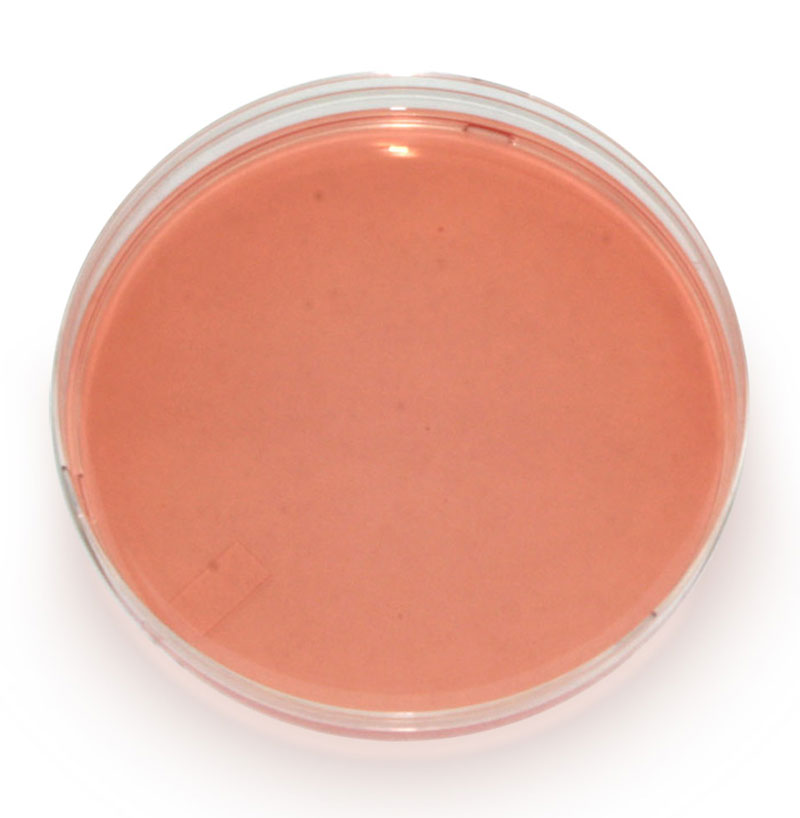
Staph. aureus will grow on general culture media such as Blood Agar and chocolated Blood Agar and therefore can be isolated from direct plating of clinical specimens. More specialised media, such as Staph/Strep Selective Medium contain antimicrobials.
What can kill Staph aureus?
A severe staph skin infection usually requires an initial course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and clear the infection. Commonly used drugs include doxycycline or a combination of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) and rifampin.
How to prevent Staphylococcus?
- First, wet your hands. ...
- Rub your hands together, palm to palm. ...
- Spread your fingers and rub your palms together with the fingers interlaced, washing the webs between the fingers. ...
- Grab your right thumb with your left hand and wash, using a circular motion. ...
- Rinse well with warm water. ...
What is the cause of Staphylococcus?
Staph infections are caused by staphylococcus bacteria, types of germs commonly found on the skin or in the nose of even healthy individuals. Most of the time, these bacteria cause no problems or result in relatively minor skin infections.
Which antibiotic is best for staph infection?
- Use a topical prescription antibiotic like Bactroban (mupirocin) inside the nostrils twice daily for 1-2 weeks. Children tend to harbor staph in their noses.
- Use a bleach solution in the bath as a body wash.
- Keep fingernails short and clean.
- Change and wash every day:

What Agar is used for Staphylococcus aureus?
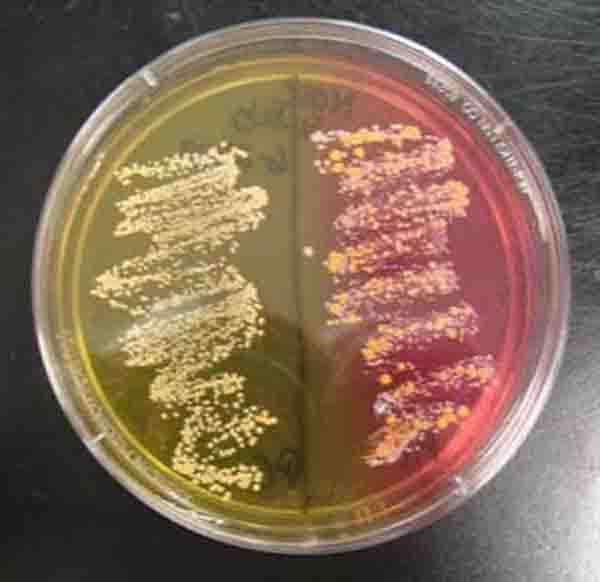
One of these selective media is mannitol salt agar (MSA), which is used for selectively and differentially recovering isolates of S. aureus (which will appear yellow on this agar; coagulase-negative staphylococci will remain the color of the agar [red]).
Does Staphylococcus aureus grow on MacConkey Agar?
MacConkey agar selects for organisms like Escherichia coli (Gram negative bacilli) while inhibiting the growth of organisms like Staphylococcus aureus (Gram positive cocci).
Does Staphylococcus grow on agar?
Staph. aureus will grow on general culture media such as Blood Agar and chocolated Blood Agar and therefore can be isolated from direct plating of clinical specimens. More specialised media, such as Staph/Strep Selective Medium contain antimicrobials.
Where does Staphylococcus aureus grow?
S. aureus is commonly found in the environment (soil, water and air) and is also found in the nose and on the skin of humans. S. aureus is a Gram-positive, non-spore forming spherical bacterium that belongs to the Staphylococcus genus.
Does Staphylococcus aureus grow on nutrient agar?
Staphylococci can be isolated in routinely used bacteriological media like nutrient agar, blood agar or specific media like mannitol salt agar (MSA), lipovitellin salt mannitol agar (LSM), Vogel-Johnson agar (VJ), Baird Parker agar, potassium thiocyanate-actidione-sodium azide-egg yolk-pyruvate agar (KRANEP), ...
Does Staphylococcus aureus grow on EMB agar?
Occasionally, some Gram-positive bacteria, such as Enterococcus and Staphylococcus will grow on this medium, but usually as pinpoint colonies. Non- pathogenic, non-lactose-fermenting organisms may grow on EMB agar as well.
Which media would be appropriate to select for Staphylococcus?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Selective and differential media used for the isolation of Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the best media for positively identifying Staphylococcus aureus?
Coagulase testing is the single most reliable method for identifying Staphylococcus aureus [9]. Coagulase production can be detected using either the slide coagulase test (SCT) or the tube coagulase test (TCT).
Does Staphylococcus aureus grow on TSA plate?
S. aureus is known to spread on the surface of TSA medium containing 0.24% agar (TSA-0.24)1.
What does Staphylococcus aureus look like on agar?
S. aureus is a facultatively anaerobic, Gram-positive coccus, which appears as grape-like clusters when viewed through a microscope, and has round, usually golden-yellow colonies, often with hemolysis, when grown on blood agar plates.
What type of medium is used to isolate Staphylococcus from the skin?
What type of medium is used to isolate Staphylococcus from the skin? Blood agar is an enriched and differential medium that can be used to isolate staphylococci from some of the other members of the normal microbiota.
Why was an LB agar plate used to test the staph culture?
An LB agar plate was used to test the Staph culture because it is a nonselective/ nondifferential agar. Therefore, it is rich in nutrients. If you used a selective or differential agar you would only be letting certain microbes grow.
Does Streptococcus grow on MacConkey agar?
Hence, it does not grow on MacConkey agar (MA) due to the absence of blood as well as due to the presence of high concentration of bile in the medium which is inhibitory to the growth of S.
What type of bacteria will grow on MacConkey agar?
Altogether, MacConkey agar only grows gram-negative bacteria, and those bacteria will appear differently based on their lactose fermenting ability as well as the rate of fermentation and the presence of a capsule or not.
Is Staphylococcus aureus lactose fermenter?
aureus strains changes the colour of media from yellow to red, indicating positive reactivity in urea hydrolysis. That may be due to the liberation of end product of urea hydrolysis which is ammonia[16]. In this study, all isolated strains showed a positive result in lactose fermentation test.
What type of bacteria does MacConkey agar select for?
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture medium for bacteria. It is designed to selectively isolate Gram-negative and enteric (normally found in the intestinal tract) bacteria and differentiate them based on lactose fermentation.
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
Last Update: August 23, 2020. Continuing Education Activity. Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacteria that cause a wide variety of clinical diseases. Infections caused by this pathogen are common both in community-acquired and hospital-acquired settings. The treatment remains challenging due to the emergence of multi-drug resistant strains ...
What are the most common infections caused by S. aureus?
aureusare one the most common bacterial infections in humans and are the causative agents of multiple human infections, including bacteremia, infective endocarditis, skin and soft tissue infections (e.g., impetigo, folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis, scalded skin syndrome, and others), osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, prosthetic device infections, pulmonary infections (e.g., pneumonia and empyema), gastroenteritis, meningitis, toxic shock syndrome, and urinary tract infections.[6] Depending on the strains involved and the site of infection, these bacteria can cause invasive infections and/or toxin-mediated diseases. [6][7] The pathophysiology varies greatly depending on the type of S. aureusinfection.[6] Mechanisms for evasion of the host immune response include the production of an antiphagocytic capsule, sequestering of host antibodies or antigen masking by Protein A, biofilm formation, intracellular survival, and blocking chemotaxis of leukocytes. [8][7] Binding of the bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins and fibronectin in infectious endocarditis is mediated by bacterial cell wall-associated proteins such as fibrinogen-binding proteins, clumping factors, and teichoic acids.[7] Also, Staphylococcal superantigens (TSST-1 or toxic shock syndrome toxin 1) are important virulence factors in infectious endocarditis, sepsis, as well as toxic shock syndrome. [9][10] Pneumonia infections are associated with the bacterial production of PVL (Panton-Valentine leukocidin), Protein A, and alpha-hemolysin, and infections are more common following influenza virus infection as well as a diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. Prosthetic device infections are often mediated by the ability of S. aureusstrains to form biofilms as well as communicate using quorum sensing in a bacterial cell density-dependent manner. [11]
What is the color of a staph?
Staphylococcus aureus is Gram-positive bacteria (stain purple by Gram stain) that are cocci-shaped and tend to be arranged in clusters that are described as “grape-like.” On media, these organisms can grow in up to 10% salt, and colonies are often golden or yellow (aureus means golden or yellow). These organisms can grow aerobically or anaerobically (facultative) and at temperatures between 18 C and 40 C. Typical biochemical identification tests include catalase positive (all pathogenic Staphylococcusspecies), coagulase positive (to distinguish Staphylococcus aureusfrom other Staphylococcusspecies), novobiocin sensitive (to distinguish from Staphylococcus saprophyticus), and mannitol fermentation positive (to distinguish from Staphylococcus epidermidis). [4][1] MRSA strains carry a mecgene on the bacterial chromosome, which is a component of the larger Staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec(SCCmec) region, conferring resistance to multiple antibiotics depending on the SCCmectype.[2] The mecgene encodes the protein PBP-2a (penicillin-binding protein 2a). PBP-2a is a penicillin-binding protein (PBP), or essential bacterial cell wall enzyme that catalyzes the production of the peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. PBP-2A has a lower affinity to bind to beta-lactams (and other penicillin-derived antibiotics) when compared to other PBPs, so PBP-2A continues to catalyze the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall even in the presence of many antibiotics. As a result, S. aureusstrains that synthesize PBP-2A can grow in the presence of many antibiotics, and these MRSA strains are resistant to many antibiotics. MRSA strains tend to be resistant to methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, and cephalosporins. [2][4]
How to prevent S. aureus infection?
Prevention of S. aureusinfections remains challenging. Despite many efforts, a routine vaccination for S. aureusinfections has remained elusive. As a result, efforts have relied on infection control methods such as hospital decontamination procedures, handwashing techniques, and MRSA transmission prevention guidelines. Topical antimicrobials such as mupirocin can be used to eliminate nasal colonization in some nasal carriers. However, usage is controversial.
How long does it take to treat S. aureus?
When prescribing antibiotics, one should limit the duration to no more than 7 to 10 days for most infections. The reason is that the empirical prescription of antibiotics has led to the development of resistant strains. Pharmacists should coordinate with the clinician to target antimicrobial therapy, and nursing can chart the progress so modification to the regimen can be made if treatment is ineffective. This kind of interprofessional coordination is necessary to treat such infections with precision.
How to diagnose S. aureus?
In many cases, routine cultures will reveal the diagnosis (i.e.,blood, sputum); however, RT-PCR (real-time PCR) for 16S rRNA genes may be necessary in some cases. Drug susceptibility testing often is required to guide treatment. If patient samples are collected for pathogen identification in the microbiology laboratory, caution must be exercised as the presence of S. aureusin the skin or mucous membrane does not necessarily indicate infection because these organisms are frequently members of the normal flora. [4]
What is the mecgene of a bacterial cell?
The mecgene encodes the protein PBP-2a (penicillin-binding protein 2a). PBP-2a is a penicillin-binding protein (PBP), or essential bacterial cell wall enzyme that catalyzes the production of the peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall.
What is the morphology of Staphylococcus aureus?
Morphology of Staphylococcus aureus. Gram-positive, singly, in pairs, or in a short chain of 3-4 bacteria. Irregular clusters of cells.
What is the Gram stain for S. aureus?
The Gram stain showing typical Gram-positive cocci that occur singly and in pairs, tetrads, short chains, and irregular grape-like clusters can be suspected to be S. aureus.
What enhances the clumping of the organism in presence of plasma?
Clumping factor: FnBP enhances the clumping of the organism in presence of plasma.
How much of the human population is affected by S. aureus?
Thirty percent (30%) of the normal human healthy population is affected by S. aureus as it asymptomatically colonizes on the skin of the human host.
How to isolate a bacterium from a blood culture?
The organism is isolated by streaking material from the clinical specimen (or from a blood culture) onto solid media such as blood agar, tryptic soy agar, or heart infusion agar.
How long does it take for a blood agar to grow?
The inoculated plates should be incubated at 35°C to 37°C for 24 to 48 hours. On Blood agar, growth occurs abundantly within 18 to 24 hours. Round, raised, opaque, yellow to golden yellow colonies of 1-2mm in diameter are seen with or without beta hemolysis.
What is the chemical that kills white blood cells?
Panton-Valentine leukocidin: composed of two components S and F which act synergistically to kill white blood cells
How long does it take for S. aureus to grow?
S. aureus is a non fastidious organism which can grow in a wide variety of media, You could grow it in LB broth medium, for 4-6 hours to obtain it in log phase. For basic culturing purposes we routinely use Tryptic soy broth for liquid cultures. Grow at 37 degrees Celsius, shaking at about 200rpm.
How hot does tryptic broth grow?
For basic culturing purposes we routinely use Tryptic soy broth for liquid cultures. Grow at 37 degrees Celsius, shaking at about 200rpm. Vinaykumar is right it will grow in a wide range of media.
Is LB broth good for staph?
Any medium is good for Staphylococci, not only LB broth. LB broth is needed only for molecular studies, and for showing aggregative properties...
Does M63 have amino acids?
Nitrogen source as ammonium sulfate or ferric ammonium citrate or ammonium chloride. DMM contained L-asparagine and M9 and M63 do not have any amino acids. None of these media are suitable for growth.
Can Staphylococcus aureus grow on blood agar?
Staphylococcus aureus easily grow on Blood agar, Brain Heart Infusion agar then you can grow it on Manitol salt agar and identification using catalase and coagulase and vitek2. Best regrades. Mohammed F Al Marjani. Cite.