
Causes
Dermatomyositis mostly affects the muscles of the hips and thighs, the upper arms, the top part of the back, the shoulder area and the neck. Dermatomyositis is one of the inflammatory myopathies, a group of muscle diseases that involves inflammation of the muscles or associated tissues, such as the blood vessels...
Symptoms
Dermatomyositis (DM), one of the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies, is a rare, systemic autoimmune muscle and skin disease that causes inflammation of the skeletal muscles, those involved with voluntary movement.
Prevention
In most cases, the cause of an inflammatory myopathy is unclear. For some reason, the body’s immune system turns against its own muscles and damages muscle tissue in an autoimmune process. In dermatomyositis, these cells attack the small blood vessels that supply muscles and skin.
Complications
Dermatomyositis is not polymyositis with skin involvement. PM and DM are very different diseases. The goals of treatment for dermatomyositis are to eliminate or reduce skin and muscle inflammation, restore muscle performance, reduce morbidity, and improve a patient’s quality of life.
What part of the body does dermatomyositis affect?
What is dermatomyositis (DM)?
What causes dermatomyositis myopathy?
Is dermatomyositis polymyositis with skin involvement?

What causes a flare up of dermatomyositis?
The cause of dermatomyositis is unknown, but the disease has much in common with autoimmune disorders, in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body tissues. Genetic and environmental factors also might play a role.
How quickly does dermatomyositis progress?
The deposits have a high calcium content and tend to be firm, white, or flesh-colored nodules over bony areas which can include the elbows, knees, and extremities. These calcifications often develop within three years of diagnosis but may develop up to 20 years later.
How does dermatomyositis affect the body?
Dermatomyositis is a rare disease that causes muscle weakness and skin rash. Symptoms include a red or purple rash on sun exposed skin and eyelids, calcium deposits under the skin, muscle weakness, and trouble talking or swallowing. There is no cure, but treatment is done to reduce the symptoms.
How can you tell the difference between dermatomyositis and polymyositis?
Two specific kinds are polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Polymyositis causes muscle weakness, usually in the muscles closest to the trunk of your body. Dermatomyositis causes muscle weakness, plus a skin rash.
Can Covid trigger dermatomyositis?
COVID-19 can induce a systemic inflammatory response, and its clinical manifestations are diverse. Recently, it has been reported that COVID-19 patients may develop myositis and interstitial pulmonary disease similar to dermatomyositis (DM).
Does dermatomyositis affect the brain?
“Bubbles in the brain”: an unusual complication of dermatomyositis - PMC.
Does exercise help dermatomyositis?
Exercise can improve mitochondrial function, angiogenesis as well as improve muscle growth and reduce inflammation in established polymyositis and dermatomyositis.
Does dermatomyositis affect your eyes?
Heliotrope eyelid eruptions are considered a hallmark of DM affecting the eye. Other ocular manifestations of DM include conjunctival edema, nystagmus, extraocular muscle weakness, iritis, cotton wool spots, optic atrophy, and conjunctival pseudopolyposis. Retinopathy is also a rare presentation.
Is there a blood test for dermatomyositis?
Dermatomyositis is usually diagnosed with blood tests and biopsies of your skin and muscles. Your provider will test your blood for: Increased amounts of specific muscle enzymes that means something is damaging them. Autoantibodies (cells that show your immune system is reacting to something it detects as harmful).
What can be mistaken for dermatomyositis?
Many skin conditions, including psoriasis, eczema and verrucae vulgaris can mimic the characteristic Gottron's papules of dermatomyositis, and allergies can mimic the heliotrope rash. Myositis syndromes are the most common causes of acquired muscle disease in adults but are still rare disorders.
Is CK always elevated in dermatomyositis?
Muscle enzyme abnormalities described for polymyositis apply equally to dermatomyositis. Serum CK is elevated in 90% of dermatomyositis patients and can be as high as 50 times the upper limit of normal. However, serum CK levels can be normal, particularly early in the course of the disease.
When should you suspect dermatomyositis?
When to suspect the diagnosis — The diagnosis of dermatomyositis (DM) or polymyositis (PM) should be suspected in patients who present with proximal muscle weakness. The suspicion for DM in particular should be further increased if the patient has a cutaneous eruption suggestive of DM.
How long do people live with dermatomyositis?
For dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and necrotizing myopathy, the progression of the disease is more complicated and harder to predict. More than 95 percent of those with DM, PM, and NM are still alive more than five years after diagnosis.
What is the death rate of dermatomyositis?
Previous studies reported that the connective tissue disease PM/DM has a poor prognosis and high I-HMR. The reported 10-year survival rate ranged between 53% and 91% [4, 9–12]. A very recent population-based study from America reported a hospital mortality of 4.5% [2].
Can you live a normal life with dermatomyositis?
If you treat it early, the prognosis for dermatomyositis is good. Some people may even recover and have their symptoms fully disappear, but this is more common in children. Patients who delay treatment may experience lung or heart problems or a permanent disability.
How long does a dermatomyositis last?
For some people, dermatomyositis resolves on its own about five years after diagnosis. In others, symptoms may last for a lifetime. NYU Langone doctors offer continued guidance and support to help you manage symptoms and improve your quality of life.
What are the symptoms of dermatomyositis?
The most common signs and symptoms include: Skin changes. A violet-colored or dusky red rash develops, most commonly on your face and eyelids and on your knuckles, elbows, knees, chest and back. The rash, which can be itchy and painful, is often the first sign of dermatomyositis. Muscle weakness.
What is the name of the disease that causes muscle weakness and rash?
Dermatomyositis (dur-muh-toe-my-uh-SY-tis) is an uncommon inflammatory disease marked by muscle weakness and a distinctive skin rash.
How old is the best age to get dermatomyositis?
In children, it most often appears between 5 and 15 years of age. Dermatomyositis affects more females than males. There's no cure for dermatomyositis, but periods of symptom improvement can occur. Treatment can help clear the skin rash and help you regain muscle strength and function.
What is progressive muscle weakness?
Muscle weakness. Progressive muscle weakness involves the muscles closest to the trunk, such as those in your hips, thighs, shoulders, upper arms and neck. The weakness affects both the left and right sides of your body, and tends to gradually worsen.
Can dermatomyositis cause heart problems?
Cardiovascular disease. Dermatomyositis can cause heart muscle inflammation. In a small number of people who have dermatomyositis, congestive heart failure and heart rhythm problems develop.
Does dermatomyositis cause cancer?
Cancer. Dermatomyositis in adults has been linked to an increased likelihood of developing cancer, particularly ovarian cancer in women. Risk of cancer appears to level off three years or so after a diagnosis of dermatomyositis. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What is dermatomyositis?
Summary. Dermatomyositis is a type of inflammatory myopathy characterized by inflammatory and degenerative changes of the muscles and skin. Associated symptoms and physical findings may vary widely from case to case as patients may present differently. Muscle abnormalities may begin with aches and weakness of the muscles of the trunk, upper arms, ...
How does dermatomyositis affect children?
Calcification of muscles and tissues is more frequent and widespread in childhood dermatomyositis as compared to adult forms. The deposits have a high calcium content and tend to be firm, white, or flesh-colored nodules over bony areas which can include the elbows, knees, and extremities. These calcifications often develop within three years of diagnosis but may develop up to 20 years later. Affected children also tend to have widespread inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis), with more frequent involvement of the GI tract. In those with GI vasculitis, associated findings may include abdominal pain; difficult, infrequent, or incomplete passing of stools (constipation); or the passage of tarry, black stools (melena) or vomiting of blood due to the development of sores or eroded areas in the lining of the GI tract (bleeding peptic ulcers). Children may also develop a tiptoe gait secondary to a stiffening of the ankles. Malignancy is rarely associated with the childhood form of dermatomyositis.
How often does dermatomyositis occur?
Dermatomyositis may occur at any time from infancy through approximately age 80, but most commonly it occurs between ages 40 to 60. The estimated incidence of dermatomyositis is 9.63 cases per million people. In children, the symptoms usually appear between the ages of five to 15 years. Approximately three in 1,000,000 children are affected by juvenile dermatomyositis. Females are affected by dermatomyositis twice as often as males.
What is the name of the disorder where the body's immune system acts against the body's own tissues?
Dermatomyositis is thought to belong to a group of disorders in which the body’s natural immune defenses inappropriately act against the body’s own tissues (autoimmune disorders). In dermatomyositis, an abnormal immune reaction appears to lead to obstructive inflammatory changes of blood vessels within muscle, connective tissues of the skin, and other tissues; patchy degeneration, wasting (atrophy), and regeneration of muscle fibers; thinning of the outermost skin layer (epidermis); and/or other associated findings.
How many children have juvenile dermatomyositis?
In children, the symptoms usually appear between the ages of five to 15 years. Approximately three in 1,000,000 children are affected by juvenile dermatomyositis. Females are affected by dermatomyositis twice as often as males.
What tests are needed for dermatomyositis?
In addition to a basic, thorough physical examination, including breast, gynecologic, and/or rectal examination, screening may include routine blood testing, analysis of urine and stool, chest x-rays, mammograms in women, and/or other tests, as well as appropriate follow-up testing as required.
Is dermatomyositis more frequent in childhood?
Onset is usually more sudden (acute) than in the adult form and often involves skin manifestations followed by muscle weakness. Calcification of muscles and tissues is more frequent and widespread in childhood dermatomyositis as compared to adult forms.
What are the symptoms of dermatomyositis?
The symptoms are caused by swelling and inflammation in the blood vessels that supply your skin and muscles, and can include:
How to treat dermatomyositis?
Treatment. There is no cure for dermatomyositis, but you can treat the symptoms with medication, physical therapy, exercise, heat therapy and rest. Medications include corticosteroids, immunosuppressant drugs and topical ointments.
How is dermatomyositis diagnosed?
The process starts with a person’s medical history and a physical exam. The health care provider will look for an underlying disease, such as cancer. Tests may also be done, such as:
What is the condition that causes rash and inflammation?
What is dermatomyositis? Dermatomyositis is a rare disease that causes muscle inflammation and skin rash. It’s one of a group of muscle diseases that cause muscle inflammation and swelling. It's different from other muscle diseases because it also causes skin problems.
What are the symptoms of muscle weakness?
Muscle weakness in the neck, hip, back, and shoulders. Trouble swallowing and voice changes. Tiredness, fever, and weight loss. Muscle aches. Trouble rising from a chair or getting out of bed due to muscle weakness. Sometimes the muscle weakness also spreads to the heart, GI tract, and lungs.
Why does my immune system attack my own tissues?
The exact cause is not known, but possible causes include: Autoimmune disease, a type of illness that causes the body’s immune system to attack its own tissues. An infection, medication, or another exposure in your environment that triggers the disease.
What causes dermatomyositis?
The exact cause of dermatomyositis isn’t known. However, it has many similarities to an autoimmune disease. An autoimmune disease occurs when your body’s disease-fighting cells, called antibodies, attack your healthy cells. Having a compromised immune system may also contribute to getting the disease.
Why is Dermatomyositis easier to diagnose?
Dermatomyositis is an easier inflammatory muscle disease to diagnose because of the rash associated with it.
What tests are done to check for abnormal muscle?
Your doctor may also order: an MRI to look for abnormal muscles. an electromyography (EMG) to record electrical impulses that control your muscles. a blood analysis to check your levels of muscle enzymes and autoantibodies, which are antibodies that attack normal cells.
Where does muscle weakness start?
This muscle weakness usually starts in your neck, arms, or hips and can be felt on both sides of your body. Other symptoms you might experience are: There is a subtype of dermatomyositis that includes the rash but not muscle weakness. This is known as amyopathic dermatomyositis.
What is a muscle biopsy?
a muscle biopsy to look for inflammation and other problems associated with the disease in a sample of muscle tissue. a skin biopsy to look for changes caused by the disease in a skin sample.
How old is dermatomyositis?
However, according to the Mayo Clinic, it’s most common in adults between the ages of 40 and 60 and children between the ages of 5 and 15. The disease affects women more often than men.
Can dermatomyositis be treated?
There’s no cure for dermatomyositis for most people, but your symptoms can be treated . Your doctor will create a treatment plan for you that will help you manage your symptoms.
How to diagnose dermatomyositis?
The diagnosis of dermatomyositis is usually confirmed by the following tests: 1 Blood tests to detect increased amounts of muscle enzymes such as creatine kinase (CK) and sometimes lactic dehydrogenase (LDH). 2 Blood tests to detect autoantibodies (antibodies that react with cells, tissues, or native proteins of the individual in which the antibodies are produced). 3 Skin biopsy of the rash. 4 Biopsy of an affected muscle. 5 Electromyography (EMG) testing. 6 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of muscles.
What test is used to diagnose dermatomyositis?
The diagnosis of dermatomyositis is usually confirmed by the following tests: Blood tests to detect increased amounts of muscle enzymes such as creatine kinase (CK) and sometimes lactic dehydrogenase (LDH).
Is mycophenolate safe for muscle?
Mycophenolate (brand name CellCept®, Myfortic®) Rituximab (brand name Rituxan®) Further treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), used to slow down the autoimmune process, has been shown to be effective and safe. Physical therapy can preserve muscle function and prevent muscle wasting.
Who is affected by Dermatomyositis?
Dermatomyositis is a rare disease. A rare disease in the U.S. is defined as a condition affecting fewer than 200,000 people.
What are the symptoms of dermatomyositis?
Not all patients display all of these symptoms. Skin rashes and discolorations which affect sun-exposed areas, cheeks, nose, shoulders, upper chest, and elbows. Proximal muscle weakness (muscles closest to the trunk, such as shoulders, thighs, and hips)
What is the identifying factor for dermatomyositis?
An identifying factor for dermatomyositis is a skin rash that precedes or accompanies progressive muscle weakness. Muscle weakness, when present, can develop over a period of days, weeks, or months.
What is DM in medical terms?
Dermatomyositis (DM) Dermatomyositis is one of a group of rare muscle diseases called inflammatory myopathies, which are characterized by chronic muscle inflammation accompanied by muscle weakness. An identifying factor for dermatomyositis is a skin rash that precedes or accompanies progressive muscle weakness.
Is dermatomyositis a rash?
A skin rash that precedes or accompanies muscle weakness is often helpful in diagnosing DM. Muscle involvement, for some, is not a part of their disease. Muscle pain (myalgia) and joint pain, with or without true arthritis and joint inflammation, can also be a part of dermatomyositis. DM is a chronic, incurable disease.
Does Dermatomyositis cause cancer?
Dermatomyositis in adults has also been linked to an increased likelihood of developing cancer post-diagnosis, particularly cancers of the cervix, lungs, pancreas, colorectal system, breasts, ovaries and gastrointestinal tract and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
What are the symptoms of dermatomyositis?
Sudden or progressive weakness in muscles in neck, hip, back, and shoulder muscles. Difficulty swallowing ( dysphagia) or a feeling of choking. Hardened lumps or sheets of calcium ( calcinosis) under the skin. If you’re experiencing any of these dermatomyositis symptoms, we’d encourage you to talk to your doctor to begin the diagnosis process.
What is the easiest type of myositis to diagnose?
Rash and Muscle Weakness. DM is usually the easiest type of myositis to diagnose because of the skin rash, which often appears before any muscle weakness is felt. The rash looks patchy, dark, and reddish or purple. It is most often found on the eyelids, cheeks, nose, back, upper chest, elbows, knees, and knuckles.
What is the name of the condition where you feel no muscle weakness?
Amyopathic Dermatomyositis. Patients who have the skin rash but feel no muscle weakness most likely have amyopathic DM, or DM sine myositis. These patients often list fatigue as a symptom, but do not experience the same muscle weakness as dermatomyositis patients.
How to tell if you have DM?
The following symptoms are common for DM patients: 1 Rash on the eyelids, cheeks, nose, back, upper chest, elbows, knees, and knuckles 2 Scaly, dry, or rough skin 3 Trouble rising from a seated position or getting up after a fall 4 General tiredness 5 Inflamed or swollen areas around fingernails 6 Sudden or progressive weakness in muscles in neck, hip, back, and shoulder muscles 7 Difficulty swallowing ( dysphagia) or a feeling of choking 8 Hardened lumps or sheets of calcium ( calcinosis) under the skin
What are the symptoms of DM?
The following symptoms are common for DM patients: Rash on the eyelids, cheeks, nose, back, upper chest, elbows, knees, and knuckles. Sudden or progressive weakness in muscles in neck, hip, back, and shoulder muscles.
What is the rash under the skin called?
Some people also develop hardened bumps under the skin, called calcinosis.
Is dermatomyositis a cure?
As with other types of myositis, there is no known cause or cure for dermatomyositis. Although there is not currently a cure, there are treatments that have seen success in managing symptoms.
How to tell if you have dermatomyositis?
If dermatomyositis occurs along with polymyositis, symptoms may also include: 1 Skin rash. This can be either raised and smooth or scaly. It may appear on the forehead, the neck, shoulders, chest and back, forearms and lower legs, elbows and knees or the joints of the fingers, toes, wrists and ankles. 2 Swelling around the eye. This may look purplish and bruised. 3 Swelling at the base and sides of the fingernails 4 Splitting of the skin of the fingers
How often does polymyositis occur?
A tumor may spark an immune reaction against both tumor and the muscle tissue. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis occur almost two times often in women than men. While it can occur at any age, it usually appears in people between the ages of five to 15 or 40 to 60.
Why do my arms and legs tighten up?
Contraction of the arms and legs. While the hands, feet and face are usually not affected by this condition, the arms and legs may tighten up in the late stages of the disease. Shortness of breath. This is caused by gradual damage and weakness of the chest wall and the muscles that move the diaphragm during breathing.
What causes weakness in the arms and legs?
These diseases cause swelling and tenderness in the muscles (polymyositis) and sometimes the skin (dermatomyositis). The disease causes weaknesses in the arms and legs.
Is polymyositis hard to treat?
Polymyositis tends to be more severe and difficult to treat if the disease affects the patient's heart or lungs. However, relatively long periods of time without symptoms (remission) or even apparent recovery do occur, especially in children.
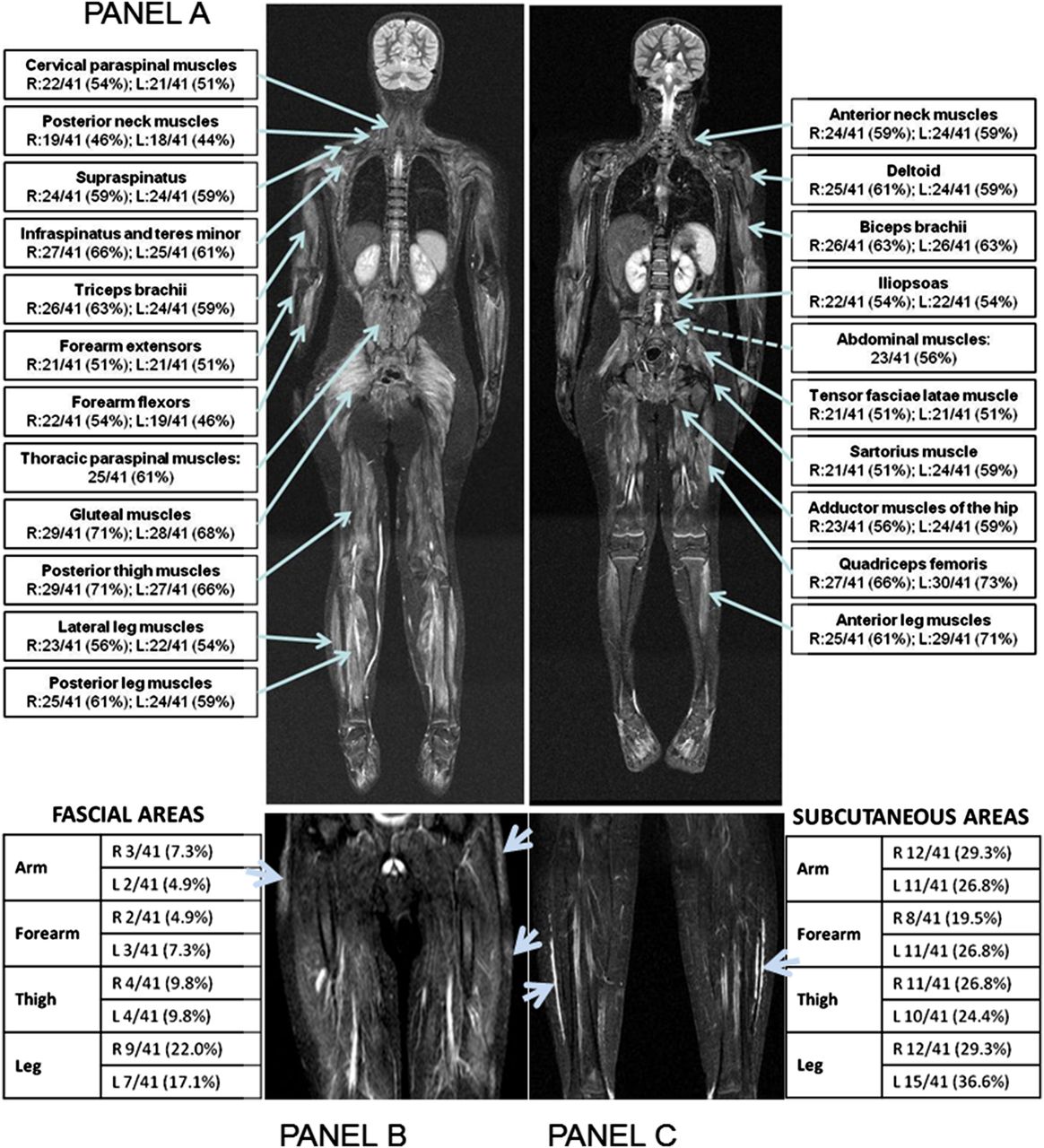
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms
Cause
Pathophysiology
Epidemiology
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prognosis
- Possible complications of dermatomyositis include: 1. Difficulty swallowing.If the muscles in your esophagus are affected, you can have problems swallowing, which can cause weight loss and malnutrition. 2. Aspiration pneumonia.Difficulty swallowing can also cause you to breathe food or liquids, including saliva, into your lungs. 3. Breathing proble...
Adverse effects
- In those with dermatomyositis, the onset of symptoms may be gradual (insidious) or sudden (acute). The symptoms often wax and wane for no apparent reason. The major symptom of the disorder is muscle weakness, most often affecting the trunk and muscles closest to the trunk (i.e., proximal muscles), such as the hips, thighs, shoulders, upper arms, an...
Resources
- Individuals with dermatomyositis also develop characteristic skin changes that, in some cases, may precede muscle weakness. These characteristic skin changes may be the only sign of dermatomyositis at the start in up to 40% of people. Skin abnormalities often include a distinctive reddish-purple or lilac (i.e., heliotrope) rash that may be present on the upper eyelids (heliotrope …
Research
- Furthermore, in some individuals with dermatomyositis, there may be an association with an underlying cancer (malignancy). Reports indicate that the malignancy may precede, occur in association with, or develop subsequent to the onset of dermatomyositis. Malignancy-associated dermatomyositis appears to occur more frequently in individuals over the age 40-50. Although t…
Selected publications
- Dermatomyositis is thought to belong to a group of disorders in which the bodys natural immune defenses inappropriately act against the bodys own tissues (autoimmune disorders). In dermatomyositis, an abnormal immune reaction appears to lead to obstructive inflammatory changes of blood vessels within muscle, connective tissues of the skin, and other tissues; patch…