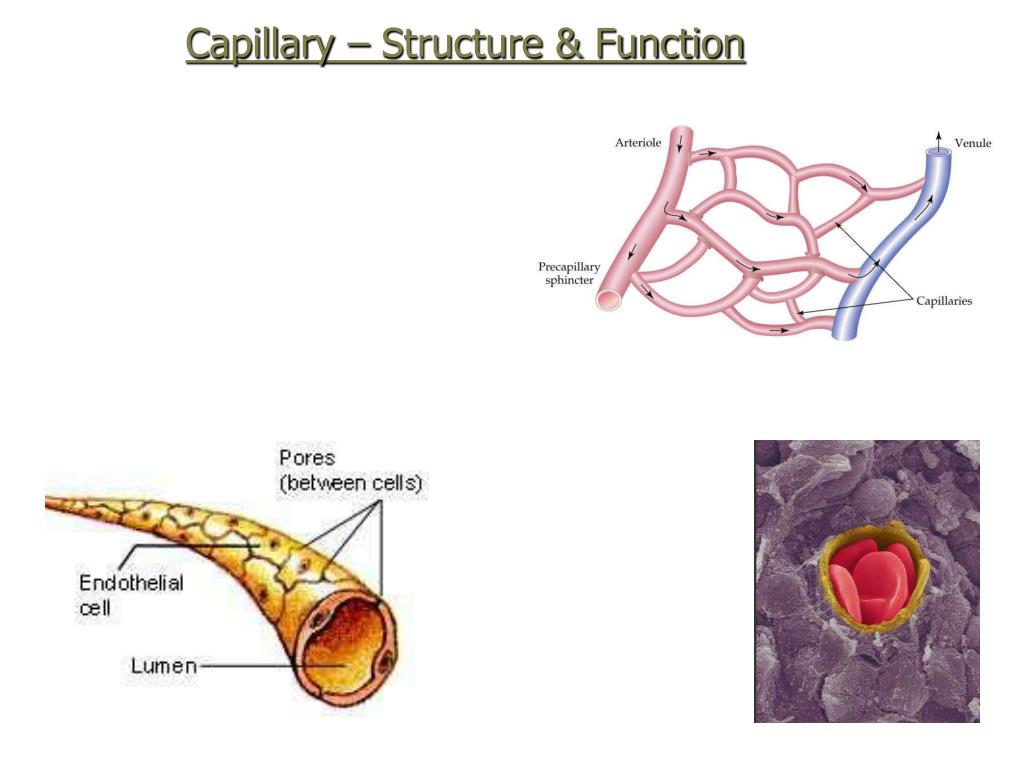
Capillary walls are thin and are composed of endothelium (a type of simple squamous epithelial tissue ). Oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged through the thin walls of the capillaries. Capillaries play an important role in microcirculation.
Where does fluid exchange take place between the capillaries and body tissues?
Fluid exchange between the capillaries and the body tissues takes place at the capillary bed. Capillaries are where fluids, gasses, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and body tissues by diffusion.

What is exchanged in the capillaries?
The exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between your blood and tissues also happens in your capillaries. This happens through two processes: Passive diffusion. This is the movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Do capillaries allow exchange of materials?
Capillaries allow exchange of substances with body tissues through their thin walls. As blood travels at high pressure in the arteries towards the capillaries, pressure filtration occurs which results in plasma passing through the capillary wall into the tissue fluid which surrounds the cell.
What feature of capillaries allows for exchange?
They contain small pores, in addition to small gaps between cells, in their walls that allow for the exchange of larger molecules.
What Cannot pass through capillaries?
Two extremes are found in the brain and the liver. In brain capillaries, the junctions between adjacent endothelial cells are so tight that only water and small ions (e.g., Na+ and Cl−) can pass through them; not even glucose or amino acid molecules can pass through these tiny pores.
Why are capillaries called exchange vessels?
Capillaries are called exchange vessels because they allow the exchange of gasses, nutrients, hormones, and other molecules in the blood. Capillari...
How does capillary exchange occur?
Capillary fluid exchange is essential because this is how gasses and nutrients are supplied to the body's cells. At the venule end of the capillary...
What determines capillary hydrostatic pressure?
Capillary hydrostatic pressure is determined by the pressure exerted on the capillary membrane by the blood within the narrow capillary. The hydros...
What are the walls of capillaries made of?
Capillary walls are thin and are composed of endothelium (a type of simple squamous epithelial tissue ). Oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged through the thin walls of the capillaries.
Where are capillaries located?
A capillary is an extremely small blood vessel located within the tissues of the body that transports blood from arteries to veins. Capillaries are most abundant in tissues and organs that are metabolically active. For example, muscle tissues and the kidneys have a greater amount of capillary networks than do connective tissues .
What happens to blood pressure in the venule end of the capillary bed?
On the venule end of the capillary bed, blood pressure in the vessel is less than the osmotic pressure of the blood in the vessel . The net result is that fluid, carbon dioxide and wastes are drawn from the body tissue into the capillary vessel.
What are the structures that control the flow of blood through the capillaries?
Microcirculation deals with the circulation of blood from the heart to arteries, to smaller arterioles, to capillaries, to venules, to veins and back to the heart.#N#The flow of blood in the capillaries is controlled by structures called precapillary sphincters. These structures are located between arterioles and capillaries and contain muscle fibers that allow them to contract. When the sphincters are open, blood flows freely to the capillary beds of body tissue. When the sphincters are closed, blood is not allowed to flow through the capillary beds. Fluid exchange between the capillaries and the body tissues takes place at the capillary bed.
What controls the flow of blood in the capillaries?
The flow of blood in the capillaries is controlled by structures called precapillary sphincters. These structures are located between arterioles and capillaries and contain muscle fibers that allow them to contract. When the sphincters are open, blood flows freely to the capillary beds of body tissue.
How is fluid exchange controlled?
Fluid exchange is controlled by blood pressure within the capillary vessel (hydrostatic pressure) and osmotic pressure of the blood within the vessel. The osmotic pressure is produced by high concentrations of salts and plasma proteins in the blood. The capillary walls allow water and small solutes to pass between its pores ...
What is the name of the fluids that are exchanged between the blood and the body tissues?
Kes47 / Wikimedia Commons / Public domain. Capillaries are where fluids, gasses, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and body tissues by diffusion. Capillary walls contain small pores that allow certain substances to pass into and out of the blood vessel.
How do capillaries facilitate efficient exchange?
The structure of capillaries facilitates efficient exchange, by optimising Fick’s law. To maximise the area available for diffusion, there are many capillaries supplying the same tissue. Moreover, a constant blood flow through the capillaries maintains a large concentration gradient to allow the molecules to be rapidly exchanged with the tissue.
Why is the renal capillary bed able to exchange water and electrolytes much more efficiently and selectively than
This is because the kidneys function to regulate ion concentrations and osmolarity while receiving approximately 25% of cardiac output.
How does Starling force affect the capillaries?
Inflammation stimulates dilation of arterioles and therefore increases the hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries. Additionally, chemicals such as histamine cause the capillaries to become more permeable and allows proteins from the blood to flow into the interstitium. This increases the colloid osmotic force from the interstitium. These two factors both cause an increase of fluid to move out into the interstitium and explains the typical swelling seen in inflamed areas.
How thick is the alveoli?
They also have an average membrane thickness of only 0.6 micrometres and form a network of capillaries over the alveoli. Furthermore, the alveoli themselves have an extremely large surface area of seventy square metres to further increase the surface area available for diffusion.
What causes diffusion to decrease?
For example, some pulmonary diseases cause fibrosis or oedema. This increases the diffusion distance that the molecule has to travel, thus decreasing the diffusion rate. Other diseases, such as emphysema, result in damage to the walls of the alveoli causing them to rupture.
Which part of the lungs is responsible for gas exchange?
Gas Exchange. A vital example of gas exchange occurs between the terminal portions of the lungs and pulmonary capillaries. Therefore, pulmonary capillaries possess characteristics that allow for rapid and efficient diffusion. The capillaries optimise the diffusion rate by receiving a constant blood supply.
Why is there a constant blood flow through the capillaries?
Moreover, a constant blood flow through the capillaries maintains a large concentration gradient to allow the molecules to be rapidly exchanged with the tissue.
What is the function of capillaries?
Capillaries allow exchange of substances with body tissues through their thin walls. As blood travels at high pressure in the arteries towards the capillaries, pressure filtration occurs which results in plasma passing through the capillary wall into the tissue fluid which surrounds the cell.
Where is blood returned to the heart?
It is returned to the heart in the veins. The capillaries connect the two types of blood vessel and molecules are exchanged between the blood and the cells across their walls. Part of. Human Biology.