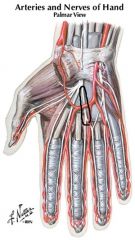
What is the innervation of the flexor pollicis brevis?
The two heads of the flexor pollicis brevis muscle differ in innervation. The superficial head receives its innervation via the recurrent branch of the median nerve (T1), while the deep head is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1). The blood supply for this muscle is derived from the radial artery.
What nerve innervates the thenar muscles?
The majority of the thenar muscles are innervated by the median nerve (T1). The exceptions are the deep head of flexor pollicis brevis and adductor pollicis muscle that receive their innervation via the ulnar nerve (C8, T1). The main function of the thenar muscles is to produce the movements of the thumb.
What nerve innervates the adductor pollicis?
The adductor pollicis muscle receives its innervation via the deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1). The blood supply for this muscle is provided by the deep palmar arch. As its name suggests, the prime function of adductor pollicis muscle is to produce strong adduction of the thumb at the first carpometacarpal joint.
What nerve innervates the lateral side of the thumb?
Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb. Action. Flexes thumb. Innervation. The flexor pollicis brevis is mostly innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve (C8, T1). The deep part is often innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve.

What nerve Innervates abductor pollicis brevis?
The median nerveThe median nerve supplies the abductor pollicis brevis (APB) muscle at the lateral border of the thenar eminence which abducts the thumb at right angles to the palm.
What nerve innervates the flexor pollicis longus?
the median nerveNerve. It is innervated by the median nerve via the anterior interosseous nerve (7th and 8th cervical nerve root).
What is the flexor pollicis brevis?
Flexor Pollicis Brevis(FPB) is present on the radial border of the palm. FPB is one of the muscle of the thenar eminence of the hand. It also falls under the intrinsic muscle of the hand. Flexor Pollicis Brevis is the small, narrow muscle consisting of the outer and inner portions.
What nerve controls thumb flexion?
The nerve starts at your armpit, but its functions all take place in your forearm or hand. The median nerve stimulates muscles in your forearm, allowing you to: Bend and straighten your wrists, thumbs and first three fingers. Rotate your forearm and hand to turn your palm downward.
Is flexor pollicis brevis is innervated by median nerve?
According to our studies with respect to the flexor pollicis brevis muscle, the superficial head receives innervation of the median nerve and the deep head receives innervation of the median and ulnar nerves (double innervation).
What supplies the flexor pollicis brevis?
Flexor pollicis brevis receives arterial supply from branches of the radial artery; superficial palmar artery, branches of the princeps pollicis artery and radialis indicis artery.
What causes flexor pollicis brevis pain?
Injuries to flexor pollicis brevis can include strain, tears, atrophy, infectious myositis, and overuse. Injury should be suspected when hand or thumb pain is present or if there is decreased flexion of the thumb.
Does flexor pollicis brevis pass through carpal tunnel?
The flexor carpi radialis tendon does not pass through the carpal tunnel. It is enveloped by an individual synovial sheath and passes through its own tubular compartment within the lateral aspect of the flexor retinaculum.
How do you palpate flexor pollicis brevis?
0:582:07So this thumb up motion is abduction versus bringing the thumb in towards the palm of the hand likeMoreSo this thumb up motion is abduction versus bringing the thumb in towards the palm of the hand like so it's going to be flexion.
What cranial nerve affects the thumb?
The median nerve is a major nerve of the upper limb as it innervates the major muscles that enable an individual to flex their wrist and fingers, and oppose their thumb.
Which nerve affects the tip of the thumb?
Median Nerve: The median nerve runs along the palm of the hand and thumb up to the tip. A common compression of the median nerve is known as carpal tunnel syndrome, as it gets squashed passing through a small tunnel on the wrist.
What nerve is responsible for thumb extension?
radial nerveExtensor pollicis longus muscleInsertionthumb, distal phalanxArteryposterior interosseous arteryNerveposterior interosseous nerve (branching from the radial nerve)Actionsextension of the thumb (metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal)10 more rows
What nerve innervates the abductor pollicis longus?
posterior interosseous nerveAbductor pollicis longus is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8), which is a continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve. The radial nerve is a branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
What is the flexor pollicis longus?
The flexor pollicis longus (FPL) muscle is one of the three deep flexors of the volar compartment of the forearm.
What nerve supplies the abductor pollicis longus?
Posterior Interosseous nerveNerve Supply It is supplied by the Posterior Interosseous nerve (C7-C8) which is a continuation of the deep branch of the Radial nerve.
What nerve root Innervates the thumb?
For example, the thumb is innervated by branches of the median nerve, which itself has fibers from the C6 nerve root.
Why is the Flexor Pollicis absent?
Flexor pollicis brevis can, rarely, be completely absent at birth due to a congenital issue (as can the other muscles of the thenar eminence ).
What is the FMA 37378?
FMA. 37378. Anatomical terms of muscle. The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
Where does the Flexor Pollicis Brevis get its blood supply?
The flexor pollicis brevis receives its blood supply from the superficial palmar branches of radial artery.
Where does the superficial head of a muscle come from?
The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum and the tubercle of the trapezium, the most lateral bone in the distal row of carpal bones. It passes along the radial side of the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus .
Where do the tendonous and sesamoid bones come from?
Both heads become tendinous and insert together into the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb; at the junction between the tendinous heads there is a sesamoid bone.
What is the abductor of the thumb?
The prime function of this muscle is the abduction of the thumb at the first carpometacarpal joint along with its long counterpart, the abductor pollicis longus muscle . Abductor pollicis brevis also takes part in the flexion and opposition of the thumb.
How does the flexor pollicis brevis differ from the superficial head?
The two heads of the flexor pollicis brevis muscle differ in innervation. The superficial head receives its innervation via the recurrent branch of the median nerve (T1), while the deep head is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1). The blood supply for this muscle is derived from the radial artery .
What are the four muscles in the thenar musculature?
The thenar musculature consists of four short muscles located on the lateral (radial) aspect of the hand . These muscles include the adductor pollicis , abductor pollicis brevis , flexor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis .
What is the function of the flexor pollicis brevis muscle?
The prime function of the flexor pollicis brevis muscle is to produce flexion of the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints. It also contributes to the medial rotation of the thumb. Start with the anatomy of the thenar muscles by exploring our videos, quizzes, labelled diagrams and articles.
What are the thenar muscles?
Key facts about the thenar muscles. Definition. Thenars are a group of four short muscles responsible for the movements of the thumb. Muscles. Adductor pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis. Innervation.
What is the name of the muscle that runs on the medial base of the proximal phalanx?
The adductor pollicis is a short and broad, fan-shaped muscle of the palm. It arises by the two muscular heads: oblique and transverse. The transverse head originates from the palmar base of metacarpal bone 3, while the oblique head arises from the capitate bone and palmar bases of metacarpal bones 2 and 3. From their origins, the muscle heads run laterally, converging into a single muscle belly that inserts onto the medial base of proximal phalanx 1.
What is the function of the thenar muscles?
The main function of the thenar muscles is to produce the movements of the thumb. More specifically, these muscles are responsible for the adduction, abduction and flexion of the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and carpometacarpal (CMC) joints. Their combined actions can produce the opposition of the thumb, ...

Overview
Innervation
The superficial head is usually innervated by the lateral terminal branch of the median nerve. The deep part is often innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1).
Origin and insertion
The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum and the tubercle of the trapezium, the most lateral bone in the distal row of carpal bones. It passes along the radial side of the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus.
The deeper (and medial) head "varies in size and may be absent." It arises from the trapezoid and capitate bones on the floor of the carpal tunnel, as well as the ligaments of the distal carpal row.
Blood supply
The flexor pollicis brevis receives its blood supply from the superficial palmar branches of radial artery.
Action
The flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint, as well as flexion and medial rotation of the 1st metacarpal bone at the carpometacarpal joint.
Pathology
Flexor pollicis brevis can, rarely, be completely absent at birth due to a congenital issue (as can the other muscles of the thenar eminence).