What organisms are capable of alcoholic fermentation?
Zymomonas mobilis is the most important bacterial species that is able to perform alcoholic fermentation. The habitat of this species is the lymph of tropical trees, such as the palma tree from where it was originally isolated.
Which organism is used in the production of alcohol?
- If Starch and sugar are used as substrate then the fermentation organism used is Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Saccharomyces ellipsoideus.
- Fermentation of alcohol from dairy waste Candida pseudotropicalis is used.
- If the Sulphite waste liquor is used from the paper industry then Candida utilis strain is used for fermentation.
What do organism use alcoholic fermentation?
Alcoholic fermentation is the best known of the fermentation processes, and is involved in several important transformation, stabilization, and conservation processes for sugar-rich substrates, such as fruit, and fruit and vegetable juices. Alcoholic fermentation is carried out by yeasts and some other fungi and bacteria. The first step of the alcoholic fermentation pathway involves pyruvate ...
What is an organism that undergoes alchoholioc fermentation?
Alcoholic fermentation does not happen in humans. Yeast is a good example of an organism that undergoes alcoholic fermentation. The same process that goes on in the mitochondria during lactic acid fermentation also happens in alcoholic fermentation. The only difference is that the byproduct of alcoholic fermentation is ethyl alcohol.

What is the pathway of alcohol fermentation?
Alcoholic fermentation involves the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway, which was described by Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas around 1940 and is also known as glycolysis.
What is the best known process of fermentation?
Alcoholic fermentation is the best known of the fermentation processes, and is involved in several important transformation, stabilization, and conservation processes for sugar-rich substrates, such as fruit, and fruit and vegetable juices. Alcoholic fermentation is carried out by yeasts and some other fungi and bacteria.
How is GSH taken up by yeast?
GSH can be taken up by the yeast from the juice with a GSH transporter (Hgt1p) ( Bourbouloux et al., 2000 ). Once in the cell, it is used in many stress-response mechanisms such as oxidative stress, the detoxification of heavy metals, and nitrogen starvation. Later increases in GSH concentrations in the must may be due to active GSH intracellular production and secretion by the yeast. Such secreted GSH may then again be taken up by the yeast, leading to fluctuations observed during alcoholic fermentation. The exact mechanism of GSH export is not known, but a novel GSH exchanger, Gex1, located at both the vacuolar and plasma membrane was recently identified in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and seems to be involved ( Kritzinger et al., 2013b ).
What is the process of converting sugars into alcohol?
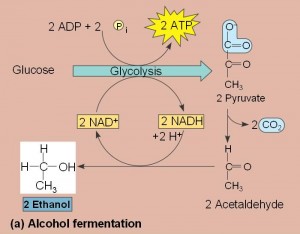
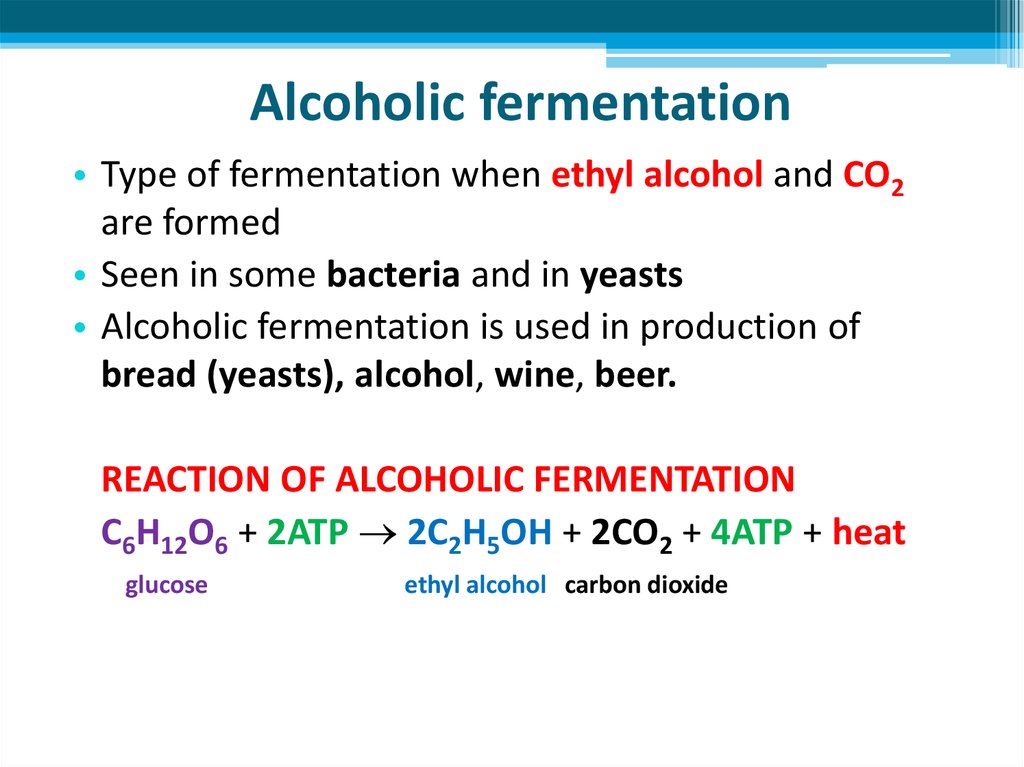
Alcoholic fermentation is a biotechnological process accomplished by yeast, some kinds of bacteria, or a few other microorganisms to convert sugars into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. In this fermentation process, yeast is mostly used as a bio-culture and aqueous solution of monosaccharide (raw materials) as the culture media for the production of beverages. In the alcoholic fermentation process, yeast generally carries out the aerobic fermentation process, but it may also ferment the raw materials under anaerobic conditions. In the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation occurs in the cytosol of yeast (Sablayrolles, 2009; Stanbury et al., 2013 ). Alcoholic fermentation begins with the breakdown of sugars by yeasts to form pyruvate molecules, which is also known as glycolysis. Glycolysis of a glucose molecule produces two molecules of pyruvic acid. The two molecules of pyruvic acid are then reduced to two molecules of ethanol and 2CO 2 ( Huang et al., 2015 ).
How much ATP is produced in alcoholic fermentation?
The ATP yield of alcoholic fermentation is 1 or 2 mol of ATP per mole of glucose oxidized via the ED and EMP pathways, respectively. Zymomonas mobilis is the most important bacterial species that is able to perform alcoholic fermentation.
How much glycerol is in wine?
Natural wines have glycerol content between 5 and 15 g/L. Acetic aldehyde accumulates in the first 2–3 days of fermentation, and the concentration varies between 40 and 50 mg/L. Aromatic aldehydes (benzoic aldehyde, vanillin, cinnamic aldehyde, acetone, diacetyl) are formed.
How much sugar is fermented in fermentation?
the main fermentation, about 80% of the initial sugar is fermented; and
What Is Alcohol Fermentation?
Bread, beer, and Bordeaux: most of us love some or all of these! But they would not exist if not for yeast, a eukaryotic microorganism that can metabolize sugars anaerobically through a pathway called alcohol fermentation. Humans have been using yeasts to make these products for thousands of years, but only learned of their existence in the last two hundred years. How exactly do these tiny creatures make these delicious food and drink items?
Where does yeast fermentation occur?
When no oxygen is readily available, alcohol fermentation occurs in the cytosol of yeast cells. Let's explore the process of alcohol fermentation then see what it means ...
Why is ethanol toxic to yeast?
Remember that from the yeast's perspective, fermentation is all about producing ATP, so the carbon dioxide and ethanol produced are byproducts. In fact, ethanol in high enough quantities is toxic for the yeast cells. This is why wine and beer have limited alcohol percentages: past a certain point, fermentation stops as the ethanol eliminates the very yeast that produced it. To produce liquor, which has a much higher alcohol content, distillation is used. By the time that distillation occurs, yeast and fermentation are no longer involved.
How much ATP does pyruvate produce?
The conversion of glucose to pyruvate creates a net total of 2 ATP. While this isn't as much ATP as aerobic respiration can produce, it's enough to keep the yeast alive until oxygen is available. This first part may look familiar because it's essentially glycolysis, or the first stage of aerobic respiration.
What is the basic equation for alcohol fermentation?
The basic equation for alcohol fermentation shows that yeast starts with glucose, a type of sugar, and finishes with carbon dioxide and ethanol. However, to better understand the process, we need to take a look at some of the steps that take us from glucose to the final products.
What happens when yeast is deprived of oxygen?
The process of fermenting alcohol occurs when yeasts are deprived of oxygen and, in turn, break down simple sugars that are then converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide. Learn more about the definition of fermentation and the organism responsible for it, and also the two-step process of alcohol fermentation. Updated: 10/26/2021
Where does pyruvate go in fermentation?
However, in alcohol fermentation, the pyruvate instead stays in the cytosol, the gooey interior space of the cell. This is where the second part of our reaction, the conversion of pyruvate to ethanol, will take place.
Where does fermentation take place?
As with glycolysis, fermentation takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. There are two different forms of fermentation— lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. Let's first take a look at lactic acid fermentation.
How does fermentation work?
Fermentation: An Introduction. Pause for a moment and take a deep breath in. As you do, air fills your lungs. Your lungs and bloodstream work to supply your cells with plenty of oxygen to generate the energy the cells need to function. Remember, cells use oxygen to generate usable energy, or ATP, from the food we eat.
What is the process of lactic acid fermentation?
Lactic Acid Fermentation. Most organisms carry out fermentation through a chemical reaction that converts the pyruvate from glycolysis into lactic acid or lactate. Lactic acid fermentation also converts NADH into NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue. The following diagram shows a summary of lactic acid fermentation.
Why do we need lactic acid?
Humans undergo lactic acid fermentation when the body needs a lot of energy in a hurry. When you are sprinting full speed, your cells will only have enough ATP stored in them to last a few seconds. Once the stored ATP is used, your muscles will start producing ATP through lactic acid fermentation.
What is the process of fermentation?
Fermentation is glycolysis followed by a process that makes it possible to continue to produce ATP without oxygen. G lycolysis is the first series of reactions that occur during cellular respiration. Glycolysis does not require oxygen to produce ATP.
How does fermentation help muscles?
Your muscles are forced to work without enough oxygen. In these situations, your working muscles generate ATP anaerobically (i .e., without oxygen) using a process called fermentation. Fermentation is beneficial in that it can generate ATP quickly for working muscle cells when oxygen is scarce.
Does yeast produce ethyl alcohol?
Yeast (a microscopic fungus) are also capable of both cellular respiration and fermentation. When yeast cells are kept in an anaerobic environment (i.e., without oxygen), they switch to alcoholic fermentation to generate usable energy from food. Like lactic acid fermentation, alcoholic fermentation generates NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to produce ATP. However, alcoholic fermentation in yeast produces ethyl alcohol instead of lactic acid as a waste product. Alcoholic fermentation also releases carbon dioxide.
What bacteria are involved in lactic acid fermentation?
Lactic acid bacteria are mainly involved in lactic acid fermentation and produce most of the lactic acids. But there are some bacteria and few fungi that use the lactic acid fermentation process. Let see the answer to what organisms use lactic acid fermentation.
Why is fungal fermentation important?
These fungi uses chemically defined medium that is why the purification process of the end products is quite simple. Therefore the fungal fermentation causes a great advantages in the food industry. These fungi produces ethanol and fumaric acid as by-products in lactic acid fermentation process. The production of these by-products results in lower ...
Why is yeast important in lactic acid fermentation?
Yeast is the key nutrient source for many fermentation processes to proceed. As a nutrient source, yeast is important because it can tolerate very low pH (1.5).
What are the two phyla of lactic acid bacteria?
But in taxonomic classification, Lactic Acid Bacteria are grouped into two distinct phyla like Firmicutes and Actinobacteria.
Which yeasts are genetically engineered to produce lactic acid?
Several yeast of species like Saccharomyces, Candida, Zygosaccharomyces, and Pichia are genetically engineered to produce larger amount of lactic acid. But the use of yeast in lactic acid fermentation process as nutrient source is very expensive.
Where are lactic acid bacteria found?
Lactic acid bacteria are mainly found in the products of milk, meats and plants. Lactic acid bacteria are classified into three group on the basis of end product of fermentation. They are obligate homofermenters, facultative heterofermenters and obligate heterofermenter.
Why is yeast important?
As a nutrient source, yeast is important because it can tolerate very low pH (1.5). Although the use of wild type yeast in lactic acid fermentation process causes a low production of lactic acids, the genetically modified yeast produces a higher amount of lactic acids.