
Do all metals expand when heated?
Yes, all metals expand when heated. This property of metals is known as thermal expansion and it occurs due to the increased kinetic energy of the atoms. The amplified movement of atoms causes them to acquire more space, hence, resulting in the expansion of the metal surface.
Are there any materials that don’t expand on heating?
Are there any materials that don’t expand on heating? Thermal expansion is the tendency for a material to change it's characteristics due to external temperature. At extremely low temperatures, silicon and germanium expand with cooling rather than heating.
What is thermal expansion of a metal?
This property of metals is known as thermal expansion and it occurs due to the increased kinetic energy of the atoms. The amplified movement of atoms causes them to acquire more space, hence, resulting in the expansion of the metal surface.
Can thermal expansion break the lattice structure between atoms in metals?
Unless a phase change occurs, the increased distance is not enough to break the lattice structure between atoms. Thermal expansion is a phenomena observed in most materials and not just in metals.
What materials dont expand when heated?
In contrast, so-called negative thermal expansion (NTE) materials never behave themselves. Discovered in 1959, they include zirconium tungstate, whose bizarre crystal structure means that it keeps shrinking as it's warmed from any temperature above absolute zero (-273°C) to over 770°C.
Do all metals expand on heating?
So, does metal expand when heated? Yes, all metals expand when heated. This property of metals is known as thermal expansion and it occurs due to the increased kinetic energy of the atoms. The amplified movement of atoms causes them to acquire more space, hence, resulting in the expansion of the metal surface.
Which solid do not expand on heating?
Solution : All solid bodies do not expand on heating. semiconductor and camphor contracts on heating.
Does anything shrink when heated?
Most materials swell when they warm, but some do the opposite; quantum effects could explain why. Summary: Most materials swell when warm, and shrink when cool.
Does stainless steel expand with heat?
Because stainless steel has a high temperature oxidation resistance, it is very valuable in the nuclear power and aerospace industries. However, while stainless steel has a significantly higher resistance than many other metals, it still expands and contracts when the temperature varies.
Does titanium expand with heat?
Titanium has a low coefficient of thermal expansion. Essentially this means, compared to most other manufacturing materials, it will not expand and contract anywhere near as much under extreme temperatures.
Does Iron expand when heated?
Metal expands when heated. Length, surface area and volume will increase with temperature.
Does glass expand when heated?
anneal SOaK: 900°F (482°C) As glass heats, it expands; as it cools, it contracts. These processes set up stresses within glass, especially between the interior and the surface of a glass body.
Which material is not affected by temperature?
Solution : Temperature does not affect molality, mole fraction and percentage by weight.
Does brass shrink when heated?
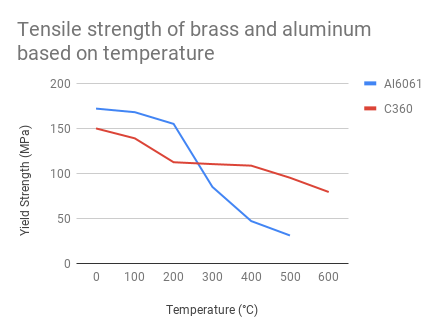
Yes it does. The standard linear expansion coefficient for brass is about 19x10-6 per degree C. To go from room temperature, 20oC to the temperature of liquid nitrogen, -196oC you would get an shrinkage factor of about 0.4 percent.
Does heating metal shrink it?
In general, be aware that the hotter you get the metal, the more it will eventually shrink. Remember, metal will initially expand when you heat it. As you hammer a nearly liquid-hot bead against a dolly, you are simply forcing the molecules into a smaller area.
Do all materials expand?
The most easily observed examples of thermal expansion are size changes of materials as they are heated or cooled. Almost all materials (solids, liquids, and gases) expand when they are heated, and contract when they are cooled.
Do all metals expand equally?
Every material or metal/metal alloy will have a slightly different expansion rate. CTE, then, is the relative expansion or contraction of materials driven by a change in temperature. Metals, ceramics and other materials have unique coefficients of thermal expansion and do not expand and contract at equal rates.
Does metal shrink or expand when heated?
Metal expands when heated. Length, surface area and volume will increase with temperature. The scientific term for this is thermal expansion. The degree of thermal expansion varies with different types of metal.
Does copper expand when heated?
Copper tubing, as well as all piping matrials, expands and contracts with temperature changes.
Does metal shrink with heat?
In general, be aware that the hotter you get the metal, the more it will eventually shrink. Remember, metal will initially expand when you heat it. As you hammer a nearly liquid-hot bead against a dolly, you are simply forcing the molecules into a smaller area.
Why does metal expand when heated?
Metal expands when heated because an increase in temperature is actually an increase in the vibration of the atoms that compose the metal, and this vibration forces the atom s slightly apart. Unless a phase change occurs, the increased distance is not enough to break the lattice structure between atoms. Thermal expansion is a phenomena observed in ...
Why do metals expand at different rates?
Different metals expand at different rates with temperature change , which is a feature used in bimetallic strip thermometers. While thermal expansion is useful in this way, it is also often a problem in construction, particularly when several different materials are used or when heating is likely to be uneven.
What is thermal expansion?
Thermal expansion is a phenomena observed in most materials and not just in metals. Thermal expansion is an important property of many materials , and few materials break the pattern of expanding as they increase in temperature.
What metals are heat treatable?
For non-ferrous materials heat treatable alloys are those containing ( in principle) copper, copper and nickel, etc. but the heat treatment of these metals involves slow cooling after heating.
What happens when two metals are bonded together?
You see, if two metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion are bonded together, and that coupling is exposed to heat different than what the other side of the metals is at, it will produce a voltage, via the Seebeck effect, which is how digital thermometers measure temperature. Conversely, if you apply a voltage to this “thermocouple” as it is called, a temperature differential will be created, where one die gets
What is the process of hardening steel?
Therefore the question refers to the heat treatment for steels and in particular to hardening which involves rapid cooling the steel by quenching into oil, or water, from high temperature and transforms the austenite into martensite. The hardness of a martensite is related to the carbon content and refers to the depth of hardening which may be obtained by the the process.
What does it depend on when you ask about expansion?
or “volumetric”. It also depends on whether you mean, by “material”, a gas, liquid, or a solid. Finally, it depends on the temperature range of interest.
What temperature does zirconium contract?
One of these is Zirconium tungstate. It contracts when heated between temperatures 0.3 K to 1050 K.
What is the change in length of a material?
The change in length ΔL, is equal to the Thermal expansion coefficient, α times the change in temperature, ΔT times the original length of the material, L. You can read about this equation and the values of α for concrete and steel on the Wikipedia page about thermal expansion.
How much does concrete expand?
So Both materials expand, but the concrete expands 4.8–4.32 = 0.48 mm more on a 20 meter span. That is less than 3/16ths of an inch on a 65 foot span.
