Where does the trachea receive sensory innervation?
The trachea receives sensory innervation from the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Arterial supply comes from the tracheal branches of the inferior thyroid artery, while venous drainage is via the brachiocephalic, azygos and accessory hemiazygos veins. At the level of the sternal angle, the trachea bifurcates into the right and left main bronchi.
What nerve innervates the bronchi?
The bronchi derive innervation from pulmonary branches of the vagus nerve (CN X). Blood supply to the bronchi is from branches of the bronchial arteries, while venous drainage is into the bronchial veins. Fig 1.2 – The trachea and bronchi.
What is the venous supply to the trachea?
Neurovascular Supply. The trachea receives sensory innervation from the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Arterial supply comes from the tracheal branches of the inferior thyroid artery, while venous drainage is via the brachiocephalic, azygos and accessory hemiazygos veins.
What is the function of the trachea?
The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is the large tube that delivers air from the upper respiratory tract (the nasal passages, throat, and larynx) to the bronchi (the two large airways that branch off into each lung). In the process, it warms and moisturizes the air and catches debris and microbes before they enter the lungs.
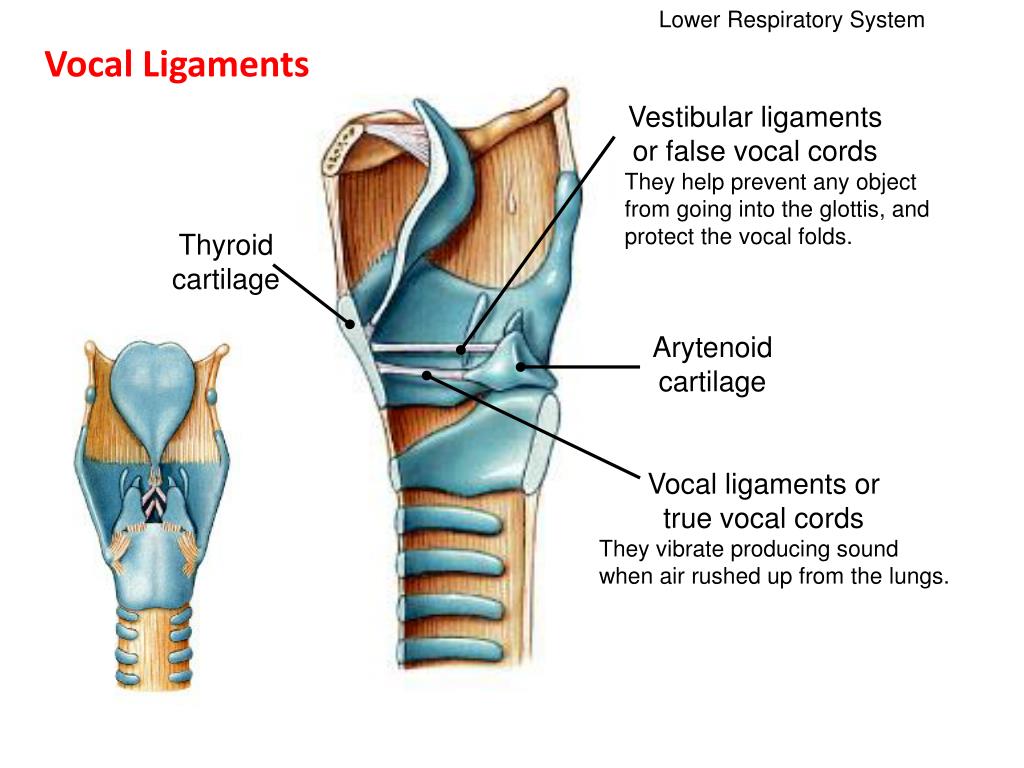
How is the trachea connected to the larynx?
The trachea is connected to the larynx via a ring of cartilage known as the cricoid cartilage . As the trachea descends the chest, it is surrounded by 16 to 22 U-shaped rings of cartilage that hold the windpipe open like scaffolding, allowing the flow of air.
What is the posterior wall of the trachea?
The posterior wall of the trachea not covered by cartilage is composed of connective tissue and smooth muscle. The muscle will flex and expand when needed to change the diameter of the trachea. The trachea ends at the carina, a ridge of cartilage that separates and forms the junction into the bronchi.
What is the trachea vulnerable to?
The trachea is vulnerable to infections, inflammation, and other stresses that can damage cells. This can lead to conditions like tracheal stenosis, in which the trachea narrows and restricts breathing, and tracheal cancer, an extremely rare form of cancer.
What is the function of lymphatic vessels in the trachea?
The lymphatic vessels help remove microbes on the surface of the wall of the trachea so they can be isolated and neutralized by the immune system. 3
What is the lining of the trachea?
Lining the trachea are mucosal membranes comprised of epithelial cells, mucus-secreting goblet cells, and hair-like projections called cilia that move foreign particles up and out of the airway.
How big is the trachea?
The trachea is roughly 4 to 5 inches long and 1 inch in diameter. It starts just under the larynx (voice box) and runs down the center of the chest behind the sternum (breast bone) and in front of the esophagus. 1 . The trachea is connected to the larynx via a ring of cartilage known as the cricoid cartilage.
Where are particles trapped in the airway?
Most particles that enter the airway are trapped in the thin layer of mucus on the trachea walls. These are then moved upwards toward the mouth by cilia, where they can be swallowed.
Which nerve innervates the trachea?
The trachea receives sensory innervation from the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Where is the trachea located?
The trachea marks the beginning of the tracheobronchial tree. It arises at the lower border of cricoid cartilage in the neck, as a continuation of the larynx. It travels inferiorly into the superior mediastinum , bifurcating at the level of the sternal angle (forming the right and left main bronchi).
What is the trachea held open by?
The trachea, like all of the larger respiratory airways, is held open by cartilage – here in C-shaped rings. The free ends of these rings are supported by the trachealis muscle.
What are the roots of the lungs?
Along with branches of the pulmonary artery and veins, the main bronchi make up the roots of the lungs.
Which bronchi are located at the level of the sternal angle?
At the level of the sternal angle, the trachea bifur cates into the right and left main bronchi. They undergo further branching to produce the secondary bronchi. Each secondary bronchi supplies a lobe of the lung, and gives rise to several segmental bronchi.
Where are the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles located?
These airways are located in the neck and thorax.
Which organs allow air to pass through the lungs?
The trachea, bronchi and bronchioles form the tracheobronchial tree - a system of airways that allow passage of air into the lungs, where gas exchange occurs.
Anatomy
Function
- The trachea serves as the main passageway through which air passes from the upper respiratory tract to the lungs. As air flows into the trachea during inhalation, it is warmed and moisturized before entering the lungs. The U-shaped sections of cartilage that line the trachea are flexible and can close and open slightly as the trachealis muscle at t...
Associated Conditions
- The trachea, like all parts of the respiratory system, is vulnerable to inhaled substances that can damage tissue and interfere with breathing. Certain infections and diseases can also affect the trachea.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
- Injuries, infections, and diseases of the trachea can cause damage to the airway, sometimes irreparably. Tracheal stenosis is one such case in which the development of fibrosis (scarring) is most often permanent. Once the underlying cause of a tracheal injury is treated, efforts may be made to repair the trachea or support its function.