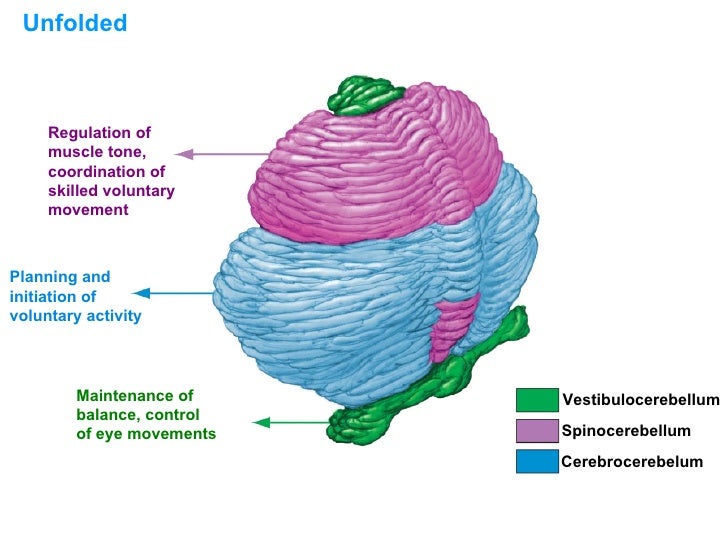
This sector of the cerebellum functions mainly to fine-tune body and limb movements. It receives proprioceptive input from the dorsal columns of the spinal cord (including the spinocerebellar tract) and from the cranial trigeminal nerve, as well as from visual and auditory systems. Click to see full answer.
Is the cerebellum part of the brain?
What nerves are connected to the cerebellum? This sector of the cerebellum functions mainly to fine-tune body and limb movements. It receives proprioceptive input from the dorsal columns of the spinal cord (including the spinocerebellar tract) and from the cranial trigeminal nerve, as well as from visual and auditory systems.
What are the efferent connections of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is a part of the brain of all vertebrates. The brain is the centre holding all necessary connections to all the sensory functions the body responds to. The brain can be considered to be a soft mass of connective tissues which also has nerves connected to the spinal cord that holds and supports the body.
What are your cranial nerves?
Jul 31, 2021 · It passes the abducens nerve and meets with the facial and vestibulocochlear nerves at the cerebellopontine angle. It then divides into two branches: one supplies the anterior inferior cerebellum while the other supplies the flocculus, choroid plexus, and the middle cerebellar peduncle. [10][11] PICA is the largest vertebral artery branch.
What nerve nuclei are found in the brainstem?
Mar 20, 2022 · This is achieved by proprioceptive input from the dorsal column pathway of the spinal cord, the cranial trigeminal nerve, the visual and auditory systems, as well as the spinocerebellar tract. This region sends its output to the deep cerebellar nuclei .
What nerve supplies the cerebellum?
This artery supplies blood to the anterior portion of the inferior cerebellum, the middle cerebellar peduncle, and to the facial (CN VII) and vestibulocochlear nerves (CN VIII).
What's connected to the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is located in the posterior cranial fossa. The fourth ventricle, pons and medulla are in front of the cerebellum. It is separated from the overlying cerebrum by a layer of leathery dura mater, the tentorium cerebelli; all of its connections with other parts of the brain travel through the pons.
What nerves are connected to the cerebrum?
The cerebrum has right and left halves, called hemispheres. They're connected in the middle by a band of nerve fibers (the corpus callosum) that lets them communicate.
What happens when your cerebellum is damaged?
Damage to the cerebellum can lead to: 1) loss of coordination of motor movement (asynergia), 2) the inability to judge distance and when to stop (dysmetria), 3) the inability to perform rapid alternating movements (adiadochokinesia), 4) movement tremors (intention tremor), 5) staggering, wide based walking (ataxic gait ...
What lobe is the cerebellum in?
The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex (Figure 5.1).
What are the 5 types of nerves?
It is conventional, however, to describe nerve types on the basis of their function: motor, sensory, autonomic or cranial.Motor Nerves. ... Sensory Nerves. ... Autonomic Nerves. ... Cranial Nerves.Jul 30, 2018
What are the four types of nerves?
These are the sensory nerves, motor nerves and mixed nerves.Oct 29, 2019
What are the 10 cranial nerves?
olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory, hypoglossal.
Q.1) What are the Main Functions of the Cerebellum?
Ans.) The cerebellum of the brain is called the little brain, however, it does perform vital functions for the brain and the body. It plays a cruci...
Q.2) What Happens When a Cerebellum is Damaged?
Ans.) Since the cerebellum is the hub and home for many neuron and nerve cells, when any sort of damage is caused to it the consequences can be lif...
Q.3) What Leads to Cerebellum Damage?
Ans.) When a major injury occurs due to accidents may be due to road or gunshots, stroke, haemorrhage and tumour are all causes that can severely i...
What are the three main arteries that supply the cerebellum?
The cerebellum receives vascular supply from three main arteries that originate from the vertebrobasilar anterior system: the superior cerebellar artery (SCA), the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA), and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA).
What is the role of the cerebellum in the brain?
The cerebellum is a vital component in the human brain as it plays a role in motor movement regulation and balance control. The cerebellum coordinates gait and maintains posture, controls muscle tone and voluntary muscle activity but is unable to initiate muscle contraction.
Which layer of the brain contains 80% of the brain's neurons?
The cerebellum is neuron-rich, containing 80% of the brain’s neurons organized in a dense cellular layer. [1][4] The cerebellar cortex is a sheet-like structure, made of a single sheet less than 1mm thick, and accordion-like folds fused at the midline (Essen 2018). Each fold is composed of an inner white matter core that is covered by gray matter. ...
Where do fibers from the fastigial nucleus exit?
Fibers from the fastigial nucleus exit through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. [1][8] Embryology. The cerebellum develops from the hindbrain vesicle that gives rise to the posterior part of the alar plates of the metencephalon. The cerebellar hemisphere and vermis form by the 12th week.
What neurotransmitter is used in mossy fibers?
Mossy fibers use glutamate, while the climbing fibers use aspartate as their main excitatory neurotransmitter to provide excitatory signals to the Purkinje cells. The climbing fibers are named so because they travel in the cortex like vine branches on a tree.
What are the layers of the cortex?
The gray matter of the cortex divides into three layers: an external - the molecular layer; a middle - the Purkinje cell layer; and an internal - the granular layer. The molecular layer contains two types of neurons: the outer stellate cell and the inner basket cell. [4][5]
What is the function of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum coordinates gait and maintains posture, controls muscle tone and voluntary muscle activity but is unable to initiate muscle contraction. Damage to this area in humans results in a loss in the ability to control fine movements, maintain posture, and motor learning. [1][2][3] Structure and Function.
What are the largest cells in the brain?
Purkinje cells. These are some of the largest cells in the brain. Purkinje cells are essential to the cerebellar circuitry, and they emit action potentials even in the absence of extrinsic synaptic input. These have a dendritic shape with profuse branching that resembles a tree.
Which fibers ascend via the inferior cerebellar peduncles and transmit proprioceptive information from
Trigeminocerebellar fibers: These ascend via the inferior cerebellar peduncles and transmit proprioceptive information from the face to the cerebellum. It's almost time to start testing your knowledge on the afferent and efferent pathways of the cerebellum!
What is the surface of the cerebellum?
The surface of the cerebellum is grey , and beneath this, we have the myelinated white matter communicating with the cerebellar cortex. Cutting the cerebellum in cross section will reveal a tree-like appearance (arbor vitae or ‘tree of life’), marked by four deep grey cerebellar nuclei.
Which peduncle connects the cerebellum to the pons?
Middle cerebellar peduncle. This is the largest peduncle and connects the cerebellum to the pons. It connects the contralateral pontine nucleus to the cerebellar cortex and also carries the input from the contralateral cerebral cortex. It is composed of three fasciculi including the superior, inferior and deep.
What is the cerebellum's main function?
Its main function is in motor control , where it enables smooth, well timed, proportional responses. However, the cerebellum has many other cortical functions including speech, emotions, as well as pleasure and fear. This article will discuss the anatomy of the cerebellum, as well as its functions and clinical relevance.
What are the crevasses in the brain called?
In the brain, the crevasses are called sulci and the elevations gyri. In the cerebellum, they are called sulci and folia respectively. A worm-like structure called the vermis wraps sagittally around its center and marks the midline.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the afferents?
It receives afferents from the locus coeruleus, and ventral spinocerebellar tract.
What are the three pairs of peduncles that connect the cerebellum to the brain?
The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem by three pairs of cerebellar peduncles: the superior peduncle with the midbrain, the middle peduncle with the pons, and the inferior peduncle with the medulla oblongata.
What is the cerebellum and brainstem?
The cerebellum and brainstem are a testament to the fact that good things do come in small packages, so this article is an overview of their anatomy. Occupying only a fraction of the volume of the cerebrum, these structures are responsible for simplifying every second of your life and keeping you alive.
How many lobes does the cerebellum have?
The cerebellum consists of two large hemispheres united in the middle by the vermis. Numerous transverse fissures divide the cerebellum into three lobes (anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular) and many lobules. The flocculonodular lobe consists of a flocculus and a nodule.
What nerve exits from the anterior face?
The superior and inferior pontine sulci (grooves) separate it from the neighboring brainstem parts, while the trigeminal (CN V), abducens (CN VI), facial (CN VII), and vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) cranial nerves exit from its anterior face. There is also a basilar groove running along it that houses the basilar artery .
Which part of the brain is responsible for autonomic functions?
The medulla oblongata is the most inferior portion of the brain stem, sitting in the posterior cranial fossa. It is continuous with the spinal cord from below and the pons above. The medulla oblongata is responsible for various autonomic functions and contains the cardiac, respiratory, reflex, and vasomotor centers.
Where are the nuclei of the reticular formation located?
The nuclei of the reticular formation are located deep within the brainstem and are divided into median, medial, and lateral groups. The afferent and efferent pathways associated with the reticular formation are the spinothalamic, dorsal column-medial lemniscus, reticulobulbar, and reticulospinal tracts.
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the senses?
Cranial nerve nuclei (posterior and sagittal views) Furthermore, both efferent and afferent cranial nerves can be: Special, responsible for innervating special senses. General, transmitting impulses to/from everywhere else other than the senses. Somatic, travelling to/from the skin and skeletal muscles.
What are the functions of the cranial nerves?
Their functions are usually categorized as being either sensory or motor. Sensory nerves are involved with your senses, such as smell, hearing, and touch. Motor nerves control the movement and function of muscles or glands. Keep reading to learn more about each of the 12 cranial nerves and how they function.
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve?
The oculomotor nerve has two different motor functions: muscle function and pupil response. Muscle function. Your oculomotor nerve provides motor function to four of the six muscles around your eyes. These muscles help your eyes move and focus on objects.
How many cranial nerves are there?
What are cranial nerves? Your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. There are 12 of them, each named for their function or structure. Each nerve also has a corresponding Roman numeral between I and XII.
What nerves are involved in smell?
I. Olfactory nerve. The olfactory nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter. When you inhale aromatic molecules, they dissolve in a moist lining at the roof of your nasal cavity, called the olfactory epithelium.
What nerve sends sensations to the heart?
The vagus nerve is a very diverse nerve. It has both sensory and motor functions, including: communicating sensation information from your ear canal and parts of your throat. sending sensory information from organs in your chest and trunk, such as your heart and intestines.
What nerve controls the muscles in your neck?
Your accessory nerve is a motor nerve that controls the muscles in your neck. These muscles allow you to rotate, flex, and extend your neck and shoulders. It’s divided into two parts: spinal and cranial. The spinal portion originates in the upper part of your spinal cord.
Where does the glossopharyngeal nerve originate?
The glossopharyngeal nerve originates in a part of your brainstem called the medulla oblongata. It eventually extends into your neck and throat region.
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Check all that are functions of the cerebellum. -receives sensory plans for movements. -acts as the "principal" of unconscious physical actions by regulating functions of motor pathways. directly controls the influences of hormones and enzymes on skeletal muscles.
What does "tap card" mean?
Tap card to see definition 👆. Processes visual information at a subconsious level. -claustrum. Stimulates muscles to produce the pattern and rhythm of walking. -caudate nucleus. Excites and inhibits the thalamus to adjust muscle tone. -globus pallidus. Involved in emotion, behavioral activity, and mood. -amygdaloid body.
Which lobe of the brain controls voluntary muscles?
Primary visual cortex (Occipital lobe) The primary motor cortex for control of voluntary muscles is found in the: -precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe. postcentral gyrus of the temporal lobe. precentral gyrus of the parietal lobe. singular gyrus of the temporal lobe.