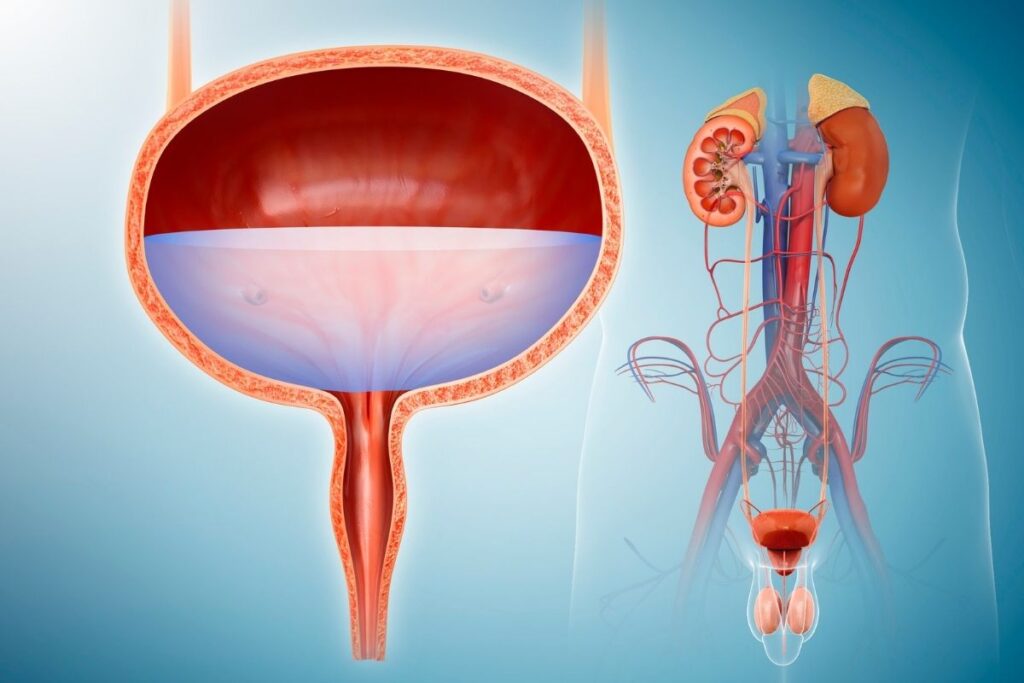
Some of these sacral nerves go to the rectum, the bladder's detrusor muscle, levator ani muscle, and external sphincter muscles, controlling their activities. Two important sacral nerves to the functioning of the bladder and bowel are the pudendal nerve and the pelvic splanchnic nerve.
What nerve controls bladder function?
Jan 19, 2020 · Two key sacral nerves that are vital to the functioning of the bowel are the pudendal nerve and the pelvic splanchnic nerve. Beside above, what causes loss of bladder and bowel control? Many conditions may affect the nerves and muscles that control the bladder and bowel. Bladder incontinence can be caused by things such as: Holding urine in too long (urine …
What nerve innervates the urinary bladder?
Apr 29, 2022 · A spinal cord injury sometimes interrupts communication between the brain and the nerves in the spinal cord that control bladder and bowel function. This can cause bladder and bowel dysfunction known as neurogenic bladder or neurogenic bowel. People with multiple sclerosis or spina bifida might have similar problems.
What spinal level controls the bladder?
Because the nerves controlling the bladder attach to the very base of the spinal cord, bladder function is almost always affected by spinal cord injury, regardless of the level at which the injury occurred. When messages can no longer be passed from the bladder muscles to the brain, the bladder is affected in one of two ways: Spastic bladder.
What are the symptoms of a neurogenic bladder?
When the bladder and bowel function normally, nerves tell certain muscles when to tense up and when to relax. Nerves in the spinal cord send messages from the brain to the bladder. Sphincter muscles control the flow of urine. Muscles in the rectum and anus control or release stool. These nerve and muscle processes allow urine and feces to be removed when you want them to.

What nerve controls bladder function?
What causes loss of control of bowels and bladder?
Can a pinched nerve cause bladder problems?
What causes neurogenic bowel and bladder?
What is it called when you poop and pee at the same time?
Why do I suddenly need to poop all the time?
Can spinal stenosis cause bladder and bowel problems?
Can neuropathy affect your bowels?
Does the vagus nerve control the bladder?
What spinal nerves affect the bowel?
Can bladder and bowel problems be related?
How do I know if I have neurogenic bowel?
Symptoms include trouble having a bowel movement, belly pain, leaking stool, and frequent bowel movement accidents. Tests for diagnosis may include an MRI or CT scan of your brain or spinal cord and an ultrasound of the anus. Treatment includes creating a bowel management program.
What is it called when you pass a stool?
What You Need to Know. Issues with urinating or passing stools are referred to as bladder and bowel dysfunction. Bladder and bowel problems often originate with nerve or muscle dysfunction, as these systems control the flow of urine and the release of stool.
What causes bowel dysfunction?
Other health issues may cause bladder and/or bowel dysfunction, including medicinal side effects, stress, neurologic diseases, diabetes, hemorrhoids and pelvic floor disorders. Therapy and management for these conditions can range from dietary changes and exercise to electrical stimulation and surgery depending on individual diagnosis.
What is bladder incontinence?
Bladder or bowel incontinence means a problem holding in urine or stool. You may have unwanted passage of urine or stool that you can’t control.
What causes incontinence in the bladder?
Bladder incontinence can be caused by things such as: Damage to nerves in sphincter muscles. Holding urine in too long (urine retention), which can damage the bladder.
How to help with constipation and diarrhea?
Changes in food or drink. Increasing your fiber intake can help manage diarrhea and constipation. Drinking plenty of fluids can also ease constipation. Not drinking fluids at certain times can help manage overactive bladder and urinary incontinence.
How to control diarrhea?
Antidiarrheal medicines can help manage diarrhea. And medicine can help bladder muscles relax to give you better control. Keeping a bathroom schedule. Setting a regular schedule for using the toilet can give you better control. This includes attempting to urinate or move your bowels at the same time each day.
How does the bowel work?
How the Bowel Works. The bowel is part of our digestive system and it works to digest the food we eat , absorb the goodness and nutrients into our blood stream , then process and expel the waste that the body cannot use. The digestive system works by pushing food through the intestines which usually takes between 24 to 72 hours.
How does the digestive system work?
The digestive system works by pushing food through the intestines which usually takes between 24 to 72 hours. Muscular contractions squeeze (peristalsis) the food through the different sections of the intestine. These different sections are separated by bands of muscles, or sphincters, which act as valves. The passage of food from one area of the ...
What are the parts of the small intestine?
There are 3 parts of the small intestine: the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. Food passes from the stomach into the duodenum, which is the tube that leads from the stomach into the intestines. The food then passes through the jejunum and ileum before going to the colon (large bowel). The small intestine absorbs nutrients and much ...
Where does food go in the body?
Food passes from the stomach into the duodenum, which is the tube that leads from the stomach into the intestines. The food then passes through the jejunum and ileum before going to the colon (large bowel). The small intestine absorbs nutrients and much of the liquid from foods. At the point where food is passed from the small intestine into ...
How big is the colon?
The colon is about 2m long and 6-7 cm wide.
What is the function of the colon?
The colon’s most important job is to store, process and get rid of waste. The colon also absorbs some nutrients and water.
What is the job of the colon?
The colon’s most important job is to store, process and get rid of waste. The colon also absorbs some nutrients and water. Key to this process are the hundreds maybe thousands of bacteria resident in the colon – both ‘good’ and ‘bad’ – which collectively make up the gut flora.
What does it mean when you have a bladder problem?
Bladder or bowel incontinence means there is a problem holding in urine or stool. You may have unwanted passage of urine or stool that you can’t control. These conditions can be stressful to deal with. But don’t feel embarrassed about talking with your healthcare provider. Providers are used to dealing with these issues and can help you manage the problem.
What causes incontinence in the bladder?
Bladder incontinence can be caused by things such as: Damage to nerves in sphincter muscles. Holding urine in too long (urine retention), which can damage the bladder.
How to treat a swollen bladder?
Some common treatments are: Changes in food or drink. Increasing your fiber intake can help manage diarrhea and constipation. Drinking plenty of fluids can also ease constipation. Not drinking fluids at certain times can help manage overactive bladder and urinary incontinence. Exercises.
How to help with constipation and diarrhea?
Changes in food or drink. Increasing your fiber intake can help manage diarrhea and constipation. Drinking plenty of fluids can also ease constipation. Not drinking fluids at certain times can help manage overactive bladder and urinary incontinence. Exercises.
How to control bladder and bowel movements?
Keeping a bathroom schedule. Setting a regular schedule for using the toilet can give you better control. This includes trying to urinate or move your bowels at the same time each day. Electrical stimulation. This therapy can stimulate damaged nerves. This may give you better muscle control in your bladder or bowel.
What to do if you have bowel incontinence?
Your healthcare provider will work with you to create a treatment plan. Both bladder and bowel incontinence can lead to a breakdown of skin. Ask your healthcare provider about correct skin care for your situation.
What causes urge incontinence?
In addition, urge incontinence may be caused by intrinsic detrusor myogenic abnormalities that result in motor detrusor instability.4. Neural Control of the Lower Urinary Tract. The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets of peripheral nerves involving the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous systems:
What nerves control the lower urinary tract?
The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets of peripheral nerves involving the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous systems: Pelvic parasympathetic nerves: arise at the sacral level of the spinal cord, excite the bladder, and relax the urethra.
Which nerves release norepinephrine?
Sympathetic (hypogastric nerve): Sympa thetic postganglionic terminals that release norepinephrine (NE) elicit contractions of bladder base and urethral smooth muscle and relaxation of the bladder body. Somatic Pathways.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat pain?
Capsaicin , Resiniferatoxin, Vanilloid Receptor, and C-Fiber Pharmacotherapy. Capsaicin and its ultrapotent analogue resiniferatoxin are vanilloids that stimulate and desensitize a specific population of sensory nerves (predominantly unmyelinated C-fibers) that transmit pain signals and release neuropeptides.
How is micturition controlled?
The process of micturition is controlled by neural circuits in the brain and spinal cord coordinating the activity of smooth muscle in the bladder and urethra. Because this process is complex, a variety of neurologic disorders and injuries can result in urge incontinence. The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets ...
What is the process of micturition?
The process of micturition is controlled by neural circuits in the brain and spinal cord coordinating the activity of smooth muscle in the bladder and urethra. Because this process is complex, a variety of neurologic disorders and injuries can result in urge incontinence. The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets of peripheral nerves: pelvic ...
Which part of the nervous system is the most inferior?
This section of the nervous system features the most inferior portion of the spinal cord along with many major nerves, plexuses, and ganglia that serve the vital organs ...
What nerves are in the lower back?
Upon exiting the vertebral canal, the spinal nerves of the lower back form into two networks known as the lumbar and sacral plexuses. The lumbar plexus supplies nerves to the skin and muscles of the lateral abdominal region, thigh, anterior thigh, and external genitals. The sacral plexus similarly supplies nerves to the skin and muscles ...
Which nerves are responsible for digestion?
The vagus nerve is a cranial nerve that wanders from the base of the brain parallel to the spinal cord to stimulate digestion in the liver, stomach, and intestines. Parasympathetic neurons in the spinal cord pass through the sacral nerves in the lower back to reach the pelvic organs such as the bladder and reproductive organs to control their ...
Which nerves pass through the spinal cord?
Parasympathetic neurons in the spinal cord pass through the sacral nerves in the lower back to reach the pelvic organs such as the bladder and reproductive organs to control their functions. Between the opposing functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS, the nervous system is effectively able to control all ...
Where is the enteric nervous system located?
A frequently overlooked portion of the nervous system is the enteric nervous system (ENS) found in the gastrointestinal tract. The ENS is a network of around 100 million neurons that regulate the functions of the digestive tract.
What is the function of the ENS?
The ENS monitors the contents of the gastrointestinal tract; decides how to digest its contents most effectively; and controls the movements of smooth muscles and the secretion of glands that results in the digestion of food to provide nutrients to the body.
Can disc herniation cause lower back pain?
A Common Denominator for Back, Bowel, and Bladder Problems. While disc herniation and degenerative disc disease can cause lower back pain, as well as numbness and weakness in the legs, other symptoms may include urinary retention or incontinence and/or bowel incontinence. Since minor discomforts can develop into more serious complications, ...
What happens if you lose control of your bladder?
Loss of Bladder Control. Nerves in the bladder send messages to the brain telling it that your bladder is full. The brain then sends signals to your bladder instructing the muscles that control the release of urine to relax. Disruption of these signals can result in urinary incontinence, bladder pain, and lower abdominal pain.
What causes lower back pain?
A herniated disc, nerve compression, or another disorder affecting the spine can interfere with the nerve signals traveling from the legs and organs in the lower pelvic region to the brain. If this happens, lower back pain may not be your only problem.
What is a herniated disc?
Herniated discs, which are also referred to as slipped discs, commonly occur in the lower back, or lumbar region of the spine. Degenerative disc disease is often a cause of disc herniation. If lumbar disc herniation is severe, besides low back pain and leg pain, you may experience loss of bowel and bladder control, rectal pain, ...
What is Cauda Equina Syndrome?
Cauda equina syndrome is a medical emergency that can cause permanent damage, including paralysis of the lower body and a loss of bladder and/or bowel control. You may need surgery to prevent these complications if nerve compression is severe. Signs that spinal nerve roots at the cauda equina are compressed include lower back pain and numbness ...
What is the best treatment for lower back pain?
Nerve compression affects people differently, and depending on the cause and severity, physical therapy and pain medication may be the only treatment you need to manage chronic lower back pain.
What causes numbness in the lower back?
Lumbar spinal stenosis, a condition characterized by a narrowing of the spinal canal in your lower back, can also cause back pain, weakness or numbness in your legs, and loss of bowel or bladder control. Pressure on the spinal cord and the nerves within this vertebral column are responsible for your symptoms, which usually begin to develop by age ...
Where does the sympathetic innervation of the bladder originate?
The sympathetic innervation of the bladder originates in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord segments (T10-L2), the preganglionic axons running to sympathetic neurons in the inferior mesenteric ganglion and the ganglia of the pelvic plexus. Click to see full answer.
What nerves supply the bladder?
In this manner, what is the nerve supply to the bladder? The bladder receives motor innervation from both sympathetic fibers, most of which arise from the superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses and nerves , and from parasympathetic fibers, which come from the pelvic splanchnic nerves.
What is the sacral micturition center?
Your sacral micturition center is an area of the spinal cord at the base of the spine. This is the area of the spinal cord that controls your bladder and sphincter. After spinal shock, your sacral micturition center it might start sending signals on its own to tell the bladder to squeeze.
