
What organelles are associated with vacuoles? Vacuoles
Vacuole
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though …
What is the central vacuole and what is its function?
The central vacuole is a large vacuole found inside of plant cells. A vacuole is a sphere filled with fluid and molecules inside a cell. The central vacuole stores water and maintains turgor pressure in a plant cell.
What organelles break down waste?
The organelles that contain digestive enzymes that break down waste material and debris in a cell in a cell are called lysosomes. Lysosomes are membrane-bound structures that will release digestive enzymes onto debris and waste materials in a cell to recycle the components of these structures.
What is the difference between a lysosome and a vacuole?
Vacuoles are fused membrane bound vesicles with a common outer membrane called tonoplast. They contain water containing organic and inorganic salts, sometimes in solid state also. Lysosomes are single-membrane bound organelles containing mainly digestive enzymes and pro-enzymes, along with their co-factors. 960 views View upvotes
What are facts about the central vacuole?
Central vacuole. The central vacuole is a cellular organelle found in plant cells. It is often the largest organelle in the cell. It is surrounded by a membrane and holds materials and wastes. It also keeps the proper pressure in the plant cells, and supports the growing plant.
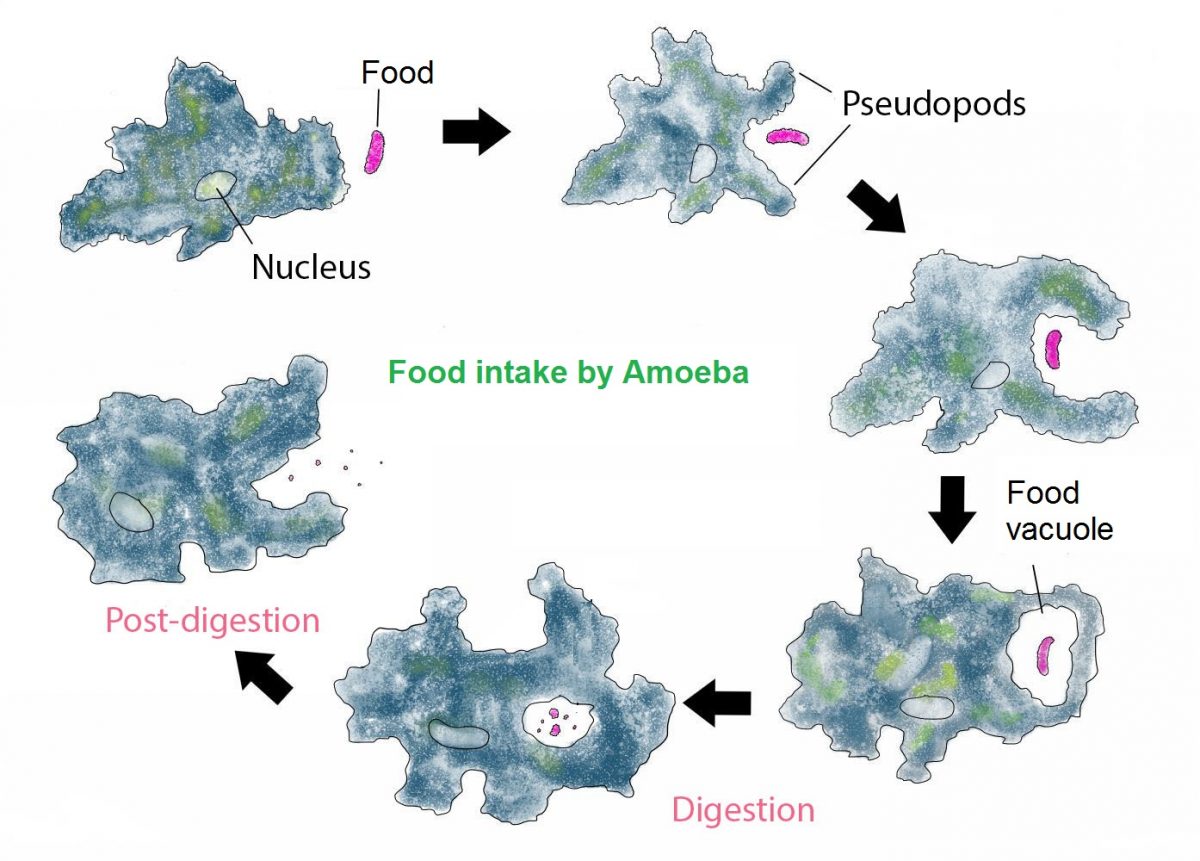
What cells do vacuoles work with?
0:281:54Vacuoles Function in Cells - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn addition to storing water vacuoles also store enzymes waste and even old damaged organelles.MoreIn addition to storing water vacuoles also store enzymes waste and even old damaged organelles. Let's take a look at the difference between a vacuole in a plant. And an animal cell on the left you'll
Do lysosomes work with vacuoles?
Lysosomes fuse with vacuoles and dispense their enzymes into the vacuoles, digesting their contents. They are built in the Golgi apparatus.
How do chloroplasts and vacuoles work together?
Photosynthesis is the production of nutrients from light energy, carbon dioxide, and water; it is how a plant makes its own food. By pushing chloroplasts closer to the surface of the cell, the central vacuole makes it possible for chloroplasts to take in more energy from sunlight.
How do vacuoles work with mitochondria?
Mitochondria are connected to the ER by ERMES and to the vacuole by vCLAMP. Lipids are imported into mitochondria through both contact sites (red arrows). Vacuoles obtain ER-synthesized lipids via Golgi-dependent vesicular traffic and possibly through direct contacts with the ER at the nucleus (N) vacuole junction.
Who do lysosomes work with?
Since lysosomes are little digestion machines, they go to work when the cell absorbs or eats some food. Once the material is inside the cell, the lysosomes attach and release their enzymes. The enzymes break down complex molecules that can include complex sugars and proteins.
What organelles do lysosomes work with?
lysosomes contain about 80% of the digestive enzymes. lysosomes are probably storage organelles for hydrolases which they keep in an inactive form under acidic conditions at about pH 5.0. lysosomes do not operate as independent organelles but meet with late endosomes to operate as an endolysosomal system.
How do the vacuole and cell wall work together?
The cell wall works with the central vacuole to maintain turgor pressure in plants. Cell walls are comprised of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate that provides both strength and flexibility to the plant cell.
How does the vacuole affect other organelles?
The vacuole interacts with other organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus. Vacuoles also play an important role in plant structure. Plants use cell walls to provide support and surround cells. The size of that cell may still increase or decrease depending on how much water is present.
What is the relationship between vacuole and cytoplasm?
Plant cells use vacuoles to adjust their size and turgor pressure. Vacuoles usually account for changes in cell size when the cytoplasmic volume stays constant. Some vacuoles have specialized functions, and plant cells can have more than one type of vacuole.
What two organelles work together?
Mitochondria and peroxisomes are closely linked through membrane contact sites. In the past, researchers verified the close relationship between the two organelles by studying their spatial structure by using a series of experimental methods [88, 101].
What organelles work with mitochondria?
Mitochondria interact with the endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, cytoskeleton, peroxisomes, and nucleus in several ways, ranging from signal transduction, vesicle transport, and membrane contact sites, to regulate energy metabolism, biosynthetic processes, apoptosis, and cell turnover.
What organelles work with the nucleus?
In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells may contain several other types of organelles, which may include mitochondria, chloroplasts, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Each of these organelles performs a specific function critical to the cell's survival.
How is lysosome related to vacuoles?
Lysosomes are like a specific type of vacuole. They hold the cell's digestive enzymes. When a cell takes in food through phagocytosis, the food vacuole fuses with the lysosome. The lysosome's enzymes will break down and digest the food, which can then be absorbed and used by the cell.
Is lysosome present in vacuole?
Lysosomes are predominantly found in eukaryotic animal cells and are responsible for breaking down cellular debris. In plants, the role of lysosomes is undertaken by the vacuoles as traditional cell biology dictates.
Why do lysosomes fuse with vacuoles?
Lysosome contains some digestive enzymes that help in digestion of food stored inside vacuoles. Moreover the undigested materials are broken down by the lysososmes only. For this reason lysosomes fuse with food vacuoles inside a cell and pass the digestive enzymes to the vacuole for digestion of food.
What is the function of lysosome and vacuole?
A lysosome, the cell organelle, is responsible for the breakdown of waste products of cells and is also known as the suicidal cell organelles of the cell. The main function of the vacuole is to maintain the osmotic or turgor pressure of the cell. They are responsible for the process of the intracellular digestion.
What is a vacuole?
Vacuole. Vacuole. =. A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products. In plant cells, vacuoles help maintain water balance. Sometimes a single vacuole can take up most of the interior space of the plant cell.
What is the function of vacuoles?
That is to say that their function is really to handle waste products, and by handle, mean take in waste products and also get rid of waste products.
Do humans have vacuoles?
The vacuoles are quite common in plants and animals, and humans have some of those vacuoles as well. But vacuole also has a more generic term, meaning a membrane-bound organelle that's lysosome-like. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
What are the toxins in the cell sap?
Lipids. Ions. The cell sap can also contain toxins that the vacuole has helped to remove from the rest of the cell. These toxins can operate as a self-defense mechanism for some plants against herbivores. The concentration of ions in the cell sap is a useful tool for moving water in and out of the vacuole via osmosis.
What is the vacuole of a plant cell?
Plant cells commonly contain one large vacuole that fills more space within the cell than any other organelle. The plant cell vacuole consists of the the tonoplast, which forms a sac around a fluid called cell sap. Cell sap contains water and a number of other substances. These can include:
What is the role of the vacuole in eukaryotic cells?
The Role of the Vacuole in Eukaryotic Cells. Eukaryotic cells include all cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells engage in cell division by the processes of mitosis and meiosis. By contrast, prokaryotic cells are typically unicellular organisms lacking any membrane-bound organelles, ...
What is the structure of a vacuole?
The Structure of the Vacuole. A vacuole is a kind of organelle called a vesicle. What differentiates vacuoles from other kinds of vesicles is its relative size and longevity. The vacuole is a sac surrounded by a single membrane called a tonoplast. This vacuole membrane structurally resembles the plasma membranes that surround every cell.
How does water move through the vacuole?
The concentration of ions in the cell sap is a useful tool for moving water in and out of the vacuole via osmosis. If the ion concentration is higher within the vacuole, water moves through the tonoplast into the vacuole. If the ion concentration is higher in the cytoplasm outside of the vacuole, water moves out of the vacuole. The vacuole enlarges or shrinks as water moves into or out of it.
Why is endocytosis important in animal cells?
Endocytosis is an important function for the vacuole in animal cells because it contributes to immunity from contagious disease. Vacuoles can bring bacteria and other microbes into cells while keeping the rest of the cell safe. Inside the vacuole, enzymes work on breaking down the dangerous pathogens.
What is the function of a vacuole?
In animal cells, they are small and typically transport materials into and out of the cell. In plant cells, vacuoles use osmosis to absorb water and swell until they create internal pressure against the cell wall. This provides cell stability and support.
What are Vacuoles?
The term “vacuole” means “empty space”. They help in the storage and disposal of various substances. They can store food or other nutrients required by a cell to survive. They also store waste products and prevent the entire cell from contamination.
What is the name of the force exerted by the vacuoles of the cell wall?
Turgor Pressure. The vacuoles are completely filled with water and exert force on the cell wall. This is known as turgor pressure. It provides shape to the cell and helps it to withstand extreme conditions.
What is the structure of the vacuole?
Structure of Vacuole. A vacuole is a membrane bound structure found in the cytoplasmic matrix of a cell. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast. The components of the vacuole, known as the cell sap, differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The membranes are composed of phospholipids.
What is the storage of salts in the vacuole?
Storage. A vacuole stores salts, minerals, pigments and proteins within the cell. The solution that fills a vacuole is known as the cell sap. The vacuole is also filled with protons from the cytosol that helps in maintaining an acidic environment within the cell. A large number of lipids are also stored within the vacuoles.
Why do plant cells have larger vacuoles?
The plant cells have larger vacuoles because they require more water, organic and inorganic components for the proper functioning of the cell.
Where are the substances stored in the cells?
The substances are taken in by a vacuole through endocytosis and excreted through exocytosis. These substances are stored in the cells, separated from the cytosol. Lysosomes are vesicles that intake food and digest it. This is endocytosis and it varies in different cells.
Which cell has more vacuoles than animal cells?
The vacuoles in plant cells are larger than those in the animal cells. The plant vacuoles occupy more than 80% of the volume of the cell. The vacuoles may be one or more in number.
What is the function of a contractile vacuole?
A contractile vacuole, as the name implies, functions mainly to expel water from the cell via contraction. It does this through to phases. The process of water entering the contractile vacuole is called diastole and the process of the expulsion of water from the contractile vacuole is called systole. The most well understood contractile vacuoles are found in the protist genera Paramecium, Amoeba, and Trypanosoma. The exact number of contractile vacuoles differ depending on the species. In protists, the contractile vacuole, along with associated structures such as membrane folds, tubules, and small vesicles, are know as the spongiome or alternatively the contractile vacuole complex (CVC). Most of the time, contractile vacuoles are found in protists that lack cell walls, though exceptions to this rule exist.
What is the vacuole of a paramecium?
The contractile vacuole of a Paramecium. The vacuole expels water by contracting via the assistance of motor proteins. Credit: Katyddd via WikiCommons CC-BY SA4.0
How do cyanobacteria control buoyancy?
Cyanobacteria have evolved a particularly nifty trick with their vacuoles. In cyanobacteria, vacuoles are freely permeable to gases. Cyanobacteria can control the amount of gas in the vacuole to control their buoyancy in water. If they need to go up, they let more gas in. If they need to go down, they let the gas out.
What is the function of the vacuole in plants?
The main function of vacuoles in plant cells is to provide hydrostatic pressure to give the cell structure. Central vacuoles fill up with water which pushes on the thick plant cell walls. This turgor pressure causes the plant to stand upright and gives the cells strength and rigidity. When water levels are low, the central vacuole deflates, releasing its pressure on the cell walls causing the plant to wilt. Proteins in the vacuole membrane control the flow of water in and out through the membrane, which causes water to flow in via osmosis. The loss of water from a plant vacuole in a hypertonic solution is called plasmolysis while the influx of water in a hypotonic solution is called cytolysis. Turgor pressure from the vacuole also pushes all the other organelles against the cell wall which keeps organelles like plasmids and chloroplasts closer to light.
What is a vacuole?
A vacuole is a cellular organelle present in all eukaryotic cells and some bacteria. Essentially, vacuoles are membrane-bound compartments that contain a liquid solution of enzymes. These membrane-bound compartments provide specialized environments for necessary biological processes.
How are vacuoles formed?
Vacuoles are made out of a phospholipid bilayer, the same kind of material that forms the outer cell membrane. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of smaller vesicles and are basically larger versions of these. The phospholipid bilayer allows vacuoles to engulf particles by enclosing them inside the membrane. The exact mechanism for vacuole biogenesis is not currently understood, though it is thought that they form via the fusion of vesicles that are secreted by the Golgi apparatus.
What happens when the vacuole is engulfed?
When waste materials are engulfed, the enzymes in the vacuole degrade the compounds and transport the waste materials out of the cell.
What is the disease of the vacuole?
Vacuole Diseases. This is a picture of a muscle cell infected with Danons disease. The vacuole is a very dangerous organelle. The malfunction of the vacuole can cause disease such as Danon disease. Danons disease is cause by mutations in the LAMP 2 gene which usually helps with the fusion of autophagic vacuoles and lysosomes.
Why is the vacuole not fit to be our chief?
The Vacuole is not fit enough to be our chief. If we have too much of the vacuole it can lead to serious diseases such as Danons disease. Too many vacuoles cause damage to the cell. This is why we should not vote for the vacuole to be our commander and chief.
How old do Danons die?
If there is a large amount of autophagic vacuoles then this leads to the breakdown of muscles cells which is shown in Danons disease. Males with Danons disease usually die at the young age of 19; while females usually die at the age of 31. The Vacuole is not fit enough to be our chief.
What do vacuoles store?
Vacuoles can store different substances depending on the type of cell they are in. For example, in fat cells, vacuoles will often store large amounts of lipids. Vacuoles in animal cells also help with the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis.
Why are vacuoles not needed in animal cells?
Vacuoles in animal cells mostly store substances; they aren’t needed as much for breaking down substances because lysosomes, another organelle in animal cells, do that. Animal cell vacuoles are typically small, and each cell can contain multiple vacuoles.
How do tonoplasts control turgor pressure?
Tonoplasts in vacuoles control turgor pressure by maintaining a particular balance of ions, which causes the vacuole to swell against the cell wall. Adjust size of the cell: Because vacuoles in plant cells can be so large, they are a key part in determining how large or small a certain plant cell is, which can in turn affect the size ...
What is the name of the vacuole that regulates the amount of water in a cell?
Protists contain a specific type of vacuole called a contractile vacuole. Instead of being used for storage, this vacuole regulates the amount of water in a cell (known as “osmoregulation”). Protists that live in freshwater can take too much water into their cells, causing them to rupture.
How does turgor pressure work?
Maintain turgor pressure: Turgor pressure is the pressure of the main area of the cell against the cell wall. It’s one of the ways plants and trees avoid being limp and grow tall and strong. Think of fresh, crisp salad greens vs. limp ones. The former have high turgor pressure. Tonoplasts in vacuoles control turgor pressure by maintaining a particular balance of ions, which causes the vacuole to swell against the cell wall.
How does the vacuole lower pH?
The vacuole lowers pH by moving protons from the cell cytosol into the vacuole. Store water: The vacuole can use proton motive force, a chemical gradient used to move materials in an out of the cell, to store water which allows the plant to survive longer in periods of drought. Maintain turgor pressure: Turgor pressure is the pressure ...
What is a vacuole?
What is a vacuole and what does it do? A vacuole is a structure found in animal, plant, bacteria, protist, and fungi cells. It’s one of the largest organelles found in cells, and it’s shaped like a large sac. Vacuoles have a simple structure: they are surrounded by a thin membrane and filled with fluid and any molecules they take in. They look similar to vesicles, another organelle, because both are membrane-bound sacs, but vacuoles are significantly larger than vesicles and are formed when multiple vesicles fuse together.
