
Is a pulse rate of 120 bad?
120 bpm resting pulse. Is a 120 pulse rate too high? A heart rate of 120 beats per minute (or 20 beats every 10 seconds) is higher than the range considered normal for adults and children over ten. 3 It is normal for children under ten to have pulses over 100. Consult the table below to determine if a 120 is normal for your child's age.
What is a dangerously low pulse rate?
The normal resting heart rate for the average person is 70–100 beats per minute, some literature points to 60–100. Anything below 60 or 70 beats per minute is considered bradycardia (slow heart rate). Besides heart disease or some othe.Doctors consider a heart rate below 60 beats per minute as low, Dr. Baez-Escudero says.
What regulates heart rate?
Heart rate is controlled by the two branches of the autonomic (involuntary) nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) releases the hormones (catecholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine) to accelerate the heart rate. Click to see full answer.
How do you treat a fast heartbeat?
This article suggests the following ways to decrease your heart rate to normal levels:
- Exercise more: daily physical activity slows your resting heartbeat.
- Reduce stress: performing yoga, daily breathing techniques, and meditation are the perfect methods to help you deal with a racing heart.
- Avoid tobacco products: smokers have higher resting heart rates. ...
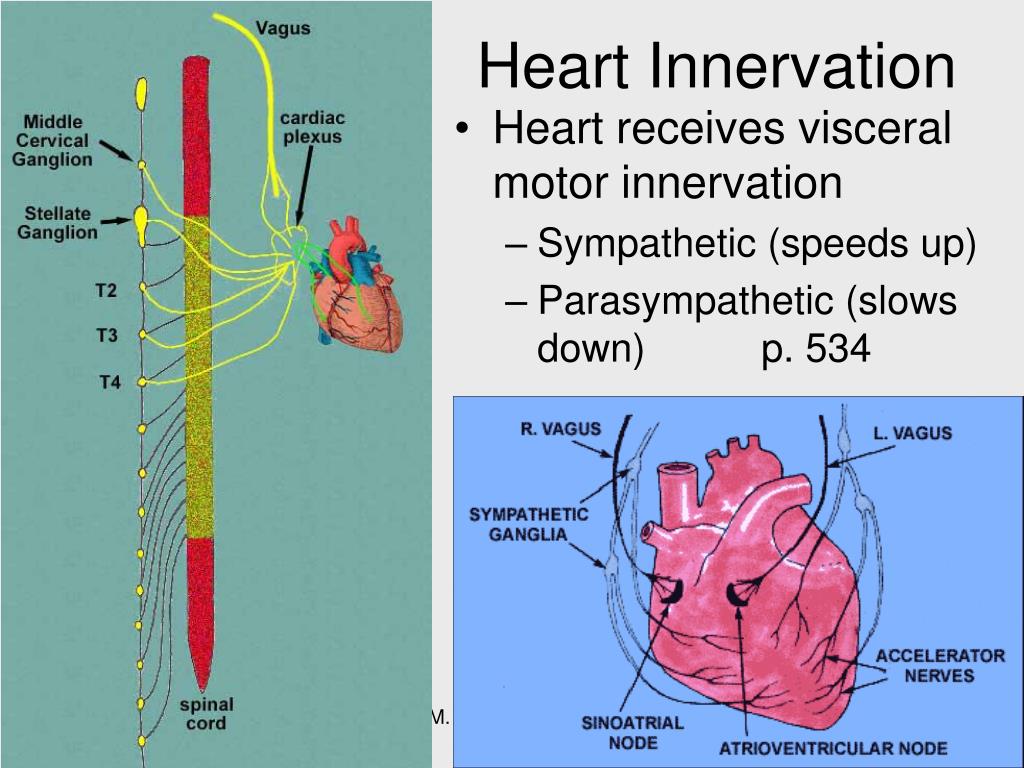
What nerve goes to the heart?
Both the right and left vagus nerves descend from the brain in the carotid sheath, lateral to the carotid artery. The nerve runs from the lower brain stem through the base of the skull to travel in the neck with the carotid artery and jugular vein. It then penetrates the chest to travel to the heart and lungs.
What does vagus nerve do to heart?
Parasympathetic control of the heart via the vagus nerve is the primary mechanism that regulates beat-to-beat control of heart rate. Additionally, the vagus nerve exerts significant effects at the AV node, as well as effects on both atrial and ventricular myocardium.
Is the heart connected to nerves?
One part of the autonomic nervous system is a pair of nerves called the vagus nerves, which run up either side of the neck. These nerves connect the brain with some of our internal organs, including the heart.
What are the 3 cardiac nerves?
They include: Superior cardiac nerve (nervus cardiacus cervicalis superior) Middle cardiac nerve (nervus cardiacus cervicalis medius) Inferior cardiac nerve (nervus cardiacus inferior)
How do I know if my vagus nerve is damaged?
What are the signs of vagus nerve problems?Abdominal pain and bloating.Acid reflux (gastroesophageal reflux disease, GERD).Changes to heart rate, blood pressure or blood sugar.Difficulty swallowing or loss of gag reflex.Dizziness or fainting.Hoarseness, wheezing or loss of voice.More items...•
What aggravates the vagus nerve?
Disruption of vagus nerve function can be caused by excessive stress, disease, certain medications, inflammation, and infections, among other things—and when disrupted, the body has an overall more difficult time relaxing and attending to its primary functions including sleeping, breathing, digestion, and movement of ...
Can the vagus nerve stop your heart?
A vagal maneuver is an action you take when you need to stop an abnormally fast heart rate. The word “vagal” refers to the vagus nerve. It's a long nerve that runs from the brain down through the chest and into the abdomen. The vagus nerve has several functions, including slowing the heart rate.
What does the vagus nerve do?
Overview over the basic anatomy and functions of the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is responsible for the regulation of internal organ functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate, as well as vasomotor activity, and certain reflex actions, such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting (17).
Which cranial nerve controls the heart muscle?
VagusSo, the correct answer is 'Vagus'
Where is your vagus nerve?
The vagus nerve runs from the brain through the face and thorax to the abdomen. Exits the brain from the medulla oblongata of the brainstem and travels laterally exiting the skull through the jugular foramen.
How many nerves are in the heart?
Recent findings: Dr. Armour, in 1991, discovered that the heart has its "little brain" or "intrinsic cardiac nervous system." This "heart brain" is composed of approximately 40,000 neurons that are alike neurons in the brain, meaning that the heart has its own nervous system.
What part of the spine controls the heart?
Thoracic (mid back) - the main function of the thoracic spine is to hold the rib cage and protect the heart and lungs. The twelve thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1 to T12.
What problems can the vagus nerve cause?
Vagal nerve dysfunction can cause both slow and fast heart rates depending on the type of dysfunction. For example, overactivity can lead to bradycardia (or slow heart rate) while disease causing insufficient activity of the vagus nerve can lead to tachycardia (fast heart rate).
How does the vagus nerve affect blood pressure?
Decreasing inflammation: The vagus nerve sends an anti-inflammatory signal to other parts of the body. Lowering the heart rate and blood pressure: If the vagus nerve is overactive, it can lead to the heart being unable to pump enough blood around the body.
Can vagus nerve cause irregular heartbeat?
Atrial fibrillation: Sympathetic nerve excitability can shorten the atrial refractory period, while vagus nerve excitation makes the atrial refractory period irregular, leading to paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
What is the main function of the vagus nerve?
The vagus nerve is responsible for the regulation of internal organ functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate, as well as vasomotor activity, and certain reflex actions, such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting (17).
What is the function of the heart's electrical system?
Your Heart’s Nerve Conduction. Your heart’s electrical system allow your heart to pump blood efficiently throughout your body. For each heart beat, the contraction of the heart muscle is initiated by electrical signals to the heart muscle:
How does the heart work?
Every single heart beat requires an electrical impulse to initiat e it.The heart contains special tissue that produces and sends electrical impulses to the heart muscle. It is these impulses that trigger the heart to contract. Each time the heart beats, it sends out an electric-like signal. The heart’s electrical signals can be measured with an EKG.
Which nerve is responsible for maintaining balance in the heart?from teachmephysiology.com
Parasympathetic. The parasympathetic input into the heart is via the vagus nerve (CN X). The vagus nerve forms synapses with postganglionic cells in SAN and AVN (atrioventricular node).
Which nerve is responsible for parasympathetic input into the heart?from teachmephysiology.com
The parasympathetic input into the heart is via the vagus nerve (CN X). The vagus nerve forms synapses with postganglionic cells in SAN and AVN (atrioventricular node). When stimulated, acetylcholine binds on to M₂ receptors, which act to decrease the slope of the pacemaker potential. This leads to a decrease in heart rate (a negative chronotropic effect).
What are the problems with conductance in the heart?from teachmephysiology.com
Narrow complex tachycardias include sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
What is the sympathetic input to the heart?from teachmephysiology.com
The sympathetic input into the heart is via the postganglionic fibres from the sympathetic trunk which innervate the SAN and AVN. The postganglionic fibres release noradrenaline, which acts on B₁ adrenoreceptors to increase the slope of the pacemaker potential. This increases the heart rate (a positive chronotropic effect), as well as the force of contraction (positive inotropic effect).
Which type of input is the sympathetic input?from teachmephysiology.com
The sympathetic input into the heart is via the postganglionic fibres from the sympathetic trunk which innervate the SAN and AVN. The postganglionic fibres release noradrenaline, which acts on B₁ adrenoreceptors to increase the slope of the pacemaker potential. This increases the heart rate (a positive chronotropic effect), as well as the force of contraction (positive inotropic effect).
What is tachycardia at rest?from teachmephysiology.com
Tachycardia is defined as a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate (over 100 beats per minute ). This can be normal in the case of exercise, however, tachycardia at rest is generally due to causes such as:
What is the normal heart rate for a SAN?from teachmephysiology.com
The parasympathetic input on the SAN dominates at rest, giving a normal resting heart rate of around 60bpm. A reduction in parasympathetic outflow results in an initial increase in heart rate, reaching over 100bmp. This is further brought about by an increase in sympathetic outflow.
Which nerve is responsible for sinus bradycardia?
The right vagus nerve supplies the sinus node, and its stimulation can produce sinus bradycardia. The left vagus nerve supplies the AV node, and its stimulation can produce a form of heart block. It is by producing transient heart block that the Valsalva maneuver can terminate many kinds of SVT. 4 .
Which nerve is responsible for the gag reflex?
The vagus nerve is responsible for the gag reflex (and the cough reflex when the ear canal is stimulated), slowing the heart rate, controlling sweating, regulating blood pressure, stimulating peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract, and controlling vascular tone.
What is the effect of vagus nerve stimulation?
Stimulating the vagus nerve can have therapeutic effects (such as stopping episodes of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) or hiccups 3 ), and can help doctors diagnose certain kinds of heart murmurs. Vagal stimulation can be achieved quite easily by employing the Valsalva maneuver .
Why is the vagus nerve important?
Because the vagus nerve has so many important functions, medical science has been interested for decades in the idea of employing vagus nerve stimulation, or vagus nerve blocking, in medical therapy. For decades, the vagotomy procedure (cutting the vagus nerve) was a mainstay of therapy for peptic ulcer disease, ...
What is the vagus nerve?
Anatomy. Function. Medical Therapy. The vagus nerve is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system and is one of the most important nerves in the body. The vagus nerve helps to regulate many critical aspects of human physiology, including the heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, digestion, and even speaking.
Where is the vagus nerve located?
The vagus nerve (also known as the 10th cranial nerve or CN X) is a very long nerve that originates in the brain stem and extends down through the neck and into the chest and abdomen. It carries both motor and sensory information, and it supplies innervation to the heart, major blood vessels, airways, lungs, esophagus, ...
How many vagus nerves are there?
While there are actually two vagus nerves (the left and the right), doctors usually refer to them together as “the vagus nerve.”
Which nerve is responsible for maintaining balance in the heart?
Parasympathetic. The parasympathetic input into the heart is via the vagus nerve (CN X). The vagus nerve forms synapses with postganglionic cells in SAN and AVN (atrioventricular node).
Which nerve is responsible for parasympathetic input into the heart?
The parasympathetic input into the heart is via the vagus nerve (CN X). The vagus nerve forms synapses with postganglionic cells in SAN and AVN (atrioventricular node). When stimulated, acetylcholine binds on to M₂ receptors, which act to decrease the slope of the pacemaker potential. This leads to a decrease in heart rate (a negative chronotropic effect).
What is the sympathetic input to the heart?
The sympathetic input into the heart is via the postganglionic fibres from the sympathetic trunk which innervate the SAN and AVN. The postganglionic fibres release noradrenaline, which acts on B₁ adrenoreceptors to increase the slope of the pacemaker potential. This increases the heart rate (a positive chronotropic effect), as well as the force of contraction (positive inotropic effect).
Which type of input is the sympathetic input?
The sympathetic input into the heart is via the postganglionic fibres from the sympathetic trunk which innervate the SAN and AVN. The postganglionic fibres release noradrenaline, which acts on B₁ adrenoreceptors to increase the slope of the pacemaker potential. This increases the heart rate (a positive chronotropic effect), as well as the force of contraction (positive inotropic effect).
What is tachycardia at rest?
Tachycardia is defined as a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate (over 100 beats per minute ). This can be normal in the case of exercise, however, tachycardia at rest is generally due to causes such as:
What is the normal heart rate for a SAN?
The parasympathetic input on the SAN dominates at rest, giving a normal resting heart rate of around 60bpm. A reduction in parasympathetic outflow results in an initial increase in heart rate, reaching over 100bmp. This is further brought about by an increase in sympathetic outflow.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for controlling many physiological functions. It induces the force of contraction of the heart and its heart rate. In addition, it controls the peripheral resistance of blood vessels. The ANS has both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions that work together to maintain balance.
How to feel your pulse?
Next, everyone feel for your pulse. Stick your hand out, thumbs up, feel for the knobby bone at the top of your wrist. Then, if you slide your hand down across the front of your wrist, you’ll feel these like strands of spaghetti—those are the tendons in your wrist.
Why should you feel your pulse speed up when you breathe in and slow down when you breathe out?
You should have felt your pulse speed up when you breathe in and slow down when you breathe out—that’s called heart rate variability, and it’s a very good thing. That’s a measure of the control our nerves have over our heart. This is the survival curve for people after a heart attack.
Why is heart rate important?from health.harvard.edu
Heart rate is important because the heart's function is so important. The heart circulates oxygen and nutrient-rich blood throughout the body. When it's not working properly, just about everything is affected. Heart rate is central to this process because the function of the heart (called "cardiac output") is directly related to heart rate ...
How to find your heart rate?from health.harvard.edu
Here's how to determine your heart rate. First, find your pulse. The side of the neck or front of the wrist are the easiest spots. Then, count the number of beats in 30 seconds. Double this number and that's your heart rate. In addition to calculating your heart rate, feeling your pulse can give you an idea of whether the rhythm is regular, ...
When should you worry about your heart rate?from health.harvard.edu
In the absence of symptoms (see below), that's not an indication of trouble. An abnormal rate or rhythm may be discovered during a physical exam, ECG, or other testing, even in healthy people who have no symptoms.
What is the best heart rate for atrial fibrillation?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Current guidelines define adequate rate control in atrial fibrillation as maintenance of the ventricular rate response between 60 and 80 beats/min at rest and between 90 and 115 beats/min during moderate exercise.3A consensus statement has suggested a target heart rate of <90 at rest and <180 bpm during exercise in patients with atrial fibrillation.4However, no controlled clinical trials have validated these target rates for preventing all‐cause cardiovascular morbidity or mortality, and such recommendations may be flawed. Few data exist that define the most robust method for the assessment of rate control.
What are the symptoms of a heart rate problem?from health.harvard.edu
fatigue. dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting or near-fainting. palpitations, or a pounding or fluttering sensation in the chest. feeling your heart racing. shortness of breath. chest pain or tightness. As you can see, some of these symptoms overlap, and many can be caused by things other than a heart rate problem.
What is considered a healthy heart rate?from health.harvard.edu
But some experts believe that an ideal resting heart rate is closer to 50 to 70. Regardless of what is considered normal, it's important to recognize that a healthy heart rate will vary depending on the situation. Here's how to determine your heart rate.
What causes a fast heart rate?from health.harvard.edu
using a stimulant, such as caffeine or cocaine. pregnant. Diseases associated with a fast heart rate include: most infections or just about any cause of fever. heart problems, for example cardiomyopathy (in which the pumping function of the heart is reduced), atrial fibrillation, or ventricular tachycardia.
Which nerve controls movement of muscles?from healthline.com
Other cranial nerves control the movement of various muscles and the function of certain glands. These are known as motor functions. While some cranial nerves have either sensory or motor functions, others have both. The vagus nerve is such a nerve. The cranial nerves are classified using Roman numerals based off of their location.
What nerve causes a sudden drop in heart rate?from healthline.com
The vagus nerve stimulates certain muscles in the heart that help to slow heart rate. When it overreacts, it can cause a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, resulting in fainting. This is known as vasovagal syncope.
What does the vagus nerve affect?from healthline.com
The vagus nerve also called the pneumogastric nerve, is responsible for various internal organ functions, including:
Why is the vagus nerve important?from verywellhealth.com
Because the vagus nerve has so many important functions, medical science has been interested for decades in the idea of employing vagus nerve stimulation, or vagus nerve blocking, in medical therapy. For decades, the vagotomy procedure (cutting the vagus nerve) was a mainstay of therapy for peptic ulcer disease, ...
What is a vagus nerve disorder?from healthhearty.com
Vagus Nerve Disorders. Vagus nerve disorders are the problems caused to the 10th cranial nerve. In this article, we will discuss the nerve damage symptoms and therapy, used for relieving this condition. Home / General Health / Vagus Nerve Disorders. Vagus nerve disorders are the problems caused to the 10th cranial nerve.
What is the vagus reflex?from verywellhealth.com
Sudden stimulation of a vagus nerve can produce what is called a " vasovagal reflex ," which consists of a sudden drop in blood pressure and a slowing of the heart rate . This reflex can be triggered by gastrointestinal illness or in response to pain, fright. or sudden stress. Some people are particularly prone to the vasovagal reflex, and their blood pressure and heart rate changes can cause loss of consciousness — a condition called " vasovagal syncope ." 2
What is the name of the nerve that overreacts to stress?from healthline.com
Vasovagal syncope. Sometimes the vagus nerve overreacts to certain stress triggers, such as: exposure to extreme heat. fear of bodily harm. the sight of blood or having blood drawn. straining, including trying to having a bowel movement. standing for a long time.
Which nerves control the diaphragm?from verywellhealth.com
The two phrenic nerves are the only nerves that control the diaphragm, and thus have a critical role in breathing. 1 They also have sensory and sympathetic functions and are well known for being responsible for the referred pain to the shoulder that can accompany abdominal disorders. Originating in the cervical spine (C3 to C5), ...
Which nerve receives input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal?from en.wikipedia.org
In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerves roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate ...
What nerves do not regenerate?from verywellhealth.com
Since nerves such as the phrenic nerve do not regenerate, complete disruption of the nerve will lead to permanent paralysis of the diaphragm.
What nerve causes hiccups?from verywellhealth.com
Hiccups. The phrenic nerve is responsible for the hiccup reflex. Stimulation by the nerve causes spasm of the diaphragm, and the sound that is heard occurs when the diaphragm contracts and pulls air against the closed larynx.
How long does it take for a phrenic nerve to heal?from verywellhealth.com
The prognosis of a phrenic nerve injury leading to paresis or paralysis of the diaphragm depends on the cause. 3 With some infectious or autoimmune conditions, or when the nerve is only injured and not destroyed such as with radiofrequency ablation, function may be restored in several months.
What nerves are causing pain in the right shoulder?from verywellhealth.com
Pain detected by the phrenic nerves is often felt in another region ( referred pain ). For example, irritation of the diaphragm (such as by carbon dioxide injected into the abdomen during laparoscopic surgery) may be felt as pain in the right shoulder.
What is the structure of the nervous system?from verywellhealth.com
Structure. Nerves such as the phrenic nerve are made up of axon fibers outside of the central nervous system, which convey information to and from the brain. Nervous tissue is one of the four types of tissue and is made up of neurons (nerve cells) and supporting cells called neuroglia.
Which nerve is responsible for vision?
The optic nerve is the sensory nerve that involves vision.
Which nerve controls the superior oblique muscle?
The trochlear nerve controls your superior oblique muscle. This is the muscle that’s responsible for downward, outward, and inward eye movements.
What are the functions of the cranial nerves?
Their functions are usually categorized as being either sensory or motor. Sensory nerves are involved with your senses, such as smell, hearing, and touch. Motor nerves control the movement and function of muscles or glands. Keep reading to learn more about each of the 12 cranial nerves and how they function.
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve?
The oculomotor nerve has two different motor functions: muscle function and pupil response. Muscle function. Your oculomotor nerve provides motor function to four of the six muscles around your eyes. These muscles help your eyes move and focus on objects.
How many cranial nerves are there?
What are cranial nerves? Your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. There are 12 of them, each named for their function or structure. Each nerve also has a corresponding Roman numeral between I and XII.
Which nerve is located in the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions?
The sensory root of your trigeminal nerve branches into the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions. The motor root of your trigeminal nerve passes below the sensory root and is only distributed into the mandibular division. VI. Abducens nerve.
Which nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter?
The olfactory nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter.
