What are the extrinsic muscles of the larynx?
- Cricothyroid muscle
- Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
- Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
- Thyroarytenoid muscle
- Vocalis muscle
- Transverse and oblique arytenoid muscles
What muscles are attached to the tongue and larynx?
Which are the intrinsic muscles of the larynx?
- Cricothyroid muscle.
- Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle.
- Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle.
- Thyroarytenoid muscle.
- Vocalis muscle.
- Transverse and oblique arytenoid muscles.
What does the larynx do in your body?
Your larynx is made of:
- The cartilage that gives it structure.
- Ligaments that connect the areas of cartilage and attach your larynx to nearby structures.
- Membranes, which also help hold cartilage together.
- Muscles, which move your larynx while swallowing, help with breathing and produce vocal sounds.
Is trachea and larynx the same?
is that larynx is an organ of the neck of mammals involved in breath control, protection of the trachea and sound production, housing the vocal cords, and that is situated at the point where the upper tract splits into the trachea and the oesophagus/esophagus while trachea is (anatomy) a thin-walled, cartilaginous tube connecting the larynx to …
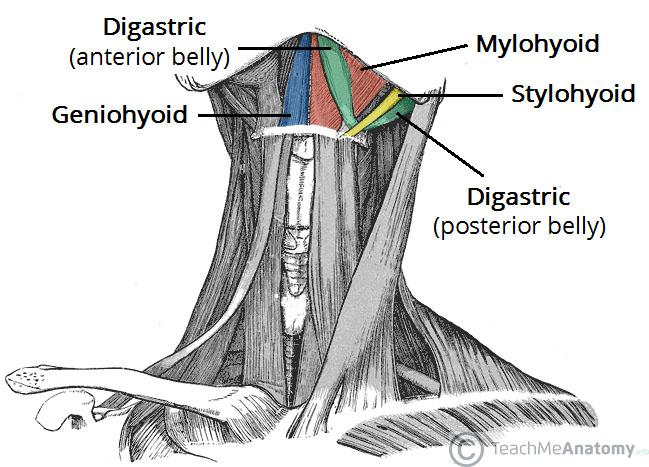
What muscles raise and lower the larynx?
The extrinsic laryngeal muscles (the thyrohyoid and the sternothyroid) change the position of the larynx in the neck by raising or lowering the thyroid cartilage, respectively. The thyrohyoid muscle plays an essential role in raising the larynx during swallowing while the sternothyroid muscle may lower voice pitch.
Does the larynx elevate?
The hyoid bone supports the larynx from above and is itself attached to the mandible by muscles and tendons. These attachments are important in elevating the larynx during swallowing and speech. The lower part of the larynx consists of a circular piece of cartilage called the cricoid cartilage.
Which muscles are responsible for elevating pitch?
The thyroarytenoid muscle (TA; a) and cricothyroid muscle (CT; b) are the primary controllers of vocal pitch. The CT rocks the thyroid cartilage forward, thereby stretching the vocal folds and raising vocal pitch.
Which of the following muscles are used to elevate the larynx quizlet?
The digastric muscle depresses the mandible and/or elevates the larynx.
What are the muscles of larynx?
Extrinsic muscles that attach directly to the larynx: Sternothyroid muscle: attaches to the anterolateral aspect of the thyroid and sternum. Causes laryngeal depression. Thyrohyoid muscle: inserts superior and medially compared to the location of the sternothyroid muscles on the thyroid.
What are the 3 important laryngeal muscles?
The muscles in this group include the stylohyoid muscle, the digastric muscle and the mylohyoid muscle. The stylopharyngeus muscle is not attached directly to the hyoid bone, however it acts indirectly to elevate both the hyoid bone and the larynx.
How do I move my larynx up and down?
Start to swallow. Use your throat muscles to stop your Adam's apple at its highest point for a couple of seconds. At first, it may help you to use fingers to help keep it up, until you understand the movement that is involved. Then finish the swallow by allowing your Adam's apple to return to a resting position.
What muscles depress the larynx?
The extrinsic laryngeal muscles move the larynx as a whole. They consist of the suprahyoid muscles that elevate the hyoid bone and the larynx during swallowing and vocalization, and the infrahyoid muscles that depress the hyoid bone and the larynx.
Why does the larynx move up and down?
This upward movement is due to the contraction of some of the extrinsic laryngeal muscles (aka the supra hyoid muscles) whose function is to raise it when we swallow. Lowering the larynx opposes these muscles during singing and will eventually help to disengage them when you don't want or need them.
How can I move my larynx down?
To drop your larynx, you can use the beginning of the yawn. Avoid intentionally pushing down the back of your tongue, as most people do when first trying to drop the larynx: If you push your tongue down, you also feel the larynx push down and you feel a tightening of the muscles under your chin.
How do I bring my larynx down?
6:268:16Lower Larynx vs Raised Larynx: Which is Right and How to Do It!YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo that you balance out right in the middle. So let's add a little bit of a Yanni feeling to that.MoreSo that you balance out right in the middle. So let's add a little bit of a Yanni feeling to that. So. You can turn into. So let's try that here keke keke keke keke keke.
Is it normal for larynx to move?
The quick answer is yes. The larynx does (and should) move when you sing, and not just for controversial techniques like belting. Even in classical singing, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) studies have confirmed that the larynx gently rises up on the higher pitches, and depresses on the lower ones.
What is the attachment of an arytenoid?
Attachments: Spans from one arytenoid cartilage to the opposite arytenoid.
What muscle is responsible for the voice?
The cricothyroid muscle stretches and tenses the vocal ligaments, and so is important for the creation of forceful speech. It also has a role in altering the tone of voice (along with the thyroarytenoid muscle), hence its colloquial name ‘singer’s muscle’.
Which muscles elevate the larynx?
As a general rule, the suprahyoid muscles and the stylopharyngeus elevate the larynx, whilst the infrahyoid muscles depress the larynx. The intrinsic laryngeal muscles act on the individual components of the larynx.
What is the voice box?
Laryngeal Muscles. The larynx (voice box) is an organ located in the anterior neck. It is a component of the respiratory tract, and has several important functions, including phonation, the cough reflex, and protection of the lower respiratory tract. The muscles of the larynx can be divided into two groups; the external muscles and ...
Which muscle group moves the larynx?
The extrinsic muscles act to move the larynx superiorly and inferiorly. They are comprised of the suprahyoid and infrahyoid groups, and the stylopharyngeus (a muscle of the pharynx). The supra- and infrahyoid muscle groups attach to the hyoid bone.
Which muscle is the major adductor of the vocal folds?
The lateral cricoarytenoid muscles are the major adductors of the vocal folds. This narrows the rima glottidis, modulating the tone and volume of speech. Attachments: Originates from the arch of the cricoid cartilage, and attaches to the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage.
Which muscle is responsible for widening the rima glottidis?
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles are the sole abductors of the vocal folds, and thus the only muscle capable of widening the rima glottidis. Attachments: Originates from the posterior surface of the cricoid cartilage, and attaches to the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage.
What are the aryepiglottic folds?
The aryepiglottic folds extend over the lateral aspects of epiglottic, cuneiform, corniculate and arytenoid cartilages. The aryepiglottic folds demarcate the opening into the laryngeal lumen. The piriform sinus can be found just lateral to the aryepiglottic folds, which form the medial border of these sinuses. This is sometimes referred to as the lateral food channel. The aryepiglottic folds serve as a protective wall that prevents food from passing into the laryngeal aditus and together, with the associated cartilages forms a protective ring. This ring is not uniform in height, at the dorsal-most aspect, there is a reduction in the height of this fold creating susceptibility to food or liquid incursions. This is called the interarytenoid notch.
What are the synovial joints in the larynx?
There are two essential synovial joints associated with the larynx. One pair of synovial joints exists between the thyroid and cricoid cartilages. This joint allows the thyroid cartilage to rotate about the cricoid cartilage and allows the cricoid cartilage to separate from or approximate to the thyroid cartilage anteriorly. The second set of synovial joints exists between the cricoid and arytenoids (cricoarytenoid synovial joint). The cricoarytenoid synovial joint allows the arytenoid cartilages to translate on both an anterior-posterior axis and lateral-medial axis, as well as rotate about a cranial-caudal axis.
What are the three unpaired cartilages in the larynx?
The larynx is composed of nine contributing cartilages: three unpaired cartilages and three paired cartilages, which share connections to each other, the hyoid (superiorly), and the trachea (inferiorly). The epiglottic, thyroid, and cricoid cartilages make up the three unpaired cartilages and are arranged superior to inferior respectively. The thyroid cartilage, with the epiglottic cartilage superior, predominates anteriorly and forms the laryngeal prominence (i.e., Adam’s Apple), while the predominate cartilage dorsally is the cricoid cartilage which sits inferior to the thyroid cartilage. The three paired cartilages include the arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform cartilages. The paired arytenoid cartilages are found on the dorsal aspect of the larynx, attached superiorly to the cricoid cartilage. Both arytenoid cartilages give off a lateral extension (muscular process) and anterior extension (vocal process) which aid in supporting the vocal ligaments. Additionally, each arytenoid cartilage has an associated corniculate and cuneiform cartilage. These two small, paired cartilages border the opening into the laryngeal vestibule both dorsally and laterally. The corniculate cartilage can be found at the apex of both arytenoid cartilages. The cuneiform cartilage can be found sitting anterior and lateral to both arytenoids. These cartilages form connections via numerous membranes, ligaments, and synovial joints.
Which artery provides the larynx with vascular supply?
Vascular supply for the larynx is derived from the superior and inferior thyroid arteries. The external carotid artery gives rise to the superior thyroid artery. The thyrocervical artery, which arises from the anterosuperior surface of the subclavian artery gives rise to the inferior thyroid artery and two other branches.
Which ligament is located within the cricovocal membrane?
The lateral cricothyroid ligament is contained within the cricovocal membrane. Like the vestibular ligament, this ligament also extends from the arytenoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. However, the lateral cricothyroid ligament also follows the cricoid cartilage as it extends inferiorly. In addition, this ligament gives rise to the vocal ligament as it thickens superiorly. The vocal ligament extends from the thyroid cartilage [luminal surface] to the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage. The conus elasticus is a collective term for the cricovocal membrane and its contained ligaments. The medial convergence of these ligaments support the vocal folds.
Where does the larynx originate?
The larynx is a complex structure of the respiratory tract composed of unpaired and paired cartilages and originates embryologically from both endoderm and mesoderm.
Which membrane gives support to the aryepiglottic folds?
The quadrangle membran e gives support to the aryepiglottic folds superiorly and continues inferiorly as the vestibular folds. The vestibular folds contain the vestibular ligament, which extends from the arytenoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. The vestibular folds appear to have no role in phonation and are relatively immobile structures.
