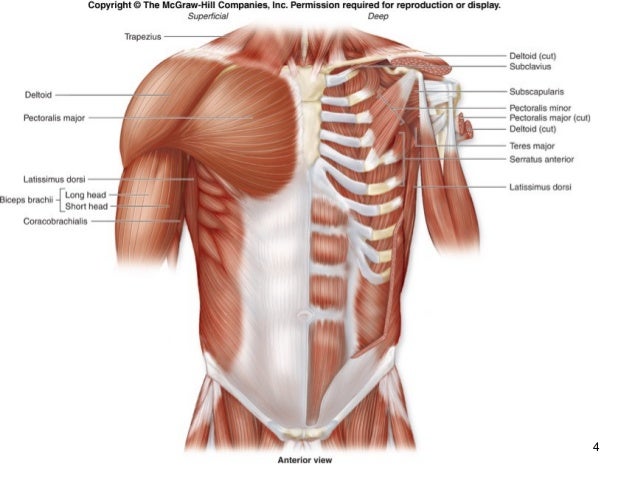
Four muscles are attached to the medial third of the clavicle:
- The sternocleidomastoid muscle, where the muscular clavicular head of the muscle is attached to the superior surface of the bone.
- The pectoralis major muscle, which is attached to the anterior surface of the bone.
- The subclavius muscle, which is attached to a groove found in the middle of the bone’s inferior surface. ...
- The sternohyoid muscle, which attaches to the medial end of clavicle.
What causes sharp pain under right clavicle?
What causes collarbone pain?
- Shoulder strain. ...
- Rotator cuff tendinitis. ...
- Biceps tendonitis. ...
- Acromioclavicular (ac) shoulder joint injury. ...
- Repetitive strain injury of the shoulder ("swimmer's shoulder") Repetitive strain injury of the shoulder is caused by consistent repetitive use.
- Myofascial pain syndrome. ...
- Recurrent shoulder dislocation. ...
What causes a hard lump on a clavicle?
Lump on collarbone Causes:
- Collarbone fracture: Fracture is a break in the bone. ...
- Lymph node enlargement: Lymph nodes are part of our lymphatic system. ...
- Ganglion Cyst: A cyst is a sac-like structure containing fluid. ...
- Aneurysmal bone cyst: An aneurysmal bone cyst is a benign tumour. ...
- Lipoma: A lipoma is a benign lump which is filled with fat tissue or adipose tissue. ...
What muscle pulls the scapula medially?
adducts, extends, and medially rotates…. Trapezius (Action) Rhomboid Major/Rhomboid Minor (Action) Levator Scapulae (Action) Teres Major/Latissimus Dorsi (Action) elevates, retracts and rotates scapula. Trapezius (Action) elevates and adducts scapula; rotates s….
What muscle is under the collar bone?
The subclavius muscle lies directly under the collarbone and the pectoralis major. This makes it a little tricky to feel. But if you bring your arm close to your body and rotate the shoulder inwards, you may be able to feel it with your fingers underneath your collarbone. If not, do not get upset or stress yourself.
What muscles attach on the clavicle?
The clavicle is an S-shaped bone that is anchored by strong ligamentous attachments on both its medial and lateral ends. Muscular attachments to the clavicle include the sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major, and subclavius muscles proximally and the deltoid and trapezius muscles distally.
What is the origin of the clavicle?
The clavicle first appears as part of the skeleton in primitive bony fish, where it is associated with the pectoral fin; they also have a bone called the cleithrum.
What muscle is on top of the clavicle?
The deltoid looks like an upside-down triangle. Tendons connect each of the three side to bones. The base of the deltoids connects to the upper part of your scapula (shoulder blade) and the side of your clavicle (collarbone).
How many muscles are attached to the clavicle?
Muscle attachments A total of six muscles are attached to the clavicle, found distributed at either the lateral third or medial two thirds of the bone. Two muscles are attached to the lateral third of the clavicle: The trapezius muscle, which is attached along the posterior surface of the bone.
Which muscle is inferior to the clavicle and stabilizes and depresses the clavicle?
The subclavius muscle is a small muscle that lies deep to pectoralis major muscle. It passes from rib I at the junction between the rib and its costal cartilage to a groove on the inferior (lower) surface of the clavicle.
What runs over the clavicle?
The supraclavicular nerve is a superficial sensory nerve that crosses the clavicle and provides sensation over the clavicle, anteromedial shoulder, and proximal chest [5, 8].
What muscles are affected by a clavicle fracture?
The muscles involved in clavicle fractures include the deltoid, trapezius, subclavius, sternocleidomastoid, and sternohyoid. The ligaments involved include the conoid ligament and trapezoid ligament.
Can you pull a muscle near your collarbone?
Pain in the collarbone is also commonly caused by muscular injury to your shoulder. Your shoulder contains a number of muscles and tendons that can be strained or torn from overuse or trauma. It is often difficult to describe this pain other than "shoulder pain".
Where is the clavicle found?
shoulderclavicle, also called collarbone, curved anterior bone of the shoulder (pectoral) girdle in vertebrates; it functions as a strut to support the shoulder.
What are the parts of the clavicle?
Structure. The clavicle joins the scapula, or shoulder blade, and sternum to form two joints on either end of the bone, which are: Acromioclavicular (AC) joint: The acromioclavicular joint forms between the acromion of the scapula and clavicle at the top of the shoulder, held together by the acromioclavicular ligament.
Where is the clavicle located?
The clavicle is the bone that connects the breastplate (sternum) to the shoulder. It is a very solid bone that has a slight S-shape and can be easily seen in many people. It connects to the sternum at a joint with cartilage called the sternoclavicular joint.
What classification of bone is the clavicle?
In human anatomy, the clavicle or collar bone is classified as a long bone that makes up part of the shoulder girdle (pectoral girdle).
What joint is the clavicle?
The clavicle joins the scapula, or shoulder blade, and sternum to form two joints on either end of the bone, which are: 1. Acromioclavicular (AC) joint: The acromioclavicular joint forms between the acromion of the scapula and clavicle at the top of the shoulder, held together by the acromioclavicular ligament.
Where is the clavicle located?
The clavicle, also referred to as the collar bone, is an elongated, S-shaped bone that sits between the shoulder and sternum at the top of the ribcage. It provides structural support between the shoulder and the rest of the skeleton, and is one of the most frequently fractured bones in the body.
How long do you need to wear a sling for a clavicle fracture?
For a clavicle fracture, you may need to wear a shoulder sling for six to eight weeks until the bone heals. 3. Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help rehabilitate ...
What is the function of the clavicle?
Function. The clavicle connects the shoulder to the rest of the skeleton. Its positioning allows for increased range of motion of the shoulder away from the body and helps protect the arm by dispersing force transmitted through direct contact. 2 .
Why does osteolysis occur at the end of the clavicle?
Osteolysis, or bone degeneration, can easily occur at the end of the clavicle due to the high degree of stress and repetitive forces placed through the small surface area of the acromioclavicular joint, especially with heavy lifting such as bench press or military press.
What is the most common fracture of the clavicle?
The relative size of the clavicle leaves it particularly susceptible to fracture. Fracture of the clavicle can occur from a fall landing on an outstretched hand or through a direct blow to the shoulder. The middle third of the clavicle is most commonly fractured, accounting for about 80% of all cases of clavicle fractures. 2
How to heal clavicle?
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help rehabilitate the structures surrounding the clavicle after injury to decrease pain, restore range of motion and proper joint mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the shoulders and shoulder blades.
What are the stabilizers of the clavicle?
Static stabilizers of the clavicle include medially, the anterior and posterior sternoclavicular ligaments, the costoclavicular ligament, and the interclavicular ligament ( Gray, 1918; Netter, 1987; Jurik and Soerensen, 2007; Warth et al., 2014 ). The anterior and posterior sternoclavicular ligaments are reinforcing the fibrous capsule around the sternoclavicular joint ( Jurik and Soerensen, 2007; Warth et al., 2014 ). The costoclavicular ligament is located under the medial third of the clavicle and extends to the contiguous costal cartilage and first rib ( Jurik and Soerensen, 2007; Warth et al., 2014 ). This ligament prevents anterior, posterior, and medial translation of the medial clavicle and might be the most important medial static stabilizer ( Jurik and Soerensen, 2007; Tubbs et al., 2009; Warth et al., 2014 ). The interclavicular ligament links both clavicles and is located between both sternoclavicular joints, adjacent to the superior sternal manubrium ( Warth et al., 2014 ). The sternoclavicular joint is also cushioned by an articular disk, which, although debated, possibly acts as a check-rein preventing medial translation of the medial clavicle ( Gray, 1918; Netter, 1987; Jurik and Soerensen, 2007 ). The primary function of the disk is thought to increase joint congruity and shock absorption ( Depalma, 1963; Emura et al., 2009; Warth et al., 2014 ). It is suggested that the disks are incomplete in up to 56% of the population and that incomplete disks are associated with progressive cartilage degeneration of the clavicular side of the joint ( van Tongel et al., 2012 ). Distally, the acromioclavicular joint is stabilized by the superior and inferior acromioclavicular ligaments and the coracoclavicular ligaments (conoid and trapezoid) ( Netter, 1987; Keener, 2014 ). The acromioclavicular ligaments are thin and provide anterior–posterior and vertical stability under small loads ( Fukuda et al., 1986; Keener, 2014 ). The conoid and trapezoid ligaments are located and originate from under the distal end of the clavicle and insert on the coracoid ( Netter, 1987; Banerjee et al., 2011 ). They provide vertical stability of the distal clavicle and are the main stabilizers to large loads across the acromioclavicular joint ( Banerjee et al., 2011; Keener, 2014 ). Furthermore, superior translation of the distal clavicle is impossible without disruption of the coracoclavicular ligaments ( Keener, 2014 ).
How much elevation does the clavicle have?
For every 10° of arm elevation, the clavicle elevates 4° (Ring and Jupiter, 2009 ). The elevation occurs between 30° and 90° of arm elevation, and rotation occurs after 70–80°. However, a poorly functioning SCJ does not entirely limit function. Fusion of the SCJ limits abduction to 90° ( Jobe et al., 2009; Ring and Jupiter, 2009 ).
What is the clavicle of a rat?
The clavicle of the rat is a very small bone, connected by synovial joints to the manubrium of the sternum, and the acromion of the scapula. In many mammals, particularly those that use their forelimbs only for running, and not for manipulation of objects, the clavicle is reduced or lost.
Why is the clavicle variable size?
This bone has a variable size in different species of mammals in accordance with the type of locomotion and coordinated movements made by the thoracic limbs. For example, in mammals that dig, climb or fly, the clavicle can be very long, whereas it is reduced in animals that lean on the thoracic limbs to walk.
Which end of the clavicle is flatter and wider than the sternal end?
The acromial end of the clavicle is flatter and wider than the sternal end. On its lateral surface is the acromial facet, for articulation with the acromial process of the scapula.
Which end of the clavicle is flatter?
b. The acromial end of the clavicle is flatter and wider than the sternal end.
How many bones are in the carpus?
The carpus is formed by two rows of bones ( Fig. 2-36 ). There is a proximal row of three bones, the intermedioradial carpal bone (formed by to the fusion of the intermediate with the radius carpal bones), the ulnar carpal and the accessory carpal bones.
What is the anatomy of the clavicle?
Clavicle Anatomy. January 9, 2021 | By : OrthoFixar | Anatomy. | Last updated on April 28, 2021. Clavicle anatomy consist s of medial end, middle and lateral end. There are many ligaments and muscle connecting to these parts of clavicle. Clavicle bone is the First bone in the body to ossify (at 5 weeks’ gestation) and last to fuse ...
Which bone articulates with the clavicle?
Laterally the clavicle articulates with the acromion bone.
What is the coracoclavicular ligament?
The coracoclavicular ligaments are stout ligaments that arise from the base of the coracoid:#N#The trapezoid (more lateral): inserts onto the small osseous ridge of the inferior clavicle.#N#Conoid (more medial): inserts onto the clavicular conoid tubercle.
Where does the pectoralis originate?
Medially: the pectoralis major muscle originates from the clavicular shaft anteroinferiorly , and the sternocleidomastoid originates superiorly. Laterally: the pectoralis origin merges with the origin of the anterior deltoid, while the trapezius insertion blends superiorly with the deltoid origin at the lateral margin.
Which capsule secures the clavicle to the sternum?
Medially the clavicle is secured to the sternum by the sternoclavicular capsule.
What is the role of the integrity of the clavicle?
Their integrity, or lack thereof, plays an important role in the decision making and fixation selection in the treatment of displaced lateral third clavicle fractures.
What is the soft tissue constraint to anterior or posterior translation of the medial clavicle?
The thickening of the posterior capsule has been determined to be the single most important soft tissue constraint to anterior or posterior translation of the medial clavicle. There is also an interclavicular ligament which runs from the medial end of one clavicle, gains purchase from the superior aspect of the sternum at the sternal notch, ...
Where is the clavicle located?
The clavicle is located at the top of the thoracic wall, just below the neck and to the sides of the sternum. It lies just above the first rib on either side of the anterior chest wall. The inner part of the clavicle is bound by the costoclavicular ligament to the first rib so that it does not elevate with the kineticism of the shoulder blade.
What is the clavicle?
Clavicle Anatomy : Muscle Attachment & Collarbone Fracture. The clavicle, or collarbone, a long bone with a shaft and two ends, it can be easily palpated, and it is one of the most ordinarily fractured bones in the body. The two clavicles, on either side of the anterior base of the neck, are horizontal, S-curved that articulate laterally articulate ...
What is the most common cause of pain in the collarbone?
Clavicle or commonly known as collarbone fractures are by far the most common cause of collarbone pain, and the most common bone to break accounting for about 5 percent of all adult fractures. Most commonly a fall onto the shoulder or on an outstretched arm or less often a direct blow to the collarbone or an RTA.
What is the lateral end of the clavicle?
Lateral End: The lateral end of the clavicle is flat, attaches to the scapula and is known as the acromial end. It then ends by joining with the acromion of the scapula to form the acromioclavicular joint or SC joints.
How long does it take for a clavicle fracture to heal?
The collarbone usually heals in 3-6 weeks in children, 6-12 weeks in adults.
What holds the clavicle in place?
Strong ligaments hold the clavicle in place at either end. The shaft of the clavicle gives attachment to the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck.
Which end of the clavicle attaches to the sternum?
Medial End: The medial end of the clavicle that attaches to the sternum is known as the sternal end. This end is roughly triangular in shape and forms a joint known as the sternoclavicular joint or SC joints.
What muscle attaches to the clavicle?
Several muscles attach to the clavicle along its length. The platysma is a thin broad muscle that originates in the subcutaneous tissue around the clavicle and attaches to the base of the mandible and angle of mouth. It is superficial to the cervical fascia. Although the platysma does not originate or attach on the clavicle, it must be divided when surgically approaching the middle one-third of the clavicle, such as during open reduction and internal fixation using a plate and screws construct. The superior surface of the clavicle is smooth and subcutaneous. The clavicular head of the pectoralis major muscle originates anteriorly on the medial two-thirds. Posterior to the pectoralis major, the clavicular head of the sternocleidomastoid originates at the middle one-third of the clavicle. Toward the lateral end of the clavicle, the origin of the deltoid muscle spans the whole anterior surface from superior to the inferior.
Which muscle attaches to the lateral end of the clavicle?
The only muscle that inserts on the superior surface of the clavicle is the upper portion of the trapezius muscle, which attaches posteriorly at the lateral end of the clavicle.
What is the anterior curve of the clavicle?
The anterior curve of the medial two-thirds of the clavicle provides a rigid arch under which the great vessels emerge as they exit the mediastinum toward the axilla. The subclavian and axillary vessels, the brachial plexus, and the lung are all located immediately posterior to the medial third of the clavicle. Hence the clavicle also functions as a bony protector of the neurovascular structures at the thoracic outlet .
Where do the supraclavicular nerves come from?
The supraclavicular nerves emerge from C3 and C4 nerve roots of the cervical plexus and divide more distally into medial, intermediate, and lateral rami . Havet et al. [ 13] conducted a cadaveric study on the anatomy of the supraclavicular nerves describing the path of the intermediate and lateral rami from a common trunk behind the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid. The intermediate ramus courses below platysma and divides into two or three terminal branches. The lateral ramus courses in a frontal plane toward the acromion process crossing the anterior belly of the trapezius. This ramus is probably the nerve that supplies the acromioclavicular joint as reported by Ebraheim et al. [ 14 ]. In about 6–10% of cases, the shaft of the clavicle has an accessory osseous canal, called the canalis nervi supraclavicularis, which allow a ramus of the medial supraclavicular nerve to traverse to the chest [ 15 ].
How much fluid is absorbed by the acromioclavicular joint?
Ultrasound image displaying the width and depth of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. The AC joint was found to absorb around 1 mL of fluid upon repeated injections under ultrasound guidance. (Borrowed from Edelson G, Saffuri H, Obid E, Lipovsky E, Ben-David D. Successful injection of the acromioclavicular joint with use of ultrasound: anatomy, technique, and follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 23 (10): e243–250, 2014)
Which clavicle is wider?
The left clavicle is wider and longer than the right one at most intervals [ 7 ]. The cortex of the clavicle is thinnest on the dorsal side at the acromial end and on the ventral side of the sternal end [ 2 ].
How long is the clavicle?
The average length of the clavicle is around 15 cm, but this varies according to laterality, gender, ethnicity, and body height [ 6 ]. Overall, the clavicle is longer, wider, and thicker in men [ 7 ]. Mathieu et al. [ 8] defined the hourglass morphology of the clavicle using anatomical and two-dimensional CT (computed tomography) study.
What is the Clavicle Bone
Clavicle, commonly known as collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped, modified long bone located at the base of the neck. It is the only long bone of the body that lies horizontally.
Where is the Clavicle Located
As stated, clavicle is located at the base of the neck and across the upper part of the ribcage. It sits between the shoulder blade ( scapula) and breastbone ( sternum ), connecting the pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle to the axial skeleton. Clavicle is the only bone that connects the axial skeleton to the appendicular skeleton.
Anatomy – Parts of the Clavicle Along With its Bony Landmarks
Being a long bone, clavicle has two ends, sternal and acromial end. The region in between the two ends is known as shaft.
Articulations
Sternoclavicular Joint: It is a synovial joint that is formed between the sternal end of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum.
Muscle Attachments
There is a total of six muscles that are attached to the clavicle. Out of these six, four muscles are attached to the sternal end or medial two-third of the clavicle, whereas two muscles are attached to the acromial end or lateral third of the clavicle.
Left and Right Clavicle – How to Identify
Here’s a quick way to distinguish between the left and right clavicle.
Which muscle is the shaft of the clavicle?
The shaft of the clavicle acts a point of origin and attachment for several muscles - deltoid, trapezius, subclavius, pectoralis major, sternocleidomastoid and sternohyoid. Acromial (lateral) End. The acromial end houses a small facet for articulation with the acromion of the scapula at the acromioclavicular joint .
What muscle pulls the lateral end of the clavicle?
The medial end is pulled superiorly by the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
What is the management of a clavicle fracture?
Management of a clavicular fracture can be conservative (e.g. sling immobilisation) or operative (e.g. open reduction and internal fixation). The supraclavicular nerves lie in close proximity to the clavicle and are occasionally sacrificed during a surgical repair - resulting in a numb patch over the upper chest and shoulder.
What is the attachment point of the conoid ligament?
Conoid tubercle – attachment point of the conoid ligament, the medial part of the coracoclavicular ligament.
What is the clavicle?
The clavicle is a slender bone with an ‘S’ shape. Facing forward, the medial aspect is convex, and the lateral aspect concave. It can be divided into a sternal end, a shaft and an acromial end.
Which ligament is the attachment point of the trapezoid line?
Trapezoid line – attachment point of the trapezoid ligament, the lateral part of the coracoclavicular ligament.
Where is the clavicle located?
Log In. The clavicle (collarbone) extends between the manubrium of the sternum and the acromion of the scapula. It is classed as a long bone and can be palpated along its length. In thin individuals, it is visible under the skin. The clavicle has three main functions:
What is the name of the muscle that stretches the clavicle?
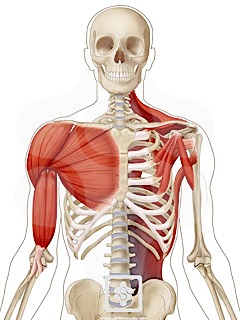
Deltoid muscle. The deltoid is a thick, triangular shoulder muscle. It gets its name because of its similar shape to the Greek letter ‘delta’ (Δ). The muscle has a wide origin spanning the clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula.
Where does the clavicular originate?
The clavicular (anterior) part originates from the superior surface and the anterior border of the lateral third of clavicle.
What are the parts of the deltoid?
The deltoid is formed of acromial, clavicular and scapular spinal parts . Acromial part (middle fibres) abducts the arm, while the clavicular and scapular spinal parts play a significant role in stabilization, ensuring a steady plane of abduction.
Why does my shoulder look flat?
In addition, the axillary nerve can also be damaged during dislocation of the glenohumeral joint or it can be compressed during incorrect use of crutches. Symptoms may include atrophy of the deltoid muscle, resulting in weakness and a loss of muscle tone, making the shoulder look flattened rather than rounded.
How many degrees of abduction do you need for the deltoid nerve?
To properly test the function of the deltoid and the axillary nerve, the arm must be beyond 15 degrees of abduction. Once the arm is in this position, the patient then pushes against resistance. If the muscle is functioning properly, contraction of the muscle should be felt near the acromion of the scapula.
Why is it important to test the function of the deltoid muscle?
Muscle testing. It is incredibly important to properly test the function of the deltoid muscle to accurately determine muscular or nervous injury. An inability to abduct the arm from a position in which the arm is resting at the side of the body does not indicate an injury to the deltoid muscle or the axillary nerve.
How did the scapula get its name?
It gets its name because of its similar shape to the Greek letter ‘delta’ (Δ). The muscle has a wide origin spanning the clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula. It passes inferiorly surrounding the glenohumeral joint on all sides and inserts onto the humerus .