Principal innervation of the thyroid gland derives from the autonomic nervous system. Parasympathetic fibers come from the vagus nerves, and sympathetic fibers are distributed from the superior, middle, and inferior ganglia of the sympathetic trunk.
What nerve is involved in enlarged thyroid?
Enlarged Thyroid. The nerve supply to the thyroid gland is derived from the superior, middle and inferior cervical sympathetic ganglia. These nerve fibers are vasomotor, causing constriction of the blood vessels. Vagus nerve and the thyroid gland.
How does the inferior ganglion innervate the thyroid?
While all three ganglia provide autonomic innervation to the thyroid gland and its vasculature, the inferior ganglion also forms a plexus around the inferior thyroid artery. This plexus also interacts with the both external and recurrent laryngeal nerves, which also provides parasympathetic innervation to the gland as well.
What is the relationship between the thyroid and the vagus nerve?
Vagus nerve and the thyroid gland. The relationship of the thyroid gland and the two vagus nerve branches, the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, is of major surgical significance because damage to these nerves leads to disability in phonation or to difficulty breathing.
Where does the right recurrent laryngeal nerve innervate?
Nerve Supply to The Thyroid Gland. The right recurrent laryngeal nerve arises from the vagus nerve, loops around the subclavian artery, and ascends behind the right lobe of the thyroid. It enters the larynx and innervates its intrinsic muscles, which produce the voice and close the laryngeal opening.
See more

Which nerve is related to upper pole of the thyroid gland?
The external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (ELN) is intimately associated with the superior thyroid artery (STA) in relation to the superior pole of the thyroid gland, rendering it vulnerable to injury during the ligation of this vessel during thyroidectomy.
Does the thyroid have parasympathetic innervation?
The thyroid and parathyroid glands are dually innervated by sympathetic (cervical sympathetic trunk [CST]) and parasympathetic (superior laryngeal nerve [SLN]) nerve fibers.
Does the vagus nerve affect the thyroid?
Vagal inhibition contributes significantly to SVI in thyroid dysfunctions, especially in hyperthyroidism.
Who stimulates the thyroid gland?
TSH, in turn, stimulates thyroid follicular cells to release thyroxine or T4 (80%), and triiodothyronine or T3 (20%). Somatostatin, on the other hand, is another hormone produced by the hypothalamus that inhibits the release of TSH from the anterior pituitary.
Can thyroid nodule affect vagus nerve?
The cervical portion of the vagus nerve is located within the carotid sheath, usually between the common carotid artery and internal jugular vein, however a bulging large thyroid nodule may alter the location of the vagus nerve, making it closer to the thyroid nodule (67-70).
What part of nervous system is thyroid?
The thyroid is part of the endocrine system, which is made up of glands that produce, store, and release hormones into the bloodstream so the hormones can reach the body's cells. The thyroid gland uses iodine from the foods you eat to make two main hormones: Triiodothyronine (T3) Thyroxine (T4)
How do you stimulate vagus nerve?
One of the main ways that you can stimulate the healthy function of the vagus nerve is through deep, slow belly breathing.Breathe more slowly (aim for six breaths per minute).Breathe more deeply, from the belly. Think about expanding your abdomen and widening your rib cage as you inhale.Exhale longer than you inhale.
What does vagus nerve do?
Overview over the basic anatomy and functions of the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is responsible for the regulation of internal organ functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate, as well as vasomotor activity, and certain reflex actions, such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting (17).
What can be done vagus nerve?
Overview. Vagus nerve stimulation involves the use of a device to stimulate the vagus nerve with electrical impulses. An implantable vagus nerve stimulator is currently FDA-approved to treat epilepsy and depression.
What regulates the thyroid gland?
The pituitary is an endocrine gland located at the base of your brain that controls your endocrine system, including your thyroid. The pituitary affects the thyroid by producing a hormone called thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH causes cells within your thyroid to make more T3 and T4 hormone.
Which can stimulate the thyroid to release it's hormones?
Regulation of thyroid hormone starts at the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) into the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary gland. TRH stimulates thyrotropin cells in the anterior pituitary to the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
What stimulates TSH release?
Thyroid-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates TSH from the pituitary, which stimulates thyroid hormone release.
Can the thyroid affect the nervous system?
Thyroid function has been shown to play a crucial role in the proper cognitive development but also in many other aspects of nervous system activity, in mechanisms involving direct interaction with intrinsic regulatory circuits or indirectly by systemic effects exerted e.g. on the circulatory system or metabolic ...
How does hyperthyroidism affect the sympathetic nervous system?
Conclusions: Hyperthyroidism is in a sympathovagal imbalanced state, characterized by both increased sympathetic and decreased vagal modulation of the heart rate.
Why does hyperthyroidism cause sympathetic overactivity?
Sympathetic overactivity: Thyroxin stimulates adrenaline surge, thus overtreating subjects with L-T4 may lead to sympathetic overactivity. 21 Studies carried out in subjects with subclinical-hyperthyroidism are characterised by increase in sympathetic activity and parasympathetic imbalances.
Can thyroid cause autonomic dysfunction?
However on the basis of individual autonomic function test and scoring analysis it was found that 95.45% (21) of subclinical hypothyroid patients and 85% (17) of hypothyroid patients had autonomic dysfunction.
Where is the thyroid gland innervated?
The thyroid gland is innervated by branches derived from the sympathetic trunk.
Where is the inferior thyroid artery located?
Inferior thyroid artery – arises from the thyrocervical trunk (a branch of the subclavian artery). It lies in close proximity to the recurrent laryngeal nerve (innervates the larynx).
What happens when the thyroid gland descends?
The descent of the developing thyroid gland forms the thyroglossal duct – an epithelialised tract that connects the gland to its origin at the foramen cecum. It usually regresses by the 10th week of gestation, but can persist in some individuals. If it fails to regress, the duct can give rise to cysts or fistulae.
What are the structures of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland is closely associated with numerous other structures in the anterior neck: 1 Anteriorly – infrahyoid muscles, namely the sternothyroid, superior belly of the omohyoid and sternohyoid 2 Laterally – carotid sheath, containing the common carotid artey, internal jugular vein and vagus nerve 3 Medially –#N#Organs – larynx, pharynx, trachea and oesophagus#N#Nervea – external laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal
What is the arterial supply to the thyroid gland?
Arterial Supply. The arterial supply to the thyroid gland is via two main arteries: Superior thyroid artery – arises as the first branch of the external carotid artery. It lies in close proximity to the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (innervates the larynx).
Which gland is wrapped around the cricoid cartilage?
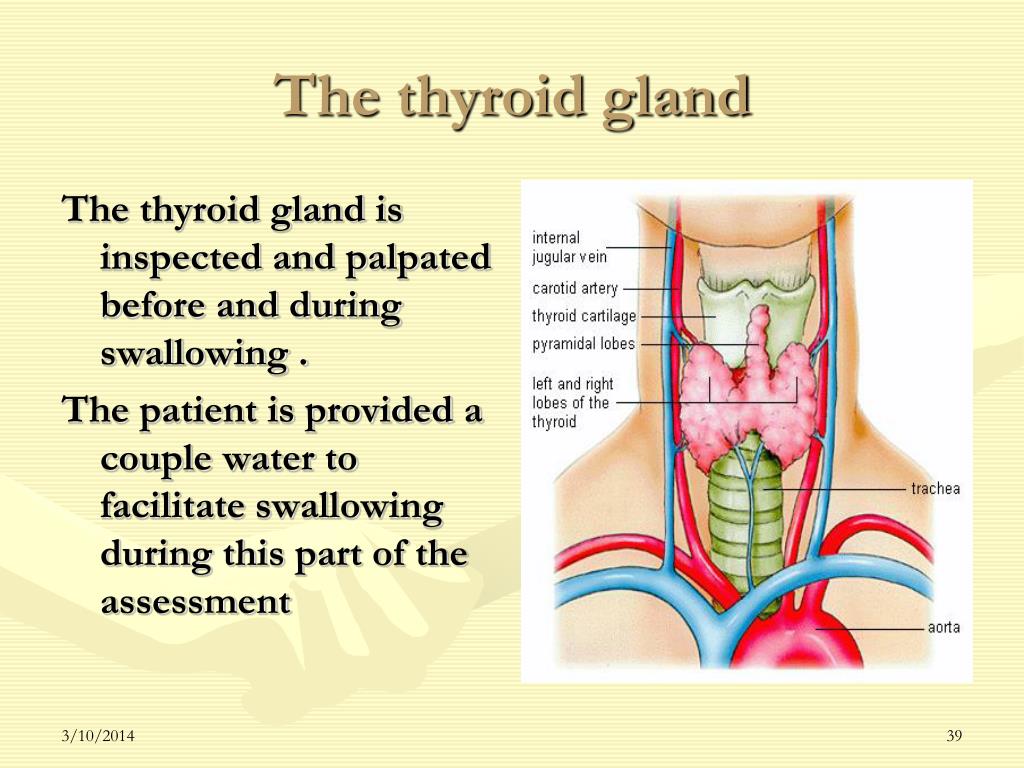
Fig 2 – The thyroid gland consists of two lobes connected by a central isthmus. It is wrapped around the cricoid cartilage and trachea anteriorly.
Which gland has two lobes?
The lobes of the thyroid gland are wrapped around the cricoid cartilage and superior rings of the trachea.
Which nerve supplies parasympathetic input?
The parasympathetic input is supplied by the superior laryngeal nerve and the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Which ganglion provides sympathetic input?
Sympathetic input is supplied by the superior cervical ganglion and the cervicothoracic ganglion. The superior cervical ganglion lies posterior to the sheath of the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein.
What is the relationship between the thyroid gland and the vagus nerve?
These nerve fibers are vasomotor, causing constriction of the blood vessels. The relationship of the thyroid gland and the two vagus nerve branches, the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, is of major surgical significance because damage to these nerves leads to disability in phonation ...
Where does the right recurrent laryngeal nerve originate?
The right recurrent laryngeal nerve arises from the vagus nerve, loops around the subclavian artery, and ascends behind the right lobe of the thyroid.
:origin()/pre00/7cc5/th/pre/f/2013/237/a/d/deviantart_8_by_sebastian_turner-d6jm98c.jpg)