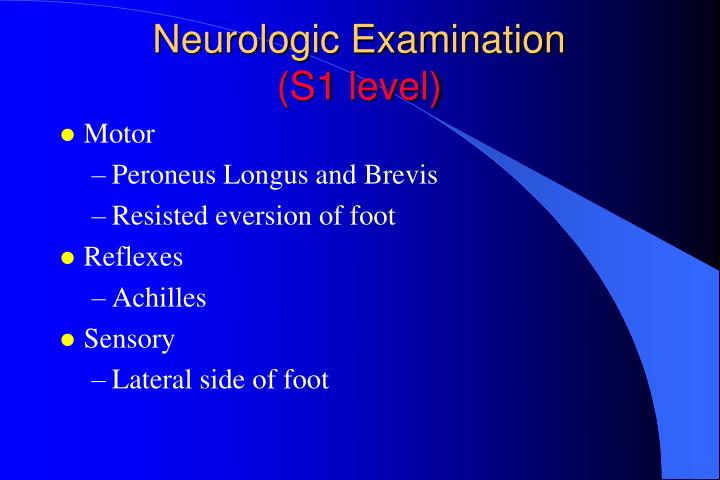
This simple reflex forms the basis of the test performed by doctors during the examination of a patient's central and peripheral nervous system. The 6 primary locations for testing reflex arcs across the spinal cord: The Achilles' tendon tests the first and second sacral nerves (S1, S2).
What is the reflex test on the Achilles tendon?
In addition to the knee, there are other nerve-function-test locations and one of these is the Achilles tendon. Not too long ago, the “reflex test” on the Achilles tendon was thought to indicate not just nerve function, but also an indicator of thyroid function.
What nerve innervates the Achilles tendon?
The Achilles tendon is innervated primarily by the S1 and S2 nerve roots of the Tibial nerve. The Achilles tendon reflex is a stretch reflex, which refers to the involuntary contraction of a muscle in response to passive stretching.
What is the LMN of the Achilles reflex?
The LMN of the Achilles reflex consists of the ventral horn of the S1 nerve root and the tibial nerve. The Achilles reflex test is performed as part of any complete physical exam, particularly when assessing the neurologic functions of the lower extremities.
What is Achilles reflex in hypothyroidism?
[2] The Achilles reflex checks if the S 1 and S 2 [3] nerve roots are intact and could be indicative of sciatic nerve pathology. It is classically delayed in hypothyroidism.

What nerves are involved in Achilles reflex?
The LMN of the Achilles reflex consists of the ventral horn of the S1 nerve root and the tibial nerve.
What nerve root is Achilles reflex?
The LMN of the Achilles reflex consists of the ventral horn of the S1 nerve root and the tibial nerve.
How do you test for Achilles reflexes?
0:080:59Achilles Heel Deep Tendon Reflex Test | Nursing Head to ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou usually want to check those two together. And what you're going to do is you're going to DorseMoreYou usually want to check those two together. And what you're going to do is you're going to Dorse dorsiflex. The foot up like that and you will see the tendon. Which is located right above the heel.
Which nerve is responsible for ankle reflex?
The ankle jerk reflex is mediated by the S1 nerve root. The plantar reflex (Babinski) is tested by coarsely running a key or the end of the reflex hammer up the lateral aspect of the foot from heel to big toe. The normal reflex is toe flexion.
How do you test for L5 nerve roots?
0:197:42Examination Of L5 Nerve Root - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAt the top of the foot. We go from l4 medial side to the top of the foot l5 to the lateral aspect ofMoreAt the top of the foot. We go from l4 medial side to the top of the foot l5 to the lateral aspect of the foot s1. There is no reflexes for le5.
What reflex is associated with the L5 nerve root?
Although the knee jerk reflex is mediated by the L3 and L4 nerve roots, evidence exists that altered knee jerk expression may occur with exclusively L5 radiculopathy.
What is the Achilles reflex used for?
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed. It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it.
What are the components of the Achilles reflex arc?
The pathway can be described as a 'reflex arc' which is made up of 5 components:A receptor – muscle spindle.An afferent fibre – muscle spindle afferent.An integration centre – lamina IX of spinal cord.An efferent fibre – α-motoneurones.An effector – muscle.
When assessing the Achilles tendon reflex the expected response would be?
Expected Response of the Achilles Deep Tendon Reflex You will see the foot plantarflex.
How do you test for ankle reflexes?
0:231:21Neurologic Examination of the Foot: Ankle Reflexes - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipVery simple test to perform first thing you want to do is put the ankle. And foot into a neutralMoreVery simple test to perform first thing you want to do is put the ankle. And foot into a neutral position then using a standard reflex hammer you're going to tap over the Achilles tendon.
Why is the Achilles reflex important for walking?
The Achilles tendon (AT) has the capacity to store and release elastic energy during walking, contributing to metabolic energy savings.
Which nerve root is affected in a patient with loss of the ankle jerk reflex?
A reduced or absent ankle jerk reflex can indicate pathology of the tibial and/or sciatic nerve.
Where is the S1 nerve root?
The S1 nerve root can be found in the lateral recess of the sacral epidural space on its way to the sacral neuroforamen. It passes medial and inferior to a bony structure equivalent to the pedicle of the lumbar vertebra.
What nerve is tested in the plantar flexion reflex?
The motor response which leads to the plantar flexion is mediated through the S1 root and tibial nerve.
Which nerve root is affected in a patient with loss of the ankle jerk reflex?
A reduced or absent ankle jerk reflex can indicate pathology of the tibial and/or sciatic nerve.
What spinal nerve does the patellar reflex test?
The patellar reflex is a deep tendon reflex, mediated by the spinal nerves from the levels L2, L3, and L4 in the spinal cord, predominantly in the root L4.
Where does the Achilles reflex originate?
The Achilles reflex originates in the S1 and S2 nerve roots. When comparing reflexes from different sites of the body, the locations of the corresponding nerve roots along the spinal cord should be considered in order to determine possible sites of injuries and differences in reflex path lengths.
How to see the first trial of Achilles Reflex?
Scroll to the beginning of the data recorded for the Achilles Reflex to display the first trial on the Main window . You can also click on MARK to show locations for all marks. Highlighting a mark and clicking GO TO MARK will take you to that mark on the data screen.
What is the purpose of the patellar reflex?
The primary purpose of the patellar reflex – the stretch reflex of the quadriceps femoris muscle – is to prevent excessive stretching of the quadriceps. The patellar reflex is illustrated in Figure 1.
What is the reflex arc?
A reflex arc refers to the neural pathway that a nerve impulse follows. The reflex arc typically consists of five components: A receptor, and independent sensory cell, or an ending of a sensory neuron, reacts to a stimulus (e.g., a stretch receptor). The sensory, or afferent, neuron sends a nerve impulse through an afferent pathway to ...
Which neuron innervates contractile extrafusal fibers?
The sensory neuron synapses with a motor neuron in the spinal cord that innervates contractile extrafusal fibers. The contraction of the extrafusal fibers, that is, contraction of the belly of the muscle, releases tension on the intrafusal fibers, decreasing stimulation to neuron.
What is reflex response?
A reflex is an involuntary (automatic) response to stimulus that quickly returns the body to homeostasis. There are several kinds of reflexes. Examples are shivering in response to low core body temperature; or withdrawing your hand from a hot stove when temperature and pain receptors in your hand register the stimulus.
Why do reflexes have a short path length?
Because integrating center processing may occur at the level of the spinal cord rather than requiring impulses to travel to the brain, reflex responses have a relatively short path length and, thus, a quick reaction time compared to voluntary or conscious body movements.
Why does my Achilles tendon hurt?
Other possible causes are: Overuse leads to excessive wear and tear of the muscle leading to injury (by far the major cause of Achilles tendonitis). incorrect footwear. improper running technique. Some kind of trauma and infection might also lead to it. Arthritis is another cause for problems in the Achilles tendon.
What test do doctors use to check the nervous system?
As you probably know, doctors will check some of our nervous system functions via another type of “reflex test”. For example, striking the knee with a rubber mallet to make the leg jump is one such “reflex test”.
What causes Achilles tendonitis?
Injuries to this tendon can be caused by general weakness and congestion. Other possible causes are: 1 Overuse leads to excessive wear and tear of the muscle leading to injury (by far the major cause of Achilles tendonitis). 2 incorrect footwear 3 improper running technique 4 Some kind of trauma and infection might also lead to it 5 Arthritis is another cause for problems in the Achilles tendon.
What is it called when you have a swollen Achilles tendon?
Any inflammation, swelling or any other kind of irritation and discomfort in the Achilles tendon is known as Achilles tendonitis.
Is the Achilles thyroid connection reliable?
Medical research that was conducted to test the Achilles-thyroid connection proved inconclusive and therefore has not been pursued as a reliable indicator.
Is the Achilles tendon the strongest?
Yes, there are points on the Achilles tendon that reflex to the body (I’ve heard it called the “hemorrhoid line”), but it doesn’t seem like the proportions are right … big strong tendon, small energy connection. The Achilles tendon is the strongest and the toughest tendon in the body. It connects the muscles of the calf to the heel.
What is the Achilles reflex?
It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it.
Which segment of the spinal cord is responsible for reflexes?
This reflex is mediated by the S1 spinal segment of the spinal cord.
What is Grade 4 hyper reflexia?
Grade 4 ankle hyper reflexia is called ankle clonus. There is repetitive ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion on passive dorsiflexion of the foot by the examiner till the force applied by the examiner is withdrawn.
Is a deep tendon reflex a stretch reflex?
Being a deep tendon reflex, it is monosynaptic. It is also a stretch reflex. These are monosynaptic spinal segmental reflexes. When they are intact, integrity of the following is confirmed: cutaneous innervation, motor supply, and cortical input to the corresponding spinal segment.
