
Full Answer
What was Hamilton's plan for the financial system?
Hamilton’s Financial System. Hamilton, therefore, believed that the federal government must be “a Repository of the Rights of the wealthy.” As the nation’s first secretary of the treasury, he proposed an ambitious financial plan to achieve that. The first part of Hamilton’s plan involved federal “assumption” of state debts,...
Why did Hamilton want a bank in the US?
With the bank, he wished to solidify the partnership between the government and the business classes who would benefit most from it and further advance his program to strengthen the national government. After Congress passed the bank charter, Hamilton persuaded Washington to sign it into law.
What was Hamilton’s third report on a National Bank?
Hamilton’s third report, the Report on a National Bank, which he submitted on December 14, 1790, advocated a national bank called the Bank of the United States and modeled after the Bank of England.
Why did Hamilton think the government should protect the rich?
If the rich needed the government, then they would direct their energies to making sure it remained solvent. Hamilton, therefore, believed that the federal government must be “a Repository of the Rights of the wealthy.” As the nation’s first secretary of the treasury, he proposed an ambitious financial plan to achieve that.
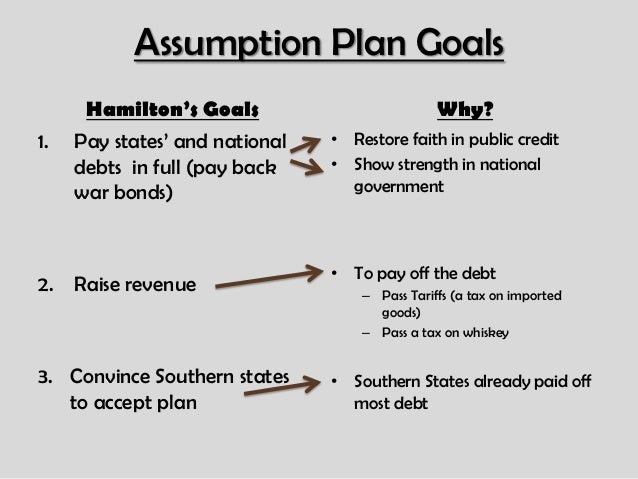
What part of his financial plan does Hamilton get?
Hamilton issued a bold proposal. The federal government should pay off all Confederation (state) debts at full value. Such action would dramatically enhance the legitimacy of the new central government. To raise money to pay off the debts, Hamilton would issue new securities bonds).
What did Hamilton's financial plan lead to?
The paramount problem facing Hamilton was a huge national debt. He proposed that the government assume the entire debt of the federal government and the states. His plan was to retire the old depreciated obligations by borrowing new money at a lower interest rate.
What were the 4 parts of Hamilton's economic plan?
Terms in this set (51) 1790-1791: tries to stable American finances. 1) Assumption of State debts 2) Creation of a National Bank 3) Promotion of the manufacturing industry. First two are passed.
What were the 3 parts of Hamilton's financial plan?
The three steps were breaking away from Britain, creating a national bank, and assuming the states' debt.
What were the three main parts of Hamilton's financial plan?
Its three major components were the federal assumption of state debts, the creation of a Bank of the United States, and support for the nation's emerging industries.
What policy did Hamilton want?
Rather than accept this condition, Hamilton wanted the United States to adopt a mercantilist economic policy . This would protect American manufacturers through direct government subsidies (handouts to business) and tariffs (taxes on imported goods). This protectionist policy would help fledgling American producers to compete with inexpensive European imports.
What was Hamilton's vision for the economy?
Hamilton's vision for reshaping the American economy included a federal charter for a national financial institution. He proposed a Bank of the United States. Modeled along the lines of the Bank of England, a central bank would help make the new nation's economy dynamic through a more stable paper currency.
Why did Hamilton favor a strong central government?
Hamilton favored an even stronger central government than the Constitution had created and often linked democratic impulses with potential anarchy. Finally, because the beneficiaries of his innovative economic policies were concentrated in the northeast, they threatened to stimulate divisive geographic differences in the new nation.
Why did Alexander Hamilton create the first bank of the United States?
Alexander Hamilton conceived of the First Bank of the United States as a way to standardize American currency and cope with national Revolutionary War debt.
What was Hamilton's bold proposal?
Hamilton issued a bold proposal. The federal government should pay off all Confederation (state) debts at full value. Such action would dramatically enhance the legitimacy of the new central government. To raise money to pay off the debts, Hamilton would issue new securities bonds). Investors who had purchased these public securities could make enormous profits when the time came for the United States to pay off these new debts.
What was Hamilton's first issue?
The first issue that Hamilton tackled as Washington's secretary of the treasury concerned the problem of public credit. Governments at all levels had taken on so much debt during the Revolution. The commitment to pay them back was not taken very seriously. By the late 1780s, the value of such public securities had plunged to a small fraction of their face value. In other words, state IOU's — the money borrowed to finance the Revolution — were viewed as nearly worthless.
What was the biggest problem facing the first federal government?
A major problem facing the first federal government was how to deal with the financial chaos created by the American Revolution. States had huge war debts. There was runaway inflation. Almost all areas of the economy looked dismal throughout the 1780s. Economic hard times were a major factor creating the sense of crisis that produced the stronger central government under the new Constitution.
What was Hamilton's plan for the United States?
The first part of Hamilton’s plan involved federal “assumption” of state debts, which were mostly left over from the Revolutionary War. The federal government would assume responsibility for the states’ unpaid debts, which totaled about $25 million. Second, Hamilton wanted Congress to create a bank—a Bank of the United States.
What was Alexander Hamilton's financial system?
Hamilton’s Financial System. Alexander Hamilton saw America’s future as a metropolitan, commercial, industrial society, in contrast to Thomas Jefferson’s nation of small farmers. While both men had the ear of President Washington, Hamilton’s vision proved most appealing and enduring. John Trumbull, Portrait of Alexander Hamilton, 1806.
What did Hamilton say about paying government debts?
Hamilton countered that government debts must be honored in full, or else citizens would lose all trust in the government.
What was Hamilton's goal in the assumption?
The goal of these proposals was to link federal power and the country’s economic vitality. Under the assumption proposal, the states’ creditors (people who owned state bonds or promissory notes) would turn their old notes in to the Treasury and receive new federal notes of the same face value. Hamilton foresaw that these bonds would circulate like money, acting as “an engine of business, and instrument of industry and commerce.” This part of his plan, however, was controversial for two reasons.
What was the purpose of the Bank of the United States?
In 1791, therefore, Congress approved a twenty-year charter for the Bank of the United States. The bank’s stocks, together with federal bonds, created over $70 million in new financial instruments. These spurred the formation of securities markets, which allowed the federal government to borrow more money and underwrote the rapid spread of state-charted banks and other private business corporations in the 1790s. For Federalists, this was one of the major purposes of the federal government. For opponents who wanted a more limited role for industry, however, or who lived on the frontier and lacked access to capital, Hamilton’s system seemed to reinforce class boundaries and give the rich inordinate power over the federal government.
Why did Jefferson and Washington choose Thomas Jefferson?
However, Washington chose Thomas Jefferson to be his secretary of state, and Jefferson was committed to restricting federal power and preserving an economy based on agriculture.
Why was the Bank of the United States important?
Hamilton, however, argued that the bank was not only constitutional but also important for the country’s prosperity. The Bank of the United States would fulfill several needs. It would act as a convenient depository for federal funds. It would print paper banknotes backed by specie (gold or silver).
Get Professional Assignment Help Cheaply
Are you busy and do not have time to handle your assignment? Are you scared that your paper will not make the grade? Do you have responsibilities that may hinder you from turning in your assignment on time? Are you tired and can barely handle your assignment? Are your grades inconsistent?
How It Works
You fill all the paper instructions in the order form. Make sure you include all the helpful materials so that our academic writers can deliver the perfect paper. It will also help to eliminate unnecessary revisions.
What was Alexander Hamilton's economic plan?
In 1790 and 1791, Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton presented four major reports that dealt with the financial, social, and constitutional future of the United States. Three were public documents, presented to Congress as proposals for policies that Congress might enact.
What did Hamilton want?
creating a national banking system. Hamilton wanted more, having in mind an American future that would resemble the reality of Britain in his own time. He had been instrumental in establishing America's first two banks, in Philadelphia in 1782 and New York in 1784.
What was Hamilton's final goal?
He did not submit his Report on Manufactures until December 1791. Within it he proposed a comprehensive program of protective taxes, government bounties, and federal public works, all with a view to nourishing the sprouts of industrialism that he could see emerging among the primarily northeastern, commercial-minded, well-off Americans with whom he felt most comfortable. As a program, it looked forward to the state-sponsored attempts at economic development of many late-twentieth-century countries. Historian John Nelson has suggested that Hamilton's ultimate goal was a neocolonial economy, subordinate to Britain, rather than independent development. However that may be, Congress rejected the report entirely. American industrial creativity and energy, however, were not to be denied. By 1860 the United States was second only to Britain among industrializing economies. But not until the administration of President Abraham Lincoln would the federal government begin to assume the active, fostering economic role that Hamilton proposed in 1791.
What did Hamilton believe about the second report on public credit?
Hamilton believed that a system of interconnected banks was necessary. Others, including Madison and Jefferson, regarded the idea with horror, particularly should the federal government became involved.
What was Hamilton's proposal to the Constitution?
Hamilton, Washington, the president's other advisers, Congress, and the interested public all understood that any other course would destroy America's financial credibility. His other proposals, however, provoked great controversy, both at the level of public policy and at the level of what the Constitution permits the government to do . The result was to open a gap among the very men who were responsible for the Constitution, beginning with Hamilton and his former close ally, James Madison. The friendship of those two highly talented thinkers came to an end; Hamilton and Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson, never close, became bitter enemies, and political parties started to emerge.
What was Hamilton's view on the public debt?
Hamilton's view was that the public debt could be a means for the new government to acquire the strength that he believed it should have.
Who proposed the role of the federal government in the economy?
But not until the administration of President Abraham Lincoln would the federal government begin to assume the active, fostering economic role that Hamilton proposed in 1791. See also Bank of the United States; Hamilton, Alexander; Jefferson, Thomas; Madison, James; Presidency, The: George Washington; Taxation, Public Finance, and Public Debt .

Paying The Debt
Creating A National Banking System
- Hamilton wanted more, having in mind an American future that would resemble the reality of Britain in his own time. He had been instrumental in establishing America's first two banks, in Philadelphia in 1782 and New York in 1784. Though he never visited England, he carefully studied its system of privately held banks under the direction of a privat...
Promoting Manufactures
- Hamilton's final proposal did not become law, but it too set the terms of a continuing debate. He wanted to set the United States on a course of industrial development emulating Britain's. He did not submit his Report on Manufactures until December 1791. Within it he proposed a comprehensive program of protective taxes, government bounties, and federal public works, all …
Bibliography
- Elkins, Stanley, and Eric McKitrick. The Age of Federalism. New York: Oxford UniversityPress, 1993. Hamilton, Alexander. The Reports of Alexander Hamilton.Edited by Jacob E. Cooke. New York: Harper and Row, 1964. Nelson, John R. Liberty and Property: Political Economy and Policymaking in the New Nation, 1789–1812. Baltimore: Johns HopkinsUniversity Press, 1987. …