Summary
- A nerve impulse begins when a neuron receives a chemical stimulus.
- The nerve impulse travels down the axon membrane as an electrical action potential to the axon terminal.
- The axon terminal releases neurotransmitters that ca rry the nerve impulse to the next cell.
How does a nerve conduct an impulse?
In conducting nerve impulse, the following play a major role:
- Axon- Helps in the propagation of nerve impulses to the target cell.
- Dendrites- Receive the signals from the axon ends.
- Axon Ending- Acts as a transmitter of signals.
What influences the time a nerve impulse is transmitted?
What factors influence the time necessary for a nerve impulse to be transmitted? Milliseconds: Nerve impulses in arms and legs typically travel at speeds over 40-50 meters/sec, as measured by EMG equipment. Nerve size, local temperature, chemic...
What happens to a nerve impulse?
impulse continues on its path. Through a chain of chemical events, the dendrites (part of a neuron) pick up an impulse that's shuttled through the axon and transmitted to the next neuron. The entire impulse passes through a neuron in about seven milliseconds — faster than a lightning strike. Here's what happens in just six easy steps:
How are nerve impulses initiated and transmitted?
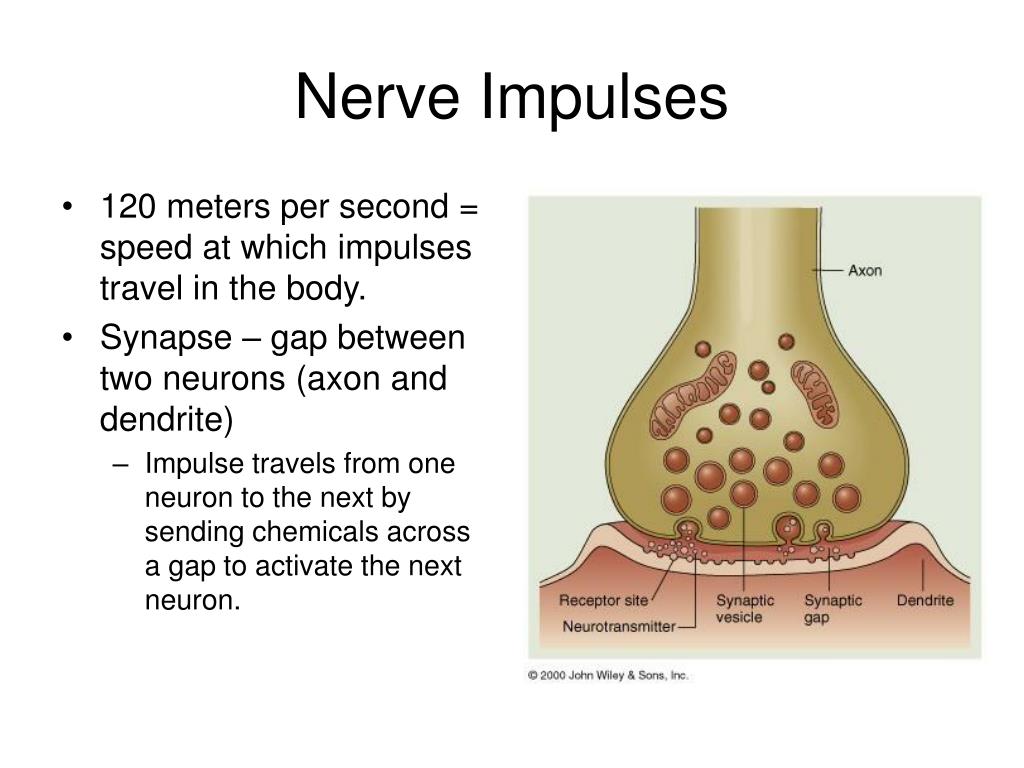
How are nerve impulses initiated and transmitted? When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon, there are some chemicals released from the neurotransmitters. They diffuse across the synaptic gap, which is the small space present between the axon and the receptors. Nerve impulses can be transmitted either by the electrical synapse or the ...
What happens during a nerve impulse quizlet?
The neuron will be at resting potential until a stimulus arrives, causing local Na+ ions to diffuse inside the neuron and depolarize the membrane. Once threshold is reached, Na+ channels will open and Na+ will rush in, causing a depolarization inside the neuron.
Where does a nerve impulse occur?
The place where an axon terminal meets another cell is called a synapse. This is where the transmission of a nerve impulse to another cell occurs. The cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell, and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell.
What are the four steps of a nerve impulse?
An action potential is a change in the electrical potential of the neuron membrane as the nerve impulse passes along the neuron. Its main stages are depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization, and a brief refractory period.
What is a nerve impulse called?
The nervous impulse is also called 'action potential'. It refers to the electric signal produced by a neuron when stimulated. This signal is then transmitted by synapses, or connections between the cells.
What are the 6 steps of a nerve impulse?
Terms in this set (6)Resting neuron: The plasma membrane at rest is polarized. ... Action potential initiation and generation: A stimulus depolarizes the neurons membrane. ... Action potential initiation and generation: ... Propagation of the action potential: ... Repolarization: ... Repolarization:
What is the process of impulse?
A nerve impulse is the electric signals that pass along the dendrites to generate a nerve impulse or an action potential. An action potential is due to the movement of ions in and out of the cell. It specifically involves sodium and potassium ions.
What is the correct order of a nerve impulse?
The correct outline for the sequence of transmission of an electrical impulse through a neuron is dendrites, cell body, axon, axon terminal.
What is the correct order of nerve impulse conduction?
Thus, the correct answer is 'Cell body-Axon-Nerve terminal'.
What are the 4 steps of the synapse?
The process of synaptic transmission involves four steps:I. Synthesis and Storage. ... II. Neurotransmitter Release. ... III. Neurotransmitter Postsynaptic Receptors. ... IV. Inactivation of Neurotransmitters. ... Types of Neurotransmitters.
What are the 4 activities our nervous system controls?
Basic body functions. A part of the peripheral nervous system called the autonomic nervous system controls many of the body processes you almost never need to think about, like breathing, digestion, sweating, and shivering.
What are the first four steps at the synapse?
Synthesis and Storage; II. Release; III. Postsynaptic Receptors; IV. Inactivation.
What are the steps of the nerve pathway?
MatchStimuli.Sensory receptor.Sensory neuron.Interneuron of spinal cord.Sensory impulse carried to brain.Interpreted by the brain stem.Signs sent to cerebral cortex.Integration at the cerebral cortex.More items...
How does nerve impulses occur?
Conduction of nerve impulse occurs due to the presence of active and electronic potentials along the conductors. Transmission of signals internally between the cells is achieved through a synapse. Nerve conductors comprise relatively higher membrane resistance and low axial resistance. The electrical synapse has its application in escape reflexes, heart and in the retina of vertebrates. They are mainly used whenever there is a requirement of fast response and timing being crucial. The ionic currents pass through the two cell membrane when the action potential reaches the stage of such synapse.
What is the purpose of nerve impulses?
Conduction of Nerve Impulse. A nerve impulse is the electric signals that pass along the dendrites to generate a nerve impulse or an action potential. An action potential is due to the movement of ions in and out of the cell. It specifically involves sodium and potassium ions.
What is the action potential of a nerve?
The nerve fibres are either depolarized or they are said to be in the action potential. The action potential travelling along the membrane is called the nerve impulse. It is around + 30 mV. The sodium-potassium pump starts to operate once the action potential is completed.
How fast is the nerve impulse in white fibres?
That is impulse jumps from node to node and it increases with increase in the speed of nerve impulse. It is around twenty times faster compared to that of the non-medullated nerve fibres. The transmission of nerve impulse would rely upon the diameter of the fibre. For instance, the nerve impulse of a mammal is one twenty meters per second whereas nerve impulse of a Frog is 30 meters per second.
How many meters per second is a frog's nerve impulse?
For instance, the nerve impulse of a mammal is one twenty meters per second whereas nerve impulse of a Frog is 30 meters per second. 60,239. To learn more about nerve impulse, download BYJU’S-The Learning App. Learn Better through BYJU'S Quiz.
Where is the electrical synapse used?
The electrical synapse has its application in escape reflexes, heart and in the retina of vertebrates. They are mainly used whenever there is a requirement of fast response and timing being crucial. The ionic currents pass through the two cell membrane when the action potential reaches the stage of such synapse.
What is the reverse order of action potential?
Now the process takes place in reverse order. It is a reversal of the process that has taken place during an action potential . Here, potassium ions will be rushed inside and sodium ions will be rushed outside. Impulse would not be transmitted through the nerve fibre during the refractory period.
Why do nerve impulses occur?
A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
Which cell receives the nerve impulse?
The cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell, and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell. Some synapses are purely electrical and make direct electrical connections between neurons. However, most synapses are chemical synapses.
What is the presynaptic area of the cell?
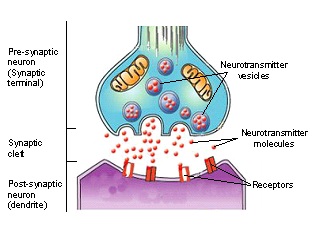
At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of the molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 11.4. 5, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called synaptic vesicles that are packed with chemicals called neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic cell, it opens channels that allow calcium to enter the terminal. Calcium causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane, releasing their contents into the narrow space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. This area is called the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter molecules travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors, which are proteins that are embedded in the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
How does neurotransmitter affect post-synaptic cells?
The effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends mainly on the type of receptors that it activates, making it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to have different effects on various target cells. A neurotransmitter might excite one set of target cells, inhibit others, and have complex modulatory effects on still others, depending on the type of receptors. However, some neurotransmitters have relatively consistent effects on other cells.
What happens when a neuron reaches a certain threshold?
The change in membrane potential results in the cell becoming depolarized.
What is action potential?
Action Potential. An action potential, also called a nerve impulse, is an electrical charge that travels along the membrane of a neuron. It can be generated when a neuron’s membrane potential is changed by chemical signals from a nearby cell.
Where do ion flows occur in myelinated neurons?
In myelinated neurons, ion flows occur only at the nodes of Ranvier. As a result, the action potential signal "jumps" along the axon membrane from node to node rather than spreading smoothly along the membrane, as they do in axons that do not have a myelin sheath.
What is the contribution of the resting membrane potential?
The main contribution to the resting membrane potential (a polarized nerve) is the difference in permeability of the resting membrane to potassium ions versus sodium ions. The resting membrane is much more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium ions resulting in slightly more net potassium ion diffusion ...
How does polarization occur?
Polarization is established by maintaining an excess of sodium ions (Na +) on the outside and an excess of potassium ions (K +) on the inside. A certain amount of Na + and K + is always leaking across the membrane through leakage channels, but Na +/K + pumps in the membrane actively restore the ions to the appropriate side.
What is resting potential?
Resting potential. The resting potential describes the unstimulated, polarized state of a neuron (at about –70 millivolts).
What happens when the K+ channels close?
Hyperpolarization. By the time the K + channels close, more K + have moved out of the cell than is actually necessary to establish the original polarized potential. Thus, the membrane becomes hyperpolarized (about –80 millivolts).
What is the transmission of nerve impulses?
The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron. The membrane of an unstimulated neuron is polarized—that is, there is a difference in electrical charge between the outside and inside of the membrane.
What happens to the Na+ membrane in response to a stimulus?
In response, Na + on the outside of the membrane becomes depolarized (as in a graded potential). If the stimulus is strong enough—that is, if it is above a certain threshold level—additional Na + gates open, increasing the flow of Na + even more, causing an action potential, or complete depolarization (from –70 to about +30 millivolts).
What happens when a stimulus opens a K+ channel?
A graded potential occurs when the stimulus causes Na + or K + gated channels to open. If Na + channels open, positive sodium ions enter, and the membrane depolarizes (becomes more positive). If the stimulus opens K + channels, then positive potassium ions exit across the membrane and the membranehyperpolarizes (becomes more negative).
What is the outer layer of myelin sheath needed for repair of damaged axons?
Neurilemma - outer layer of myelin sheath needed for repair of damaged axons.
What is the place where impulses are transmitted from one neuron to another?
The place where impulses are transmitted from one neuron to another (the postsynaptic neuron).
What is the difference between the exterior and interior of a resting neuron?
The exterior of a resting neuron has a slight _ charge, whereas the interior has a slight _ charge.
What is the meaning of "muscle coordination"?
Muscle coordination; maintenance of equilibrium and posture.
Where are Schwann cells located?
Schwann cells form myelin sheaths on axons of the PNS.
Which small cells move in inflamed brain tissue carrying on phagocytosis?
Microglia - small cells that move in inflamed brain tissue carrying on phagocytosis.