Deep Peroneal Nerve. This branch of the common peroneal nerve innervates the ankle extensor muscles, the ankle joint and the web space between the first and second toes. As it approaches the ankle, the nerve crosses the anterior tibial artery from a medial to lateral position.
What nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the leg?
The deep fibular nerve innervates the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg, including: Tibialis anterior Extensor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum longus Fibularis tertius
What nerve innervates the dorsum of the foot?
The deep fibular (peroneal) nerve runs through extensor digitorum longus and down the interosseous membrane. Then it crosses the tibia and gets in the dorsum of the foot. It innervates the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg and the dorsum of the foot.
What muscles does the deep fibular nerve innervate?
The deep fibular nerve provides several muscular and articular branches on its path through the anterior compartment of the leg. The muscular branches innervate the following muscles: tibialis anterior , extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus and fibularis tertius .
What nerve innervates the extensor digitorum brevis?
The deep fibular nerve also innervates the extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis, which are intrinsic muscles of the foot. These muscles are responsible for extending the toes at the metatarsophalangeal joints and interphalangeal joints.

What does the peroneal nerve innervate?
The common peroneal nerve, also known as the common fibular nerve, is a major nerve that innervates the lower extremity. As one of the two major branches off the sciatic nerve, it receives fibers from the posterior divisions of L4 through S2.
What nerve controls the ankle?
The branches of the common peroneal nerve innervate and control the muscles in the legs that lift the ankle and toes upward (dorsi flexion). Mild peroneal nerve injuries can cause numbness, tingling, pain and weakness.
What muscle does deep peroneal nerve innervate?
The deep peroneal nerve supplies the following muscles: Tibialis anterior. Extensor digitorum longus. Peroneus tertius.
What nerve Innervates the toe extensors?
After its bifurcation past the ankle joint, the lateral branch of the deep fibular nerve innervates the extensor digitorum brevis and the extensor hallucis brevis, while the medial branch goes on to provide cutaneous innervation to the webbing between the first and second toes.
What does the tibial nerve innervate?
The tibial nerve starts above the knee in the back of the leg. As it travels downward, it branches off to innervate muscles in the hamstrings. Continuing toward the heel, the sural nerve branches off, which innervates the calf. Once the tibial nerve reaches the foot, it passes through the tarsal tunnel.
What are symptoms of peroneal nerve damage?
SymptomsDecreased sensation, numbness, or tingling in the top of the foot or the outer part of the upper or lower leg.Foot that drops (unable to hold the foot up)"Slapping" gait (walking pattern in which each step makes a slapping noise)Toes drag while walking.Walking problems.Weakness of the ankles or feet.More items...
What Innervates peroneus longus?
superficial peroneal nerveThe superficial peroneal nerve supplies motor innervation to the following muscles: Peroneus longus muscle.
What does the femoral nerve innervate?
The femoral nerve is a mixed nerve of the lower limb that innervates the muscles and skin of the hip and thigh. The femoral nerve originates from the lumbar plexus, arising from the anterior rami of spinal nerves L2-L4.
What does the sciatic nerve innervate?
The undivided sciatic nerve innervates the 4 hamstring muscles and the short head of the biceps femoris muscle along the back of the thigh. The nerve also partially supplies the adductor magnus muscle along the inner front side of the thigh.
What nerve root Innervates the extensor hallucis longus?
The deep peroneal nerve innervates the extensor hallucis longus. The deep peroneal nerve is one of the terminal branches of the common peroneal nerve, which originates from the sciatic nerve—the sciatic nerve branches at the apex of the popliteal fossa into the tibial and common peroneal nerves.
What Innervates the extensor digitorum brevis?
On the electrophysiological basis, extensor digitorum brevis(EDB) muscle is innervated electrophysiologically not only by deep peroneal nerve(DPN) but also by accessory deep peroneal nerve(ADPN), an anomalous branch of superficial peroneal nerve, with a prevalence of 17-28%.
What nerve does ankle eversion?
Foot dorsiflexion and eversion (peroneal nerve)
What does nerve damage in ankle feel like?
Symptoms of foot and ankle neuropathy and nerve entrapment depend on the cause, but the most common symptoms include: Numbness. Sharp or burning pain. Tingling sensations or feeling that your foot has fallen “asleep”
How do you release a trapped nerve in your ankle?
Home remediesRest up. Try to avoid any movements or activities that aggravate the pinched nerve.Adjust your footwear. Make sure your shoes fit well and provide support. ... Apply ice. ... Try massage. ... Use a brace. ... Take over-the-counter (OTC) medications.
Does peripheral neuropathy affect your ankles?
Peripheral neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that typically affects the feet and legs and sometimes affects the hands and arms. This type of neuropathy is very common.
What does saphenous nerve pain feel like?
Saphenous Nerve entrapment is described as pain on the inside of the thigh, knee, or calf. The pain is described as dull and achy pain and it may have a burning or electric type feel. Pressure on the inside of the knees will aggravate sensations such as having something resting on the persons lap.
Which nerve innervates the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg?
The deep fibular nerve innervates the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg, including: These muscles are responsible for dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle joint. During the gait cycle for walking, dorsiflexion is required: When a person strikes their heel on the floor in the stance phase.
Which nerve is responsible for extending the toes at the metatarsophalangeal joints and interpha
These muscles are responsible for extending the toes at the metatarsophalangeal joints and interphalangeal joints. Sensory Functions. The deep fibular nerve terminates in the dorsum of the foot as a cutaneous nerve. This innervates the webbed space of skin between the great toe (hallux) and the second toe.
What causes the deep fibular nerve to become entrapped?
This causes paralysis of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg, and so a patient loses the ability to dorsiflex the foot.
Why is the deep fibular nerve compressed?
There are two main reasons why the deep fibular nerve could be compressed. The first is that the anterior leg muscles have been excessively used and so are compressing the nerve within the anterior compartment. The patient will experience pain in the anterior leg.
What is the function of the nerve roots?
Motor function: Innervates the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg, as well as some of the intrinsic muscles of the foot. Sensory function: Supplies the triangular region of skin between the 1st and 2nd toes.
What is the deep peroneal nerve?
The deep fibular nerve (deep peroneal nerve) is a nerve of the leg. It is one of the terminal branches of the common fibular nerve. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the deep fibular nerve – its anatomical course, motor and sensory functions, and any clinical relevance.
Which nerve descends first, the tibialis anterior or the extensor hallucis longus
During its descent, the deep fibular nerve is initially lateral, then anterior and finally medial to the anterior tibial artery.
What nerve terminates around the ankle joint?
This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve. Key facts about the nervus peroneus (perone alis) fibularis. Origin. Nervus fibularis communis (L4-S2)
Which nerve innervates the articular and muscular muscles?
Branches and innervation. The deep fibular nerve provides several muscular and articular branches on its path through the anterior compartment of the leg. The muscular branches innervate the following muscles: tibialis anterior , extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus and fibularis tertius . The articular branches innervate the ...
Which nerve supplies the extensor hallucis brevis?
In addition, the media l branch of the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve gives an articular branch to the first metatarsophalangeal joint . The lateral terminal branch runs deep to the extensor digitorum brevis muscle as it crosses the ankle joint. It supplies the extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis muscles, ...
Where is the deep fibular nerve located?
The deep fibular nerve is located in the anterior compartment of the leg .
Which nerve terminates with a bifurcation between the fibula and the proximal part of
The common fibular nerve terminates with a bifurcation between the fibula and the proximal part of fibularis longus , providing two terminal branches: the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve and the superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve. .
Where does the nerve go in the foot?
Just proximal to the ankle joint, the nerve is again positioned lateral to the artery and together, they enter the dorsum of the foot deep to the extensor retinaculum.
What causes a deep fibular nerve to swell?
This syndrome is caused by bleeding or swelling within an enclosed bundle of muscles – known as a muscle compartment. The muscle compartment does not have the ability to increase its size and volume capacity due to surrounding tough fascia. Thus, any major swelling leads to the compression of the neurovascular structures that run through the compartment.
Which nerve innervates the i ntrinsic muscles of the foot?
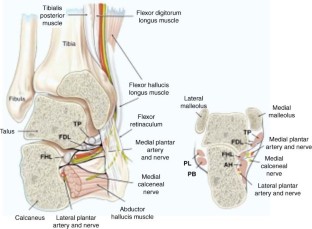
The medial and lateral plantar branches of the tibial nerve provide innervation to all the i ntrinsic muscles of the foot (exept the extensor digitorum brevis, which is innervated by the deep fibular nerve). Sensory Functions. In the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve gives off cutaneous branches.
What nerve is responsible for innervating the sole of the foot?
Within this tunnel, branches arise from the tibial nerve to supply cutaneous innervation to the heel. Immediately distal to the tarsal tunnel, the tibial nerve terminates by dividing into sensory branches, which innervate the sole of the foot.
What is the cause of tibial nerve damage?
Damage to the tibial nerve is rare, and is often a result of direct trauma, entrapment through narrow space or compression for long period of time. Damage results in loss of plantar flexion, loss of flexion of toes and weakened inversion (The tibialis anterior can still invert the foot).
What is the tibial nerve?
Tibial Nerve. The tibial nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the lower limb. It has several cutaneous and motor functions in the leg and foot. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the tibial nerve – its anatomical course, functions and clinical correlations.
Which nerve innervates the posterior leg?
The tibial nerve innervates the muscles of the posterior leg and the majority of the intrinsic foot muscles. Posterior Compartment of the Leg. The muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg are organised into a superficial and deep compartment. They are all innervated by the tibial nerve.
Which nerve gives rise to the sural nerve?
It travels through the popliteal fossa, giving off branches to muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg. Here, the tibial nerve also gives rise to branches that contribute towards the sural nerve, which innervates the posterolateral aspect of the leg.
Which nerve innervates the posterior compartment of the leg and the majority of the intrinsic foot muscles?
Motor: Innervates the posterior compartment of the leg and the majority of the intrinsic foot muscles. Anatomical Course. The tibial nerve is a branch of the s ciatic nerve, and arises at the apex of the popliteal fossa . It travels through the popliteal fossa, giving off branches to muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg.
