
Some commonly prescribed alpha-blockers include:
- Cardura (doxazosin)
- Regitine (phentolamine)
- Flomax ( tamsulosin)
- Hytrin (terazosin)
What are the names of alpha blocker drugs?
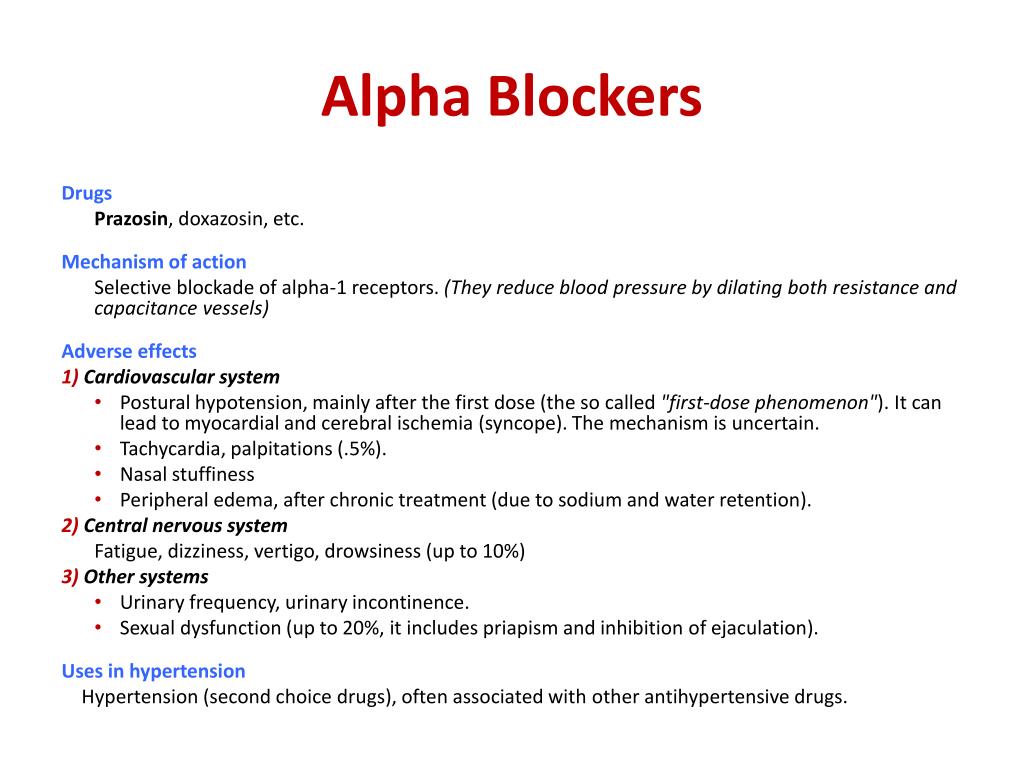
They are alfuzosin, doxazosin, indoramin, prazosin, tamsulosin, and terazosin. Alpha blockers, α-blockers, or alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists medicines are mainly used to treat hypertension and enlarged prostate gland in men with problem passing urine.
What are the side effects of an alpha blocker?
- Low blood pressure (hypotension). Alpha-blockers are very effective at lowering blood pressure. ...
- First-dose effect. An extremely common side effect of A1-blockers is that the first dose has a much stronger effect on blood pressure than later doses. ...
- Sexual dysfunction. Alpha-blockers can cause priapism, an erection that lasts four or more hours. ...
Are alpha blockers available over the counter?
Over-the-counter alpha blockers are not yet available. Ongoing studies will determine whether appropriate safety and usage criteria can be achieved. No direct or indirect commercial incentive associated with publishing this article.
What are examples of alpha blockers?
Examples of alpha blockers used to treat high blood pressure include:
- Doxazosin (Cardura)
- Prazosin (Minipress)
- Terazosin
What is the best alpha blocker?
Many consider alfuzosin 10 mg to be the superior alpha blocker currently available for treating BPH because it achieves clinically significant improvements in LUTS and has no significant effects on dizziness, asthenia, and ejaculatory dysfunction.
What high blood pressure meds are alpha blockers?
Alpha-blockers are a type of medicine that can be used to treat high blood pressure. They work by allowing the blood vessels to relax and widen, so the blood has more space to flow through. They include doxazosin, indoramin, prazosin, and terazosin.
Who should not take alpha blockers?
Kidney disease, circulatory diseases or respiratory infections. Non-selective alpha-blockers may not be an option if you have one or more of these conditions.
Is losartan a alpha blocker?
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). It works by blocking a substance in the body that causes blood vessels to tighten. As a result, losartan relaxes the blood vessels. A lower blood pressure will increase the supply of the blood and oxygen to the heart.
What is the safest alpha-blocker?
Silodosin — a safer alpha-blocker targeting benign prostatic hyperplasia.
What are the 4 best blood pressure drugs?
The four best types of blood pressure drugs that are considered the first choices to lower blood pressure include thiazide diuretics, ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), and calcium channel blockers.
What are the most common side effects of alpha blockers?
The most common side-effects are slight drowsiness, headaches and dizziness. More rarely they can cause sexual problems. Alpha-blockers are also associated with an increased risk of falling and of breaking a bone (fracture) when they are first started.
Is Viagra a alpha-blocker?
Flomax is an alpha-blocker prescribed to treat difficulty urinating a symptom of BPH. Viagra is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor (PDE-5 inhibitor) prescribed to treat impotence, another symptom of BPH. Both drugs are available in generic form.
Do alpha blockers cause weight gain?
For alpha-blockers, weight gain is not a commonly reported side effect. In general, changes in weight for alpha-blockers appear to be minor or nonexistent, with the average changes in weight following clonidine (0.4–1.4 kg155,156) and prazosin (0.0–0.5 kg157,158) being <1.5 kg.
What is the safest high blood pressure medication?
Safe medications to use include methyldopa and potentially some diuretics and beta-blockers, including labetalol.
Why was losartan taken off the market?
Why were these products recalled? Losartan was recalled due to impurities found while testing finished products. The impurity found in these batches is N-Methylnitrosobutyric acid (NMBA). This is the third type of impurity to cause recalls of these medications.
Is atorvastatin an alpha blocker?
The type of α-blocker used was tamsulosin, 0.2 mg, terazosin, 2 mg, and alfuzosin, 10 mg, and the type of statin used was atorvastatin, 10 mg, fluvastatin, 80 mg, and simvastatin, 20 mg.
Are alpha blockers good for high blood pressure?
Alpha blockers are a type of blood pressure medication. They lower blood pressure by preventing a hormone called norepinephrine from tightening the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins. As a result, the blood vessels remain open and relaxed. This improves blood flow and lowers blood pressure.
Is metoprolol an alpha-blocker?
Metoprolol is a drug called a beta-blocker. It's used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and angina (chest pain).
Is atorvastatin an alpha-blocker?
The type of α-blocker used was tamsulosin, 0.2 mg, terazosin, 2 mg, and alfuzosin, 10 mg, and the type of statin used was atorvastatin, 10 mg, fluvastatin, 80 mg, and simvastatin, 20 mg.
What's the difference between an alpha-blocker and a beta-blocker?
5:1811:06Pharmacology - ALPHA & BETA BLOCKERS - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSuch as epinephrine. And norepinephrine which leads to decrease in sympathetic effects mainly onMoreSuch as epinephrine. And norepinephrine which leads to decrease in sympathetic effects mainly on cardiovascular. System. This is why beta blockers are useful in the treatment of hypertension.
Overview
Alpha-blockers are medications that treat high blood pressure. They can also treat some conditions affecting the circulatory system, prostate, and help with treating certain types of tumors. They work by slowing down specific types of cell activity in your nervous system.
Recovery and Outlook
Depending on the medication and the treated condition, you can take selective A1-blockers for extended periods. Non-selective alpha-blockers are meant for short-term use.
When to Call the Doctor
In general, you should contact your provider if you have any questions about your medications or any sudden changes in your symptoms, especially when side effects or symptoms interfere with your regular activities.
How does alpha blocker work?
Alpha blockers are a type of blood pressure medication. They lower blood pressure by preventing a hormone called norepinephrine from tightening the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins. As a result, the blood vessels remain open and relaxed. This improves blood flow and lowers blood pressure.
Why do doctors prescribe alpha blockers?
In addition to high blood pressure, doctors prescribe alpha blockers to prevent, treat or improve symptoms of an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
Can alpha blockers help with prostate?
Because alpha blockers also relax other muscles throughout the body, these medications also can help improve urine flow in older men with prostate problems.
Does alpha blocker increase cholesterol?
Alpha blockers may improve total cholesterol. However, some research has found that long-term use of some alpha blockers can increase the risk of heart failure.
Can you take alpha blockers with diuretics?
Alpha blockers typically aren't the first treatment option for high blood pressure. Instead, they're used in combination with other drugs, such as diuretics, when high blood pressure is difficult to control.
What is an alpha blocker?
Alpha blockers are both selective and non-selective for alpha1 and alpha2 receptors. They are often used in a combination for an effective treatment. Alpha blockers (also commonly known as the alpha-adrenergic antagonist) are used for the treatment of a number of conditions like Raynaud’s disease, benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension.
Who Should Not Be Prescribed Alpha Blockers?
Under certain circumstances, alpha blocker is not prescribed to women because it tends to cause stress incontinence and diminishes the control over bladder. All those women who are trying to get pregnant or are already pregnant or nursing their babies must take these drugs only upon doctor’s recommendation based on the risk-benefit ratio. They are also contraindicated in people with:
What is angiotensin II blocker?
ARBs: angiotensin II receptor blockers assist in dilation of blood vessels by inhibiting the function of naturally existing chemical, angiotensin II, that under normal conditions cause the constriction of the blood vessels. These are drugs of choice in patients with chronic kidney disease along with hypertension.
How does an alpha blocker work?
Alpha blockers produce its action by inhibiting norepinephrine from causing the constriction of muscles inside the walls of small veins and arteries. As a result the vessels stay dilated and relaxed ultimately controlling the high blood pressure across the vessel walls.
What is the effect of ACE inhibitors?
ACE inhibitors: they produce their effect by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I into angiotensin II, as a result of which the blood vessels undergo dilation and relaxation. These are drugs of choice in case of chronic kidney disease along with hypertension.
What is the best medication for benign prostatic hyperplasia?
Silodosin- used for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prazosin- used for hypertension. Tamsulosin - used for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Alfuzosin- used for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Terazosin- used for benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension. Yohimbine- used to relieve vasoconstriction associated with Reynaud’s disease. ...
What happens if you take an alpha blocker?
An alpha blocker may produce a "first-dose-effect" i.e. the blood pressure drops several points and the patient may feel dizzy and faint after rising from a lying or sitting position. For this reason it is recommended to take the first dose at bedtime. The other side effects that this class of drug may produce include: Weight gain.
What is an alpha blocker?
Alpha-blockers are medications used in the management and treatment of essential hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and pheochromocytoma.
How do alpha blockers work?
Alpha-blockers produce their pharmacological effects through alteration of the sympathetic nervous system.
What is selective alpha-1 antagonist?
Selective alpha-1 antagonists are commonly used agents in an outpatient setting for patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy.
What is the effect of nonselective alpha-adrenergic antagonists on vaso?
Nonselective alpha-adrenergic antagonists cause vasodilation by blocking both alpha-1 and alpha-2 receptors. The blockage of alpha-2 receptors will increase the NE release, which will reduce the force of the vasodilation induced by the blockade of the alpha-1 receptors.
What are the side effects of alpha blockers?
Adverse Effects. Adverse effects of nonselective alpha-blockers include hypotension, weakness, tachycardia, and tremulousness. Hypotension is due to inhibition of the alpha-1 receptors, which causes vascular smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation.
What is the suffix for alpha 1 blocker?
Selective alpha-1 blocker ends with the suffix "-osin." These medications include alfuzosin, doxazosin, terazosin, tamsulosin, and prazosin.
Which receptor has a higher affinity for epinephrine?
Norepinephrine has a higher affinity for this receptor than epinephrine. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors are located on peripheral nerve endings and inhibit the release of NE when activated; this provides a feedback mechanism for NE to inhibit its release.
WHAT ARE ALPHA BLOCKERS AND HOW DO THEY WORK?
Alpha blockers, also known as alpha-adrenergic antagonists, are used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, benign prostatic hyperplasia (age-associated prostate gland enlargement that can cause urination difficulty), and Raynaud’s disease, which is a rare circulatory disorder affecting hands and feet. Alpha blockers affect the sympathetic nervous system and work by inhibiting alpha receptors. Alpha receptors are of two types: alpha receptor 1 and alpha receptor 2.
What is the purpose of alpha blockers?
These alpha blockers inhibit norepinephrine from activating the alpha 1 receptors, causing widening of the blood vessels.
What happens when you block alpha 1 receptors?
The blocking of alpha 1 receptors causes the widening of the blood vessels by inhibiting the action of catecholamines that cause vasoconstriction. The blocking of alpha 2 receptors increases the release of norepinephrine. This reduces the force of the vasodilation caused by the blocking of alpha 1 receptors. These drugs are used in conditions that ...
How do alpha blockers affect the sympathetic nervous system?
Alpha blockers affect the sympathetic nervous system and work by inhibiting alpha receptors. Alpha receptors are of two types: alpha receptor 1 and alpha receptor 2. Alpha 1 receptors are present on the vascular smooth muscle of the skin, sphincters of the gastrointestinal system, kidney, and brain. They cause constriction of the vessels ...
What receptors inhibit the release of norepinephrine?
Alpha 2 receptors are present on the peripheral nerve endings. These receptors inhibit the release of norepinephrine when activated. This is a feedback mechanism to maintain the levels of norepinephrine, which maintains the blood flow by constriction and dilation of the blood vessels. Alpha blockers are divided into three types:
What is the mechanism of action for beta blockers?
Beta blockers make your heart to beat slower and with less force, lowering your blood pressure. Beta-blockers also aid in the opening of veins and arteries, which improves blood flow. They are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure), anxiety, and stress.
What effect do beta blockers have on a client?
Beta blockers, commonly known as beta-adrenergic blocking medicines, are blood pressure drugs. They may also be used to control symptoms of anxiety or panic attacks.
