
Is glycerol the same thing as glycerin?
The main difference between glycerol and glycerin is glycerol is a pure form on the other hand glycerin contains 95% glycerol. Although that chemical formula is the same they cannot be used interchangeably especially when purity is preferred. It is a simple polyol compound, which is pure form.
What is glycerol a building block for?
Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths (between 12 and 20 carbon atoms). Two important representatives of the lipids are triglyceride (90% of fats) and cholesterol.
Is glycerol a monomer or polymer?
The classes of biological molecules may be grouped into the types of polymers they form and the monomers that act as subunits: Lipids – polymers called diglycerides, triglycerides; monomers are glycerol and fatty acids. Proteins – polymers are known as polypeptides; monomers are amino acids. Subsequently, question is, are fatty acids polymers?
Is glycerol considered a monomer?
Therefore, it is proposed that glycerol is a monomer of suberins in general and can cross-link aliphatic and aromatic suberin domains, corresponding to the electron-translucent and electron-opaque suberin lamellae, respectively. This proposal is consistent with the reported dimensions of the electron-translucent suberin lamellae.
What is a molecule that has a glycerol backbone two fatty acid chains?
1: Phospholipid Molecule: A phospholipid is a molecule with two fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. The phosphate may be modified by the addition of charged or polar chemical groups.
What lipid has a glycerol backbone?
phospholipidsLike triglycerides, phospholipids have a glycerol backbone. But unlike triglycerides, phospholipids only have two fatty acid molecules attached to the glycerol backbone, while the third carbon of the glycerol backbone is bonded to a phosphate group—a chemical group that contains the mineral phosphorus.
Do fatty acids have a glycerol backbone?
Fats and oils A fat molecule consists of two kinds of parts: a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid tails. Glycerol is a small organic molecule with three hydroxyl (OH) groups, while a fatty acid consists of a long hydrocarbon chain attached to a carboxyl group.
Do all phospholipids have a glycerol backbone?
Phospholipids are amphiphilic lipids consisting of a glycerol backbone or an amino-alcohol sphingosine backbone, which is esterified to one or two fatty acids, a phosphate group and a hydrophilic residue.
Where is the glycerol backbone?
The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides.
Do triglycerides have a glycerol backbone?
Definition. A triglyceride (TG) molecule consists of a glycerol backbone esterified with three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituent of vegetable and animal fats in the diet, and are the main constituent of the body's fat stores.
What is the structure of a glycerol molecule?
The chemical formula for Glycerol is C3H8O3. Its compound contains more than one group of hydroxyls. glycerol contains three hydroxyl groups in its chemical structure, which are -OH groups bound to the carbon atoms. It has 3 Carbon atoms, 3 Oxygen atoms, and 8 Hydrogen atoms.
Which type of lipid doesn't have glycerol?
SphingolipidsSphingolipids are a second type of lipid found in cell membranes, particularly nerve cells and brain tissues. They do not contain glycerol, but retain the two alcohols with the middle position occupied by an amine.
What are the 3 types of lipids?
Lipids are important fats that serve different roles in the human body. The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, and sterols.
What are the 2 types of phospholipids?
Phospholipids are an important class of membrane lipids that contain two categories of lipids, glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids.
What are the 4 main phospholipid types?
Four major phospholipids predominate in the plasma membrane of many mammalian cells: phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin. The structures of these molecules are shown in Figure 10-12.
What are phospholipids examples?
Phospholipids are esters of glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid, and other alcohols. The most common phospholipids are phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, and phosphatidylserine.
Which elements make up the backbone of a lipid?
Lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a phosphate group (hydrophilic).
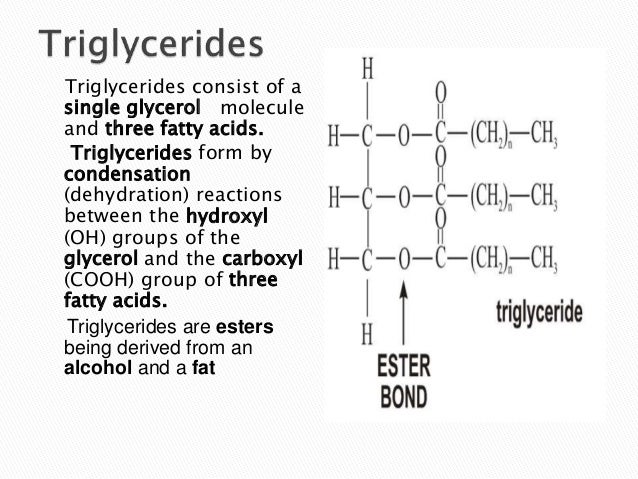
What is triglyceride?
Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) found in your blood. When you eat, your body converts any calories it doesn't need to use right away into triglycerides. The triglycerides are stored in your fat cells.
What lipid is composed of three fatty acids and glycerol?
TriglycerideTriacylglycerol (Triglyceride) Triacylglycerol is the major form of dietary lipid in fats and oils, whether derived from plants or animals. Triacylglycerol is composed of three fatty acids esterified to a glycerol molecule (Figure 4).
What has a backbone of 4 fused carbon rings?
Steroids are composed of a backbone of four fused carbon rings and are formed from a cholesterol precursor in body cells. Steroids differ from each other by the arrangement of atoms in the carbon rings and the groups attached to the backbone.
Which type of fatty acid has two or more double bonds?
Have double bonds. They can be divided into monounsaturated fatty acids (one double bond) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (two or more double bonds)
What are the atoms in a CHO?
Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO), like carbohydrates. They have long hydrocarbon tails that make them very hydrophobic
Is cholesterol a lipid?
Is also a lipid molecule that is a component of the cell membranes and is amphipathic. It is the most common precursor to steroid hormones (lipids that have four hydrocarbon rings). Cholesterol is also the starting material for vitamin D and bile acids

Overview
Glycerol , also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Because it has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in FDA approved wound and burn treatments. Conversely, it is also used as a b…
Structure
Although achiral, glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a "sn-" prefix before the stem name of the molecule.
Production
Glycerol is generally obtained from plant and animal sources where it occurs in triglycerides, esters of glycerol with long-chain carboxylic acids . The hydrolysis, saponification, or transesterification of these triglycerides produces glycerol as well as the fatty acid derivative:
Triglycerides can be saponified with sodium hydroxide to give glycerol and fatty …
Applications
In food and beverages, glycerol serves as a humectant, solvent, and sweetener, and may help preserve foods. It is also used as filler in commercially prepared low-fat foods (e.g., cookies), and as a thickening agent in liqueurs. Glycerol and water are used to preserve certain types of plant leaves. As a sugar substitute, it has approximately 27 kilocalories per teaspoon (sugar has 20) and is 60% as sw…
Metabolism
Glycerol is a precursor for synthesis of triacylglycerols and of phospholipids in the liver and adipose tissue. When the body uses stored fat as a source of energy, glycerol and fatty acids are released into the bloodstream.
Glycerol is mainly metabolized in the liver. Glycerol injections can be used as a simple test for liver damage, as its rate of absorption by the liver is considered an accurate measure of liver health. …
Historical cases of contamination with diethylene glycol
On 4 May 2007, the US Food and Drug Administration advised all US makers of medicines to test all batches of glycerol for the toxic diethylene glycol. This followed an occurrence of hundreds of fatal poisonings in Panama resulting from a falsified import customs declaration by Panamanian import/export firm Aduanas Javier de Gracia Express, S. A. The cheaper diethylene glycol was relabeled as the more expensive glycerol. Between 1990 and 1998, incidents of DEG poisoning r…
Etymology
The origin of the gly- and glu- prefixes for glycols and sugars is from Greek γλυκύς glukus which means sweet.
See also
• Dioxalin
• Epichlorohydrin
• Nitroglycerin
• Oleochemicals
• Saponification/Soapmaking