Mouth
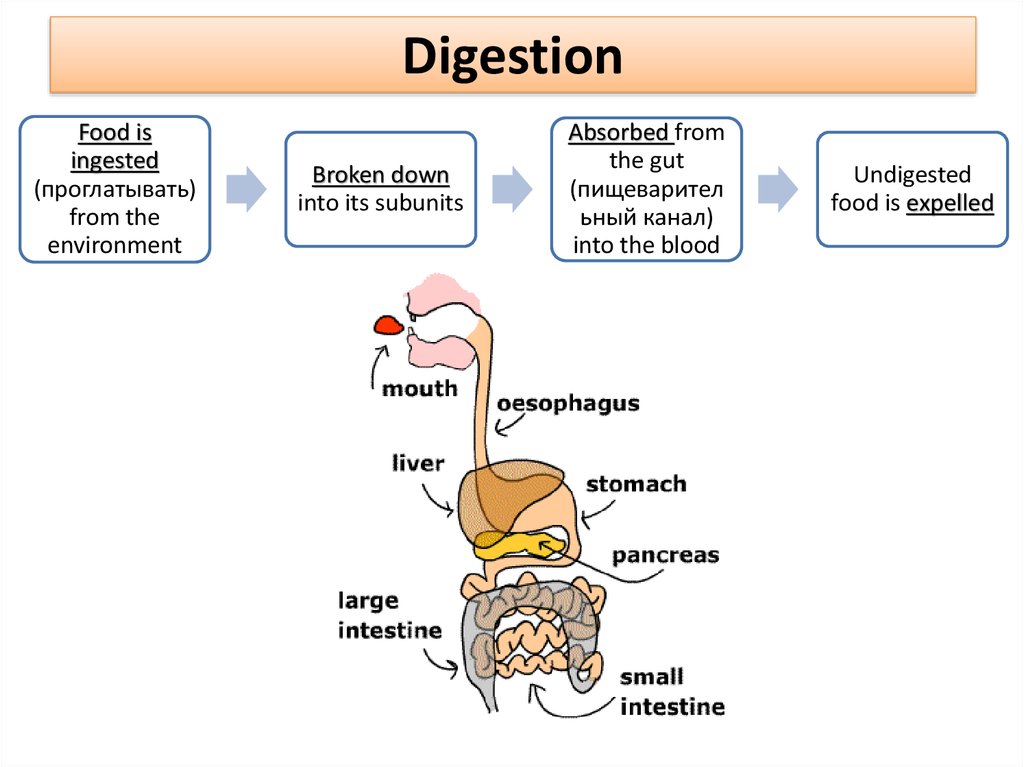
The main organs that make up the digestive system (in order of their function) are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. Helping them along the way are the pancreas, gall bladder and liver. Here’s how these organs work together in your digestive system.
Esophagus
We all know the importance of a healthy digestive system in the human body. The system comprises the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and the anus. These hollow organs are interconnected to form the digestive system, that helps the body in breaking down the food we eat and absorb the nutrients in it.
Stomach
Vital Organs
- Brain. The human brain serves as the body’s command and control centre, receiving and transmitting signals to other organs via the nervous system and secreted hormones.
- Heart. The human heart is in charge of pumping blood throughout our bodies.
- Kidney. The kidneys’ function is to remove waste and excess fluid from the blood. ...
- Liver. ...
- Lungs. ...
Small intestine
Shikha Goyal
- Mouth. Food is ingested to mouth. ...
- Oesophagus or Food Pipe. The slightly digested food goes to the stomach through the Food Pipe or Oesophagus. ...
- Stomach. Do you know that food is churned in the stomach for three hours? ...
- Small Intestine. The small intestine is a long, thin tube about 1 inch in diameter and about 10 feet long. ...
- Large Intestine. ...
Colon
Which organs and structures carry out digestion?
What organs can affect the digestive system?
Which organs are vital in the digestive system?
What organs assist digestion?

What are the main organs of the digestive system?
The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are the solid organs of the digestive system. The small intestine has three parts. The first part is called the duodenum. The jejunum is in the middle and the ileum is at the end. The large intestine includes the appendix, cecum, colon, and rectum.
How does the digestive system help the body?
Each part of your digestive system helps to move food and liquid through your GI tract, break food and liquid into smaller parts, or both. Once foods are broken into small enough parts, your body can absorb and move the nutrients to where they are needed.
Why is digestion important?
Digestion is important because your body needs nutrients from food and drink to work properly and stay healthy. Proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins. , and water are nutrients. Your digestive system breaks nutrients into parts small enough for your body to absorb and use for energy, growth, and cell repair. .
What breaks down nutrients into small parts?
Your digestive system breaks nutrients into parts small enough for your body to absorb and use for energy, growth, and cell repair. Proteins break into amino acids. Fats break into fatty acids and glycerol. Carbohydrates break into simple sugars.
What muscle is used to make food pass through the esophagus?
Once you begin swallowing, the process becomes automatic. Your brain signals the muscles of the esophagus and peristalsis begins. Lower esophageal sphincter. When food reaches the end of your esophagus, a ringlike muscle—called the lower esophageal sphincter —relaxes and lets food pass into your stomach.
What muscle moves food forward?
The muscle behind the food contracts and squeezes the food forward, while the muscle in front of the food relaxes to allow the food to move. The digestive process starts when you put food in your mouth. Mouth. Food starts to move through your GI tract when you eat.
What is the digestive system made of?
The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract —also called the GI tract or digestive tract—and the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus.
What organs are in the digestive system?
The digestive tract includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and anus. So-called "accessory" organs include the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder;
Which organs are essential to digestion?
So-called "accessory" organs include the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder; food doesn't move through these organs, but they secrete hormones and chemicals that are essential to digestion. 1 Here's what to know about your digestive system organs and functions.
What is the gallbladder made of?
Tucked under the liver, your gallbladder is a storage container for bile, a yellow-green fluid made up of salts, cholesterol, and lecithin. Your small intestine uses bile to digest fats. 1
What is the name of the enzymes that digest food?
Inside your stomach, food is mixed with enzymes and acid until it becomes a liquid, called chyme. The stomach is the main site for protein digestion and uses powerful enzymes, known as pepsins, as well as hydrochloric acid, to digest foods like meats, milk, and cheese.
What are the parts of the small intestine?
The small intestine is an approximately 20-foot-long muscular tube, which is divided into three distinct parts: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. 5 Each of the three parts plays a major role in digestion and absorption.
What does the small intestine produce?
First, it produces bile, which the small intestine uses to help digest the fats in food. It also metabolizes proteins, carbohydrates, and fats; helps regulate blood sugar levels; stores glycogen for quick energy; makes fibrinogen, which clots blood; makes vitamin A; and recycles worn-out red blood cells. 1.
Why is my large intestine sore?
Problems with your large intestine can be caused by diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis as well as celiac disease. If parts of these organs become seriously diseased, they may require surgical removal.
What are the three digestive organs?
Three accessory digestive organs (pancreas, liver, gallbladder) 1 Pancreas: Although the pancreas is mostly known for its blood sugar regulatory function with the production of insulin (as part of the endocrine system -- he insulin goesdirectly from the gland into the bloodstream), it is the main producer of digestive enzymes as part of the exocrine system (the enzymes produced by the gland pass through a duct into the intestines ). These enzymes are released into the duodenum and help with the digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.. 2 Liver: The liver produces bile for fat digestion and elimination. In addition, nutrients are stored in the liver, and toxins and chemicals are filtered by liver. 3 Gallbladder: Bile is stored and released from the gallbladder. When fatty food enters the duodenum, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile.
What is the digestive system?
The digestive system involves organs that turn food into energy and eliminate waste. The energy required for all the processes and activities that take place in our bodies is derived from the foods we ingest. The digestive system allows us to utilize food from such diverse sources as meat from an animal and the roots of a plant, ...
What is the main mechanism by which food moves through the digestive system?
Peristalsis is the main mechanism by which food moves through our digestive system. Once the food approaches the stomach, a muscular valve (the lower esophageal sphincter) relaxes and lets the food pass into the stomach. This sphincter has the important function of closing the stomach so no food or stomach acid reenters the esophagus ...
Why is the digestive system important?
Whether it is the ability to coordinate the chewing of the food without injuring our tongue and lips or the propulsion of the food from the stomach into the duodenum while releasing the appropriate enzymes, our digestive system allows us to manage the process without much thought and often while performing other tasks.
How long is the colon?
The large intestine (colon) has four parts: ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and. sigmoid colon. All together the colon is approximately 7 feet long and connects to the rectum. Here as in most other parts of the GI system, the waste product is moved along by peristalsis.
How long does it take for food to be excreted?
The time it takes for food to travel from entering the mouth to be excreted as waste is around 30 to 40 hours.
Which part of the digestive system is responsible for the absorption of nutrients from processed food into the bloodstream?
The first segment is the duodenum where further breakdown of the food takes place. The next two parts of the small intestine (jejunum and ileum) are mostly responsible for the absorption of nutrients from the processed food into the bloodstream through the walls of the intestine.
What is the digestive system?
The digestive tract (or gastrointestinal tract) is a long twisting tube that starts at the mouth and ends at the anus. It is made up of a series of muscles that coordinate the movement of food and other cells that produce enzymes and hormones to aid in the breakdown of food. Along the way are other 'accessory' organs that are needed ...
What organ holds food?
The stomach is a sac-like organ with strong muscular walls. In addition to holding food, it serves as the mixer and grinder of food. The stomach secretes acid and powerful enzymes that continue the process of breaking the food down and changing it to a consistency of liquid or paste.
How does stool pass through the colon?
As stool passes through the colon, any remaining water is absorbed.
What is the small intestine made of?
Made up of three segments -- the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum -- the small intestine also breaks down food using enzymes released by the pancreas and bile from the liver.
How does food get into the stomach?
Food is pushed through the esophagus and into the stomach by means of a series of contractions called peristalsis. Just before the opening to the stomach is an important ring-shaped muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This sphincter opens to let food pass into the stomach and closes to keep it there.
Which organ is the work horse of digestion?
The small intestine is the 'work horse' of digestion, as this is where most nutrients are absorbed. Peristalsis is also at work in this organ, moving food through and mixing it up with the digestive secretions from the pancreas and liver, including bile.
Where does bile go when you don't need it?
If the intestine doesn't need it, the bile travels into the gallbladder, where it awaits the signal from the intestines that food is present. Bile serves two main purposes. First, it helps absorb fats in the diet, and secondly, it carries waste from the liver that cannot go through the kidneys.
Which organs are involved in the digestion process?
The mouth further contains three basic organs – the salivary glands, tongue and the teeth.
What organ guides the food?
This primary organ of taste has much more to it than just taste buds. It helps in the chewing and swallowing process which is also known as deglutition. The tongue guides the food and keeps it between the upper and lower teeth. The masticated food, called bolus is then swallowed.
Why is the small intestine called the small intestine?
However, it is called the small intestine because it has a smaller diameter than the large intestine. The main purpose of the small intestine is to absorb nutrients from the food during digestion. It is made up of three parts – the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum.
What is the function of the large intestine?
Its main function is to absorb the remaining water from the indigestible food matter and pass unwanted waste matter from the body. The large intestine is divided into three parts – the cecum, the colon and the rectum.
What is the function of the duodenum?
The main function of the duodenum is to break down the food using enzymes secreted by the pancreas and bile secreted by the liver. Jejunum: The jejunum is the mid-section of the small intestine. The most important function of this organ is the absorption of carbohydrates and proteins.
What organs are responsible for the production of saliva?
When our primary organs like the eyes, nose, and ears sense the presence of food, they alert the other organs to start the production of saliva and different digestive juices which are vital for digestion. Digestion is the process of breaking down food into smaller molecules, that can be easily absorbed by the body to use as energy to build ...
What organ breaks down fats and carbohydrates?
Pancreas. The pancreas secrete enzymes into the duodenum which breaks down the fats, carbohydrates, and protein. Another important function of the pancreas is to make insulin that is the chief hormone for metabolizing sugar. Together, the above organs, with their respective functions, help keep our body working.
What is the digestive system?
The digestive system is one of the most important systems in our body. Its primary function is to turn food into energy needed to get through the day and pass the waste disposal the body is not needed. Now that you have known how important the digestive system is, let us get acquainted with it even more. To help us better understand how it works;
What is the largest organ in the digestive system?
Colon (large intestine) One of the most important digestive system organs is the colon or large intestine. As a part of the final stages of digestion, it is a large muscular tube which escorts waste from the body. Colon is much wider than the small intestine, but is also much shorter, around 6 feet (1.8m) long.
How does the digestive system work?
This is where the digestive system begins. As a matter of fact, digestion begins in the mouth even before you take that first bite. When you smell the food, your mouth drools as it secretes saliva triggered by the salivary glands. When you actually put that food in your mouth, the saliva increases. More saliva is produced as you try to chew and break down the food. This is when the process of food breakdown into a form that your body can absorb starts.
What is the small intestine?
The small intestine is a 22-foot long muscular tube that is made up of three parts – the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. It is called the “work horse” of digestion, where 90% of the digestion and absorption occurs while the other 10% takes place in the stomach and large intestine.
What organ connects the colon and the anus?
Rectum. This organ connects the colon and the anus. Rectum’s primary function is to receive the stool from the colon, send a signal to the person that he needs to evacuate the stool and holds the stool until defecation happens.
What organs are responsible for secreting bile?
Liver. This organ performs several functions in the body, but two of its most important functions are to secrete bile and process the blood coming from small intestine that contains the nutrients.
What is the final part of the digestive system that allows fossils to excrete from the human body?
Anus. Anus is the final part of the digestive system which allows the fossils to excrete from human body. Its primary job is to regulate waste discharge and indigestible substances out of the body. It is consist of:
What are the organs that make up the digestive system?
The solid organs — pancreas, liver, and gallbladder — add various products into the mix. Aside from the solid and hollow organs, the nervous and circulatory systems are also important in digestion, as are the bacteria that live in the gut. Digestion is often broken down into two types:
What is the digestive system?
In a nutshell, digestion involves breaking down large food molecules into water-soluble molecules that can be passed into the blood and transported to the body’s organs. For instance, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, proteins into amino acids, and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
What is the process of digestion that starts with saliva?
Once the food is inside the mouth, it is moistened by saliva, and the teeth and tongue begin the process of mechanical digestion . Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch.
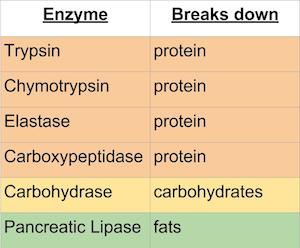
What enzymes digest protein?
Protein — digested by three enzymes called pepsin (in the stomach), trypsin , and chymotrypsin (in the duodenum, secreted by the pancreas). Fat — lingual lipase begins fat digestion in the mouth. However, most fat is broken down in the small intestine by pancreatic lipase.
What is the slow contraction of smooth muscles around the pipes of the digestive system?
Peristalsis. Peristalsis is the slow contraction of smooth muscles around the pipes of the digestive system. Slow waves of contraction run along the gut, pushing the bolus along in the right direction — away from the mouth and toward the anus.
What are the two types of digestion?
Digestion is often broken down into two types: 1 Mechanical digestion — food is physically broken into smaller parts. For instance, by chewing. 2 Chemical digestion — food is broken down by acids and enzymes into its basic units.
What is the hormone control of digestion?
Hormonal control of digestion. Digestion is a complex process that requires different organs to make moves at the right time. For instance, the right enzymes need to be squirted into the right place at the right time and in the right amounts.