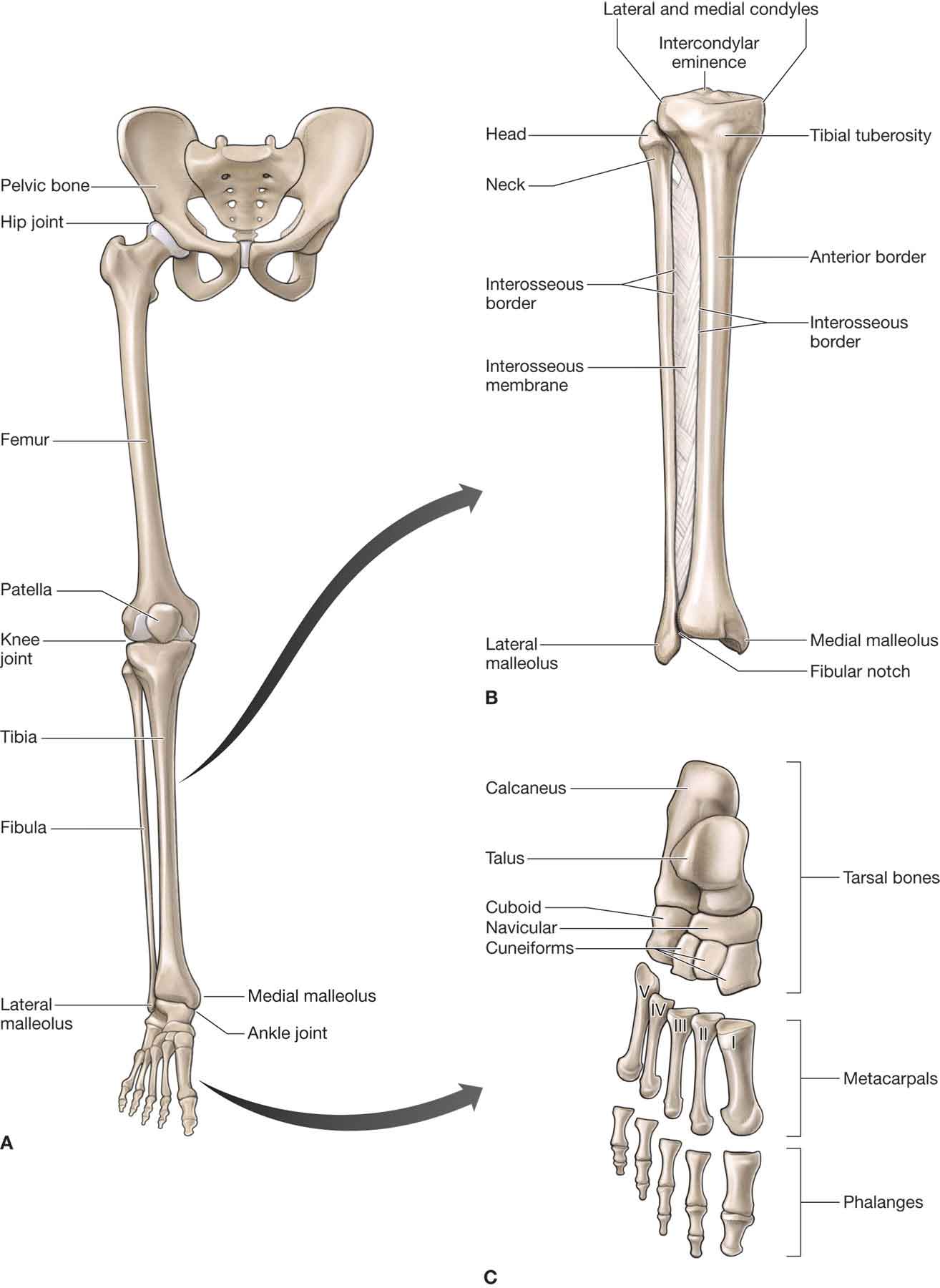
Thus, plantarflexion and dorsiflexion are the main movements that occur at the ankle joint. Eversion and inversion are produced at the other joints of the foot, such as the subtalar joint. Plantarflexion – produced by the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and posterior tibialis).
What muscles invert the ankle?
Which ankle muscles plantar flex the ankle (plantar flexion)?
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
- Flexor hallucis longus
- Flexor digitorum longus
- Tibialis posterior
- Peroneus brevis
- Peroneus longus
What muscle is involved with ankle dorsiflexion?
These include:
- tibialis posterior.
- flexor digitorum longus.
- gastrocnemius.
- soleus.
What is an inversion of the ankle?
Inversion of the Ankle. Tilting of the sole of the foot inwards to face medially. This looks like you are pushing your little toes into the ground and lifting the big toe up. The movement is occurring at the SubTalar Joint which is where the talus meets the calcaneus.
What are the muscles of the ankle?
- The peroneals ( peroneus longus and peroneus brevis) on the outside edge of the ankle and foot bend the ankle down and out.
- The calf muscles ( gastrocnemius and soleus) connect to the calcaneus by the Achilles tendon. ...
- The posterior tibialis muscle supports the arch and helps turn the foot inward.
- The anterior tibialis pulls the ankle upward.
Which muscles are involved in inversion of the ankle?
The ankle invertor muscles included the tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum, flexor hallucis, and extensor hallucis.
What muscle is involved in dorsiflexion and inversion of the ankle joint?
tibialis anterior muscleThe tibialis anterior muscle, found in the anterior compartment of the leg, is the primary muscle that facilitates dorsiflexion of the ankle joint.
What is inversion of the ankle joint?
0:111:20Inversion and Eversion of the Foot, Ankle | Body Movement ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMentioned a lot when people refer to ankle sprains for example an inversion ankle sprain means thatMoreMentioned a lot when people refer to ankle sprains for example an inversion ankle sprain means that the foot soul turned medially causing injury to the ligaments on the lateral.
What muscles are involved in subtalar joint inversion?
Muscles acting on the subtalar joint Supination in the subtalar joint is primarily produced by tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior, with assistance from extensor hallucis longus, flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus.
What muscles do inversion?
There are two muscles that produce inversion, tibialis anterior, which we've seen already, and tibialis posterior.
What muscle facilitates inversion of the foot?
Inversion of the Foot (tilting of the sole of the foot inwards towards the midline): Performed by the tibialis posterior and tibialis anterior.
What 3 ligaments are damaged when the ankle in inverted?
The most common type of ankle sprain is an inversion injury, or lateral ankle sprain. The foot rolls inward, damaging the ligaments of the outer ankle — the anterior talofibular ligament, the calcaneofibular ligament, and the posterior talofibular ligament.
Where do inversion and eversion occur in the ankle?
Subtalar (ST) Joint The subtalar joint allows inversion and eversion of ankle and hindfoot.
What are the structures ligaments muscles tendons that could be injured during an inversion ankle sprain rolling the ankle )?
These include the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), and the posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL). The most common type of ankle injury (inversion) usually involves two ligaments, the ATFL and CFL.
Does gastrocnemius invert the foot?
2020) have observed that inversion-eversion torques derive, in part, from the gastrocnemius muscles. More specifically, during ankle-joint inversion, the inversion moment arm increases for the LG (Lee and Piazza 2008) .
Which muscle is responsible for lifting toes and inverting the foot?
The tibialis anterior muscle is the most medial muscle of the anterior compartment of the leg. It is responsible for dorsiflexing and inverting the foot, and is the largest dorsiflexor of the foot.
Where does inversion and eversion occur?
The distribution of inversion and/or eversion and rotation across the two joints has been an area of greater contention, with some studies indicating eversion to occur at the subtalar joint and rotation/inversion to occur at the tibiotalar, whereas others have shown version to be distributed across both joints.
What muscle is used in dorsiflexion?
There's one muscle on the front of the leg for dorsiflexion, tibialis anterior. There are three on the back of the leg for plantar flexion, gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris.
Which muscle Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot quizlet?
PLANTAR FLEXES AND INVERT THE FOOT. Deep to the Extensor digitorum longus, sits between the tibia and fibula on the anterior side. Starts mid-leg and extends down to hallux via tendons. DORSIFLEXES FOOT AND EXTENDS HALLUX.
What muscle Dorsiflexes and Everts?
Extensor digitorum longus: Extends the toes and dorsiflexes and everts the foot.
What joint allows inversion and eversion of the foot?
Subtalar (ST) Joint There are three facets on each of the talus and calcaneus. The posterior subtalar joint constitutes the largest component of the subtalar joint. The subtalar joint allows inversion and eversion of ankle and hindfoot.
Where does the arterial supply to the ankle joint come from?
The arterial supply to the ankle joint is derived from the malleolar branches of the anterior tibial, posterior tibial and fibular arteries.
Where are inversion and eversion produced?
Eversion and inversion are produced at the other joints of the foot, such as the subtalar joint. Plantarflexion – produced by the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and posterior tibialis).
What are the different types of talus?
The body of the talus fits snugly into the mortise formed by the bones of the leg. The articulating part of the talus is wedge shaped – it is broad anteriorly, and narrow posteriorly: 1 Dorsiflexion – the anterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is more stable. 2 Plantarflexion – the posterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is less stable.
What is the socket of the talus called?
This socket is known as a mortise. The body of the talus fits snugly into the mortise formed by the bones of the leg. The articulating part of the talus is wedge shaped – it is broad anteriorly, and narrow posteriorly: Dorsiflexion – the anterior part of the talus is held in the mortise , and the joint is more stable.
What is the anterior talofibular?
Anterior talofibular – spans between the lateral malleolus and lateral aspect of the talus.
Which part of the talus is held in the mortise?
Dorsiflexion – the anterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is more stable. Plantarflexion – the posterior part of the talus is held in the mortise, and the joint is less stable. By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 2 – X-ray of a normal ankle joint.
What type of joint is the shin joint?
Functionally, it is a hinge type joint, permitting dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot.
What muscles are involved in ankle joint?
Movements and Muscles Involved in Ankle Joint 1 Dorsiflexion – Produced by the in the anterior compartment of the leg muscles; tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus. 2 Plantarflexion – Offered by the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg; gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and posterior tibialis.
What are the ligaments of the ankle joint?
Ligaments of Ankle Joint. There are two sets of ligaments, that originate from individual malleolus. The medial ligament (known as deltoid ligament) is connected to the medial malleolus. It consists of four separate ligaments, that fan out from the malleolus, connecting to the talus, calcaneus, and navicular bones.
What are the three bones that make up the ankle joint?
Articulating Surfaces of Ankle Joint. The ankle joint is composed of three bones; the tibia and fibula of the lower limb, including the talus of the foot: The tibia and fibula are connected together by powerful tibiofibular ligaments, providing a bracket shaped socket, that is covered in hyaline cartilage.
Which joint is only used for plantarflexion?
Therefore, plantarflexion and dorsiflexion are the only movements that happen at the ankle joint. Inversion and Eversion are allowed at the other joints of the foot, such as the subtalar joint.
What is the principal action of the medial ligament?
The principal action of the medial ligament is to resist over-eversion of the foot.
Which ligament spans the lateral malleolus?
Calcaneofibular ligaments: Spans within the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus.
Which part of the talus is wedge shaped?
The articulating part of the talus is wedge-shaped. It is broader anteriorly, and thinner posteriorly. While dorsiflexion, the anterior part of the bone is held in the mortise, and the joint is stronger stable (vice versa for plantarflexion).
What is the main action of the ankle joint?
The main action of the ankle joint is to allow dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot, as well as some degree of pronation and supination with subtalar and midtarsal joints. The joint also acts as a shock absorber as the heel strikes the ground during the first phases of gait. Key facts about the ankle joint. Type.
What are the articular surfaces of the ankle joint?
The ankle joint is a complex of articulations between the distal ends of the tibia and its medial malleolus, lateral malleolus of the fibula, and the trochlear surface of the talus. All of the articular surfaces of the ankle joint are covered with hyaline cartilage. There are three articulations in the ankle joint: ...
What are the ligaments in the ankle?
The lateral collateral ligament is a strong compound ligament that reinforces the lateral aspect of the ankle joint. It is comprised of three distinct bands: 1 Anterior talofibular ligament: a weak, flat band that originates on the lateral malleolus of the fibula and extends anteromedially to the lateral side of the neck of the talus. 2 Posterior talofibular ligament: a strong band that extends medially and posteriorly from the distal part of the lateral malleolar fossa of the fibula to the lateral tubercle of the talus. It is also connected to the medial malleolus by a tibial slip of fibres. 3 Calcaneofibular ligament: a long band that originates from the apex of the lateral malleolus of the fibula, and extends posteroinferiorly to attach on a tubercle on the lateral aspect of the calcaneus.
What is a tibia and fibula joint?
It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations. It is often described as a tenon and mortise joint, as the tibia and fibula act as a mortise and form a notch in which the body of the talus fits, acting as the tenon.
Where is the anterior talofibular ligament?
Anterior talofibular ligament: a weak, flat band that originates on the lateral malleolus of the fibula and extends anteromedially to the lateral side of the neck of the talus.
Where does the Calcaneofibular ligament originate?
Calcaneofibular ligament: a long band that originates from the apex of the lateral malleolus of the fibula, and extends posteroinferiorly to attach on a tubercle on the lateral aspect of the calcaneus.
What is the name of the joint that connects the bones of the leg, the fibula and tibi?
Last reviewed: May 31, 2021. Reading time: 10 minutes. Ankle joint (articulatio talocruralis) The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, is a synovial joint that connects the bones of the leg, the fibula and tibia, with the talus of the foot. It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations.
Which muscles are involved in inversion?
These horizontal movements in the sagittal plane most often occur in combination with supination and pronation. The tibialis anterior and gastrocnemius are the primary muscles working during inversion; and the fibularis (peroneus) brevis and longus are primarily responsible for eversion (Moore 1992).
What ligaments stabilize the lateral aspect of the ankle joint?
Three separate ligaments stabilize the lateral aspect of the ankle joint: the anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular and posterior talofibular ligaments. Medially, support comes from a collective group of ligaments known as the deltoid ligament. Inversion/Eversion.
What muscles are involved in plantar flexion?
The gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis posterior, fibularis brevis and longus, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus and plantaris are the primary muscles acting in plantar flexion; and the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus and peroneus tertius are primarily responsible for dorsiflexion (Moore 1992).
How to raise calf without dropping hip?
clocks (3 reps, 4 seconds lowering, 2 seconds raising) Stand on one leg on a 6- to 10-inch step. Without dropping the hip, lower the working leg to a 12 o’clock position (forward) just short of the floor surface by bending the support leg’s knee.
What is the talus?
The talus is a wedge-shaped bone that fits into the mortise formed by the bound tibia and fibula (Moore 1992). Multiple ligamentous attachments, muscular attachments and a fibrous capsule maintain the articulation of all three bones. Three separate ligaments stabilize the lateral aspect of the ankle joint: the anterior talofibular, ...
What are the bones that make up the ankle?
The bones involved in ankle articulation include the tibia, fibula and talus. The tibia and fibula are the long bones of the lower leg; the fibula, a relatively thinner bone, is lateral to the tibia. These two bones are bound together by the ligaments and the interosseous membrane. The talus is a wedge-shaped bone that fits into ...
What are the bones that are involved in ankle articulation?
Anatomy, common injuries and postrehab strategies. The bones involved in ankle articulation include the tibia, fibula and talus. The tibia and fibula are the long bones of the lower leg; the fibula, a relatively thinner bone, is lateral to the tibia. These two bones are bound together by the ligaments and the interosseous membrane.
Which muscle is the largest and most superficial of the ankle muscles?
Gastrocnemius is the largest and most superficial of the ankle muscles. Together the Gastrocnemius, Soleus, and Plantaris are known as Triceps Surae. The Gastrocnemius is the main propellant in walking and running.
What bones are in the ankle joint?
The ankle joint consists of the tibia and fibula shin bones, which sit on the talus and calcaneus at the back of the foot. The foot itself comprises 26 bones. The movements available are:
What muscle is used to bend the big toe?
Flexor Hallucis Longus bends the big toe when you curl up your foot. It is called ‘Hallucis’ as the word Hallux means great or big toe in Latin. This muscle also supports the longitudinal arch of the foot.
What is the name of the muscle that attaches to the fibula?
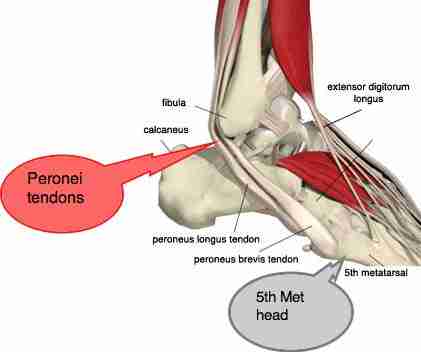
Peroneus Brevis is one of the peroneal muscles in the ankle which passes down the outside of the lower leg and everts (turn outwards) the foot. These muscles are sometimes referred to as Fibularis brevis and longus due to their attachments on the fibula. Origin: Lower 2/3 of the lateral surface of the fibula.
What muscle is used to grip the floor?
Flexor Digitorum Longus causes the toes to grip and mold to the floor’s surface which is vital in maintaining balance on rough surfaces. The tendons pass under the foot. Walking barefoot on an uneven surface is an excellent exercise for this muscle.
Which muscle group is located on the outside of the lower leg?
Peroneus Longus is one of the peroneal muscle groups which passes down the outside of the lower leg and everts (turn out) the foot. These muscles are sometimes referred to as fibularis longus and brevis due to their attachments on the fibula.
What is the tibialis anterior?
Tibialis anterior forms the main fleshy part of the outside of the shin. It is a dorsiflexor of the ankle. Origin: Upper 1/2 of lateral and anterior surfaces of the tibia. Insertion: Inner surface of the medial cuneiform and 1st metatarsal. Actions: Inversion & Dorsiflexion.
Which muscle is located on the posterior aspect of the scapula above the spine?
A) They are a group of muscles that lie superior to the hyoid bone and hero form the floor of the oral cavity. The supraspinatus is named for its location on the posterior aspect of the scapula above the spine.
How many times can a muscle change direction?
A) The muscle is able to change direction twice, three times , or four times faster than other muscles, respectively.