
All animals have a true nervous system except sea sponges. Cnidarians, such as jellyfish, lack a true brain but have a system of separate but connected neurons called a nerve net. Echinoderms
Echinoderm
Echinoderm is the common name given to any member of the phylum Echinodermata of marine animals. The adults are recognizable by their radial symmetry, and include such well-known animals as starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilie…
What is the central nervous system?
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the most complex organ in the body and uses 20 percent of the total oxygen we breathe in. The brain consists of an estimated 100 billion neurons, with each connected to thousands more. The brain can be divided into four main lobes: temporal, parietal, occipital and frontal.
What are the different parts of the nervous system?
1 Central Nervous System– It consists of the brain and spinal cord. It’s location is in the head and continues along the back. ... 2 Peripheral Nervous System– It consists of all the nerves continuing from the central nervous system to the entire body. ... 3 Autonomous Nervous System– It is made up of both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
Do all animals with a central nervous system have brains?
Not all animals with a central nervous system have a brain, although the large majority do. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals.
What is an example of an organism with a divided nervous system?
Example: The organism which are divided on the basis of head and tail, then in them they have a web like nerve cell which is spreaded throughout the body. Organisms who have a well defined head, then their nervous system is divided into three parts, they are: the Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System, and Autonomous Nervous System.
Which organisms have a CNS?
The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts.
What two organism make up the central nervous system?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord.
What is the central nervous system in animals?
In all the vertebrates, the central nervous system comprises the brain and the spinal cord. The brain contains centres that process the signals received, regulate the homeostasis, and control emotions and intelligence. The spinal cord helps in the transfer of information to and from the brain.
Do all mammals have a CNS?
Abstract. Forty years since the initial discovery of neurogenesis in the postnatal rat hippocampus, investigators have now firmly established that active neurogenesis from neural progenitors continues throughout life in discrete regions of the central nervous systems (CNS) of all mammals, including humans.
Do plants have a central nervous system?
Although plants do not have a nervous system according to this phylogenetic definition, a growing body of botany research from the past 25 years shows that many plants transmit electrical signals to and from different parts of their bodies to respond to environmental stimuli.
Do jellyfish CNS?
Do they have brains? No, jellyfish have no single centralized brain. Instead, they have radially distributed nervous systems that are adapted to their unique body plan.
What animals do not have a CNS?
Sponges are the only multicellular animals without a nervous system. They do not have any nerve cells or sensory cells. However, touch or pressure to the outside of a sponge will cause a local contraction of its body.
Do pigs have a central nervous system?
The nervous system of the pig consists of four basic parts. The brain - The nervous tissue enclosed by the skull. Part of the central nervous system (CNS). It is covered completely by clear membranes called the meninges.
Do cows have a central nervous system?
The present study found detailed results in CNS embryology in cattle from 17 days, until late pregnancy. As demonstrated, the CNS has a complex system of anatomical and tissue differentiation.
Do all living things have a CNS?
The only multicellular animals that have no nervous system at all are sponges and microscopic bloblike organisms called placozoans and mesozoans.
Do fish have a CNS and PNS?
As with all invertebrates, the central nervous system of fish is composed of the spinal cord and brain, into which signals from the peripheral nervous system are delivered.
Do worms have a CNS?
It has a central and peripheral nervous system. Its central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve running along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment.
What is the central nervous system in dogs?
The central nervous system includes the spinal cord and the brain. The brain is divided into 3 main sections—the brain stem, which controls many basic life functions, the cerebrum, which is the center of conscious decision-making, and the cerebellum, which is involved in movement and motor control.
What is the central nervous function?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord: The brain controls how we think, learn, move, and feel. The spinal cord carries messages back and forth between the brain and the nerves that run throughout the body.
What is central nervous system in biology?
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord. Figure 11.5. 2 shows the central nervous system as one of the two main divisions of the total nervous system. The other main division is the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What are the 3 central nervous system?
The CNS has three main components: the brain, the spinal cord, and the neurons (or nerve cells).
What is the difference between the CNS and the peripheral nervous system?
Microscopically, there are differences between the neurons and tissue of the CNS and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is composed of white and gray matter. This can also be seen macroscopically on brain tissue. The white matter consists of axons and oligodendrocytes, while the gray matter consists of neurons and unmyelinated fibers.
Why is the CNS called the CNS?
The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals —i.e., all multicellular animals except sponges and jellyfish.
What is the CNS filled with?
Within the CNS, the interneuronal space is filled with a large amount of supporting non-nervous cells called neuroglia or glia from the Greek for "glue". In vertebrates the CNS also includes the retina and the optic nerve ( cranial nerve II), as well as the olfactory nerves and olfactory epithelium.
What are the parts of the CNS?
In vertebrates the CNS also includes the retina and the optic nerve ( cranial nerve II), as well as the olfactory nerves and olfactory epithelium. As parts of the CNS, they connect directly to brain neurons without intermediate ganglia. The olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue outside the meninges in direct contact with the environment, which opens up a pathway for therapeutic agents which cannot otherwise cross the meninges barrier.
What is the midbrain?
The midbrain, or mesencephalon, is situated above and rostral to the pons. It includes nuclei linking distinct parts of the motor system, including the cerebellum, the basal ganglia and both cerebral hemispheres, among others. Additionally, parts of the visual and auditory systems are located in the midbrain, including control of automatic eye movements.
What are the diseases of the CNS?
There are many CNS diseases and conditions, including infections such as encephalitis and poliomyelitis, early-onset neurological disorders including ADHD and autism, late-onset neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and essential tremor, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, genetic disorders such as Krabbe's disease and Huntington's disease, as well as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and adrenoleukodystrophy. Lastly, cancers of the central nervous system can cause severe illness and, when malignant, can have very high mortality rates. Symptoms depend on the size, growth rate, location and malignancy of tumors and can include alterations in motor control, hearing loss, headaches and changes in cognitive ability and autonomic functioning.
How many genes are involved in the nervous system of planarians?
The nerves projecting laterally from the CNS form their PNS. A molecular study found that more than 95% of the 116 genes involved in the nervous system of planarians, which includes genes related to the CNS, also exist in humans.
What are the three membranous coverings that protect the spinal cord and brain?
These meninges are called pia mater, arachnoid mater and dura mater. Pia mater is the layer closest to the nervous tissue and dura mater lies next to the bone.
How many segments does the spinal cord have?
It can be divided into 31 segments, each giving rise to a pair of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves carry both sensory and motor signals between the body and the spinal cord. The central part of the spinal cord consists of an H-shaped grey column containing the cell bodies of spinal cord neurons.
How does the CNS affect the skeletal muscle?
Based on these stimuli, the CNS alters skeletal muscle contraction. Once infants learn to walk, this happens involuntarily, no longer requiring conscious thought or concentration. A similar process of receiving complex stimuli and generating a coordinated response is required for vastly varied activities – whether it is balancing a bicycle, maintaining a conversation or mounting an immune response.
How does the CNS regulate the body?
For instance, long-term and short-term metabolism and homeostasis are regulated through close interaction between the central nervous system and the endocrine system.
What is the CNS response?
The CNS receives input from a variety of different sources, and implements an appropriate response to the stimuli, in a co hesive manner. For instance, in order to walk the CNS needs visual and integumentary cues – the texture of the surface, its incline, the presence of obstacles, and so forth.
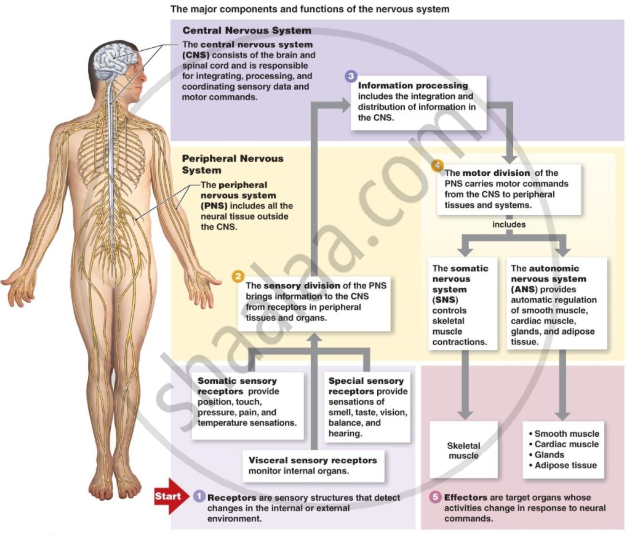
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. This body system is responsible for integrating and coordinating the activities of the entire body. Through these physical structures, thought, emotion, and sensation are experienced, and body movements are coordinated.
Why is the CNS important?
The key to the work of the CNS is integration. It receives input from various sources and creates a cohesive response. This is particularly important for animals in complex social structures, like human beings. For instance, meeting an old friend and catching up over coffee can seem like a relaxing event.
What are the two types of nerve fibers?
Peripheral nervous system has two types of nerve fibers: A. Afferent nerve fibers – These nerve fibers are responsible for transmission of messages from tissues and organs to the central nervous system. B. Different nerve-fibers – These nerve fibers are responsible for sending messages from CNS to the corresponding peripheral organ.
How do animals detect the nervous system?
Nervous system structure can be detected by studying the body plan of the organism body. Example: The organism which are divided on the basis of head and tail, then in them they have a web like nerve cell which is spreaded throughout the body. Organisms who have a well defined head, then their nervous system is divided into three parts, they are: the Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System, and Autonomous Nervous System.
What are the three parts of the nervous system?
Organisms who have a well defined head, then their nervous system is divided into three parts, they are: the Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System, and Autonomous Nervous System.
Which structure connects the brain to the spine?
This spine connects all parts of the human body to the brain. It starts in continuation with the medulla and extends towards downward direction. It is covered by a bony cage called the vertebral column and surrounded by a membranous structure known as meninges. 2. Peripheral Nervous System– It consists of all the nerves continuing from ...
What is the shortest fiber in the cell?
Neurons are known as structural and functional units of the nervous system. It is of irregular shape and has the capability to conduct electrical signals. Neurons are further divided into different parts, which are discussed below: A. Dendrite: It is the shortest fiber in the cell and extends out from the cell body of a neuron.
What is the brain's function?
It controls all the functions of the nervous system, which help in getting messages and giving response to the human body. Human brain is covered by the skull, which provides protection from the frontal, lateral and dorsal side. The human brain is further divided into three major parts:
Which part of the nervous system connects the CNS to the rest of the body?
2. Peripheral Nervous System – It consists of all the nerves continuing from the central nervous system to the entire body. It is the lateral most part of the human nervous system which helps in connecting different parts of the body with CNS.
What neuronal circuits are involved in the knee jerk reflex?
The simplest neuronal circuits are those that underlie muscle stretch responses, such as the knee-jerk reflex that occurs when someone hits the tendon below your knee (the patellar tendon) with a hammer. Tapping on that tendon stretches the quadriceps muscle of the thigh, stimulating the sensory neurons that innervate it to fire. Axons from these sensory neurons extend to the spinal cord, where they connect to the motor neurons that establish connections with (innervate) the quadriceps. The sensory neurons send an excitatory signal to the motor neurons, causing them to fire too. The motor neurons, in turn, stimulate the quadriceps to contract, straightening the knee. In the knee-jerk reflex, the sensory neurons from a particular muscle connect directly to the motor neurons that innervate that same muscle, causing it to contract after it has been stretched. Image credit: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/ap-biology/human-biology/neuron-nervous-system/a/overview-of-neuron-structure-and-function, modified from “Patellar tendon reflex arc,” by Amiya Sarkar (CC BY-SA 4.0). The modified image is licensed under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license.
Why are reflexes so fast?
Reflexes are so fast because they involve local synaptic connections in the spinal cord , rather than relay of information to the brain. For example, the knee reflex that a doctor tests during a routine physical is controlled by a single synapse between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. While a reflex may only require the involvement of one or two synapses, synapses with interneurons in the spinal column transmit information to the brain to convey what happened after the event is already over (the knee jerked, or the hand was hot). So this means that the brain is not involved at all in the movement associated with the reflex, but it is certainly involved in learning from the experience – most people only have to touch a hot stove once to learn that they should never do it again!
How many different classes of neurons are there in the nervous system?
There are three different classes of neurons that make up the nervous system:
What is the nervous system made of?
The nervous system is made up of neurons, specialized cells that can receive and transmit chemical or electrical signals , and glia, cells that provide support functions for the neurons by playing an information processing role that is complementary to neurons. Nerves are bundles of nervous tissue, often containing hundreds to thousands of axons wrapped in connective tissue. Nerves in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) carry information to and from neurons in the the central nervous system (CNS), where information is integrated and processed.
What are the parts of the vertebrate brain?
The vertebrate brain includes the cerebrum, cerebral cortex, diencephalon, cerebellum, and the brain stem . Image credit: OpenStax Biology.
Where are the interneuons located?
Interneuons, which are found only in the CNS , connect one neuron to another. They receive information from other neurons (either sensory neurons or interneurons) and transmit information to other neurons (either motor neurons or interneurons).
How many hemispheres are there in the cortex?
The cortex is made up of two hemispheres (right and left) and four lobes ( frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital ). The two hemispheres are joined by a thick fiber bundle called the corpus callosum (Latin: “tough body”) which connects the two hemispheres and allows information to be passed from one side to the other.
How many spinal cords are there?
Spinal cord: The spinal cord proper extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebrae. It creates a two-way pathway between the brain and the body and divides into four regions - cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. These regions are then broken down into 31 segments with 31 pairs of spinal nerves. There are 8 cervical nerves, 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, 5 sacral nerves, and 1 coccygeal nerve. Each nerve exits the vertebral column passing through the intervertebral foramina and to its designated location in the body.
What is the function of the spinal cord?
The purpose of the spinal cord is to send motor commands from the brain to the peripheral body as well as to relay sensory information from the sensory organs to the brain. Spinal cord protection is by bone, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluids.
Where does sensory information travel?
Ascending pathway to the brain: Sensory information travels from the body to the spinal cord before reaching the brain. This information ascends upwards using first, second, and third-order neurons. First-order neurons receive impulses from skin and proprioceptors and send them to the spinal cord. They then synapse with second-order neurons. Second-order neurons live in the dorsal horn and send impulses to the thalamus and cerebellum. Lastly, third-order neurons pick up these impulses in the thalamus and relay it to the somatosensory portion of the cerebrum. Somatosensory sensations are pressure, pain, temperature, and the body's senses.
What is the difference between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system?
The nervous system subdivides into the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of everything else. The central nervous system's responsibilities include receiving, processing, and responding to sensory information.
What is the brain responsible for?
The brain is an organ of nervous tissue that is responsible for responses, sensation, movement, emotions, communication, thought processing, and memory. Protection for the human brain comes from the skull, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluids. The nervous tissue is extremely delicate and can suffer damage by the smallest amount of force. In addition, it has a blood-brain barrier preventing the brain from any harmful substance that could be floating in the blood.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Where is the pons located?
Pons: Found in the brainstem, the pons connects the medulla oblongata and the thalamus. It is composed of tracts responsible for relaying impulses from the motor cortex to the cerebellum, medulla, and thalamus.

Summary
Development
During early development of the vertebrate embryo, a longitudinal groove on the neural plate gradually deepens and the ridges on either side of the groove (the neural folds) become elevated, and ultimately meet, transforming the groove into a closed tube called the neural tube. The formation of the neural tube is called neurulation. At this stage, the walls of the neural tube contain proliferating neural stem cells in a region called the ventricular zone. The neural stem cell…
Overview
In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolved in the blood, protecting the brain from most neurotoxins commonly found in food. Within the meninges the brain and spinal cord are bathed in cerebral spinal fluid which replaces the body fluid found outside the cells of all bilateral animals.
In vertebrates, the CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain is housed in the cranial …
Structure
The CNS consists of two major structures: the brain and spinal cord. The brain is encased in the skull, and protected by the cranium. The spinal cord is continuous with the brain and lies caudally to the brain. It is protected by the vertebrae. The spinal cord reaches from the base of the skull, and continues through or starting below the foramen magnum, and terminates roughly level with the first or second lumbar vertebra, occupying the upper sections of the vertebral canal.
Clinical significance
There are many CNS diseases and conditions, including infections such as encephalitis and poliomyelitis, early-onset neurological disorders including ADHD and autism, seizure disorders such as epilepsy, headache disorders such as migraine, late-onset neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and essential tremor, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, genetic disorder…
External links
• Overview of the Central Nervous System at the Wayback Machine (archived 2012-02-18)
• High-Resolution Cytoarchitectural Primate Brain Atlases
• Explaining the human nervous system.
• The Department of Neuroscience at Wikiversity