Where do synaptic vesicles fuse and release acetylcholine?
Synaptic vesicles fuse to the plasma membrane of the axon terminal and release acetylcholine. Acetylcholine binds to its receptor in the sarcolemma and triggers __________. the opening of ligand-gated cation channels Sodium and potassium ions do not diffuse in equal numbers through ligand-gated cation channels. Why?
How is acetylcholine cleared from the synaptic cleft?
What is the primary mechanism by which ACh is cleared from the synaptic cleft? Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, as some poisons can do, causes repeated muscle action potentials and near-constant muscle contraction.
What is the difference between acetylcholine receptors and synaptic vesicles?
Acetylcholine receptor: a type of chemically-gated ion channel located on the junctional folds of the muscle fiber. Synaptic vesicle : membranous sac located in the axon terminal that contains neurotransmitter.
How does acetylcholine cause multiple action potentials in muscle fibers?
Multiple action potentials would occur in the muscle fiber. Action potentials will not cease until acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft. Therefore, the constant presence of acetylcholine would cause multiple muscle action potentials and near-constant muscle contraction

What causes the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles quizlet?
An action potential in the motor neuron causes ACh to be released into the synaptic cleft. Binding of ACh to sarcolemma receptors initiates graded potentials.
What was necessary for acetylcholine release into the synaptic cleft?
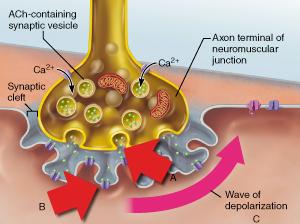
The release of acetylcholine occurs when an action potential is relayed and reaches the axon terminus in which depolarization causes voltage-gated calcium channels to open and conduct an influx of calcium, which will allow the vesicles containing acetylcholine for release into the synaptic cleft.
What most directly causes the exocytosis of ACh in synaptic vesicles?
What most directly causes the exocytosis of Ach in synaptic vesicles? synaptic cleft. When calcium ions enter the synaptic terminal, they cause vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse to the plasma membrane of the sending neuron.
What directly triggers the release of acetylcholine from a terminal bulb?
Acetylcholine is released into the cleft by active transporters in the plasma membrane of the axon terminal. Cation channels open and sodium ions enter the axon terminal while potassium ions exit the axon terminal. Synaptic vesicles fuse to the plasma membrane of the axon terminal and release acetylcholine.
What triggers the release of acetylcholine from a neuron quizlet?
Calcium enters the presynaptic cell and causes the release of ACh. As a presynaptic action potential reaches the synaptic terminal, voltage-gated calcium channels open.
What ion is necessary for the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles?
The calcium influx triggers synaptic vesicles, which package neurotransmitters, to bind to the presynaptic membrane and to release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis.
Which of the following toxin induces release of acetylcholine?
Abstract. Clostridium botulinum type toxin A (BoTx) blocks stimulus-induced acetylcholine (ACh) release from presynaptic nerve terminals at peripheral neuromuscular junctions.
What means of membrane transport is used to release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft?
What means of membrane transport is used to release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft? exocytosis. (Yes, the synaptic vesicles (where the neurotransmitter is stored) merge with the membrane and release the neurotransmitter by exocytosis.)
Which ion is required for exocytosis of ACh?
Arrival of an impulse at the axon terminal activates voltage-gated calcium ion channels, resulting in the influx of calcium ions that initiate the calcium-dependent release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) by exocytosis.
What causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters?
The elevated intracellular concentration of the Ca+2 ions initiates a signaling cascade, which results in release of the synaptic vesicles. Ca+2 ions cause fusion of the synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic cell membrane, and then the neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis.
What triggers synaptic transmission?
Synaptic transmission is initiated when an action potential invades a nerve terminal, opening Ca2+ channels, which gate a highly localized, transient increase in intracellular Ca2+ at the active zone (Fig.
What triggers for synaptic transmission to happen?
Synaptic transmission involves communication between two or more cells. However, synaptic communication is triggered by electrical activity within neurons and involves the movement of electrical charges carried by ions.
What causes sodium channels to open in the motor end plate?
Binding of the neurotransmitter causes chemically gated sodium channels to open in the motor end plate. Binding causes voltage-gated sodium channels to open in the motor endplate. Binding of the neurotransmitter causes chemically gated sodium channels to open in the motor end plate.
When ADP is released from the myosin head, what happens?
when ADP is released from the myosin head. The power stroke cocks the myosin head. The sliding of the actin myofilament during the power stroke re-cocks myosin heads that have previously delivered their power stroke. After the myosin head detaches, energy from ATP hydrolysis is used to re-cock the myosin head.
What causes cross bridge detachment?
Tropomyosin pushes the myosin head away , causing cross bridge detachment. Tropomyosin binds to calcium, causing muscle relaxation. The displacement of tropomyosin exposes the active sites of actin, allowing cross bridges to form. Tropomyosin moves the actin filament relative to the myosin filament.
What blocks the active sites on actin?
The actin myofilament can only move in one direction relative to the myosin filament. Calcium blocks the active sites on actin. There are always some myosin heads attached to the actin myofilament when other myosin heads are detaching.
What ion is responsible for myosin head power stroke?
Calcium ions provide the energy necessary for the myosin head power stroke. Calcium ion movement depolarizes the sarcolemma at the synaptic cleft. Calcium ions bind to tropomyosin, exposing the active sites on actin. Calcium ions bind to troponin, changing troponin's shape.
What is the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles?
Release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles. Calcium ions enter the axon terminal when voltage-gated calcium channels open in response to the arrival of an action potential. The presence of calcium causes synaptic vesicles to release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft.
What is the drug that binds to and inactivates acetylcholinesterase?
a drug that binds to and inactivates acetylcholinesterase (neostigmine) The progressive destruction of ACh receptors leads to a progressive decline in the strength of end-plate potentials. To counteract this problem, drug therapy focuses on increasing the concentration of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
How does the cross bridge cycle end?
The cross bridge cycle ends when Ca2+ are actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The cycle repeats as long as the binding sites on actin remain exposed, and both Ca2+ and ATP are available.
What is the cause of myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis is a disease resulting from an autoimmune attack on the ACh receptors of the motor end plate. Binding of antibodies to the ACh receptors results in generalized muscle weakness that progresses as more ACh receptors are destroyed.
Where does action potential travel?
An action potential traveling down a motor neuron arrives at the axon terminal and causes exocytosis of the neurotransmitter ACh into the synaptic cleft. ACh diffuses into the synaptic cleft, binds to the receptor proteins on the junctional folds of the muscle sarcolemma (motor end plate), and initiates graded potentials. ...
Which neuron transmits action potentials from the brain or spinal cord to muscle fibers?
Motor neuron. The motor neuron transmits action potentials from the brain or spinal cord to muscle fibers by releasing acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. Drag each tile to the appropriate bin to indicate whether it shows the neuromuscular junction at rest or active (in the process of transmitting a signal).
What is Ca2+ released from?
Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to troponin. The release of Ca2+ is triggered by the propagation of an action potential along a skeletal muscle fiber. Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and into the sarcoplasm of the muscle fiber.
Where does acetylcholine bind to?
Hints. Synaptic vesicles fuse to the plasma membrane of the axon terminal and release acetylcholine. Acetylcholine binds to its receptor. Acetylcholine is released into the cleft by active transporters in the plasma membrane of the axon terminal.
What is the shape change that occurs in voltage sensitive proteins in the sarcolemma?
Excitation refers to the shape change that occurs in voltage-sensitive proteins in the sarcolemma. Excitation, in this case, refers to the propagation of action potentials along the sarcolemma. Excitation refers to the propagation of action potentials along the axon of a motor neuron.
What enzyme breaks down acetic acid?
ACh is broken down into acetic acid and choline by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). ACh diffuses away from the synaptic cleft. ACh is taken up by the axon terminal via endocytosis. ACh is broken down into acetic acid and choline by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
What binds to the myosin head and detaches it from actin?
ATP binds to the myosin head and detaches it from actin. ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi and the energy released re-cocks the myosin head. The thin filaments are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere by the myosin heads of the thick filament.
What binds to troponin?
Calcium binds to troponin, altering its shape. Calcium binds to myosin, causing the myosin head to release from the actin myofilament. Calcium binds to troponin, exposing the active site on troponin. Calcium binds to active sites on actin, forming the cross bridge. Calcium binds to troponin, altering its shape.
Which binds actin to myosin?
Calcium binds actin to myosin to begin the cross bridge cycle. Myosin heads bind to the newly exposed myosin-binding sites on actin to form cross bridges. Tropomyosin binds to myosin heads and actin bridges with tropomyosin. Myosin heads bind to the newly exposed myosin-binding sites on actin to form cross bridges.
Which step of the cross bridge cycle is the correct order?
Place the steps that occur during a single cross bridge cycle in the correct order from left to right. The activated myosin head binds to actin, forming a cross bridge. ADP is released and myosin slides the thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere. ATP binds to the myosin head and detaches it from actin.
Where do multiple action potentials occur?
Multiple action potentials would occur in the muscle fiber. The site where a motor neuron excites a skeletal muscle fiber is called the neuromuscular junction. This activity will test your understanding of the sequence of events that occur at the neuromuscular junction.
What is the term for the propagation of action potentials along the sarcolemma?
Excitation , in this case, refers to the propagation of action potentials along the sarcolemma. Excitation of the sarcolemma is coupled or linked to the contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber.
Where are calcium ions stored in the skeletal muscle fiber?
Where are calcium ions stored within the fiber? Calcium ions are stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. After a power stroke, the myosin head must detach from actin before another power stroke can occur.
What happens to myosin after it detaches?
After the myosin head detaches, energy from ATP hydrolysis is used to re-cock the myosin head. BMD (2,3-butanedione 2-monoximime) inhibits myosin, such that ATP can bind to myosin but myosin is unable to hydrolyze the bound ATP.
How does acetylcholine bind to receptors?
Step 3: Synaptic vesicles fuse to membrane of axon terminal. Step 4: Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft. Step 5: Acetylcholine binds to its receptors on the junctional folds.
Which vesicle contains neurotransmitter?
Synaptic vesicle : membranous sac located in the axon terminal that contains neurotransmitter. Calcium channel : a type of voltage-gated ion channel located on the axon terminal. Sodium channel : a type of voltage-gated ion channel located on the sarcolemma of the muscle fiber. Acetylcholine : neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle ...
What enzyme breaks down acetic acid and choline?
Select all the correct answers. -ACh diffuses away from the synaptic cleft. -ACh is broken down into acetic acid and choline by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Action potential propagation in a skeletal muscle fiber ceases when acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft.
How does K+ diffuse out of muscle fiber?
K+ diffuses out of the muscle fiber through open chemically gated ion channels. 2. The end plate potential is primarily, and most directly, caused by the movement of Na+. 3. ACh binds to ACh receptors, causing them to open chemically gated ion channels.
Where is acetylcholinesterase located?
Acetylcholinesterase : enzyme located in the synaptic cleft that breaks down acetylcholine. Synaptic cleft : the space between the axon terminal and junctional folds. Arrange the sequence of events at the NMJ from first to last. Rank the sequence of events at the NMJ that initiate an action potential in the muscle fiber, from first to last.
Where do multiple action potentials occur?
Multiple action potentials would occur in the muscle fiber. The site where a motor neuron excites a skeletal muscle fiber is called the neuromuscular junction. This activity will test your understanding of the sequence of events that occur at the neuromuscular junction.
Does EGTA bind calcium ions?
Do not overlap any events. EGTA is a substance that binds calcium ions. Imagine an experimental setup with a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. Stimulation of the motor neuron causes contraction of the muscle fiber through activity at the neuromuscular junction and excitation-contraction coupling.
