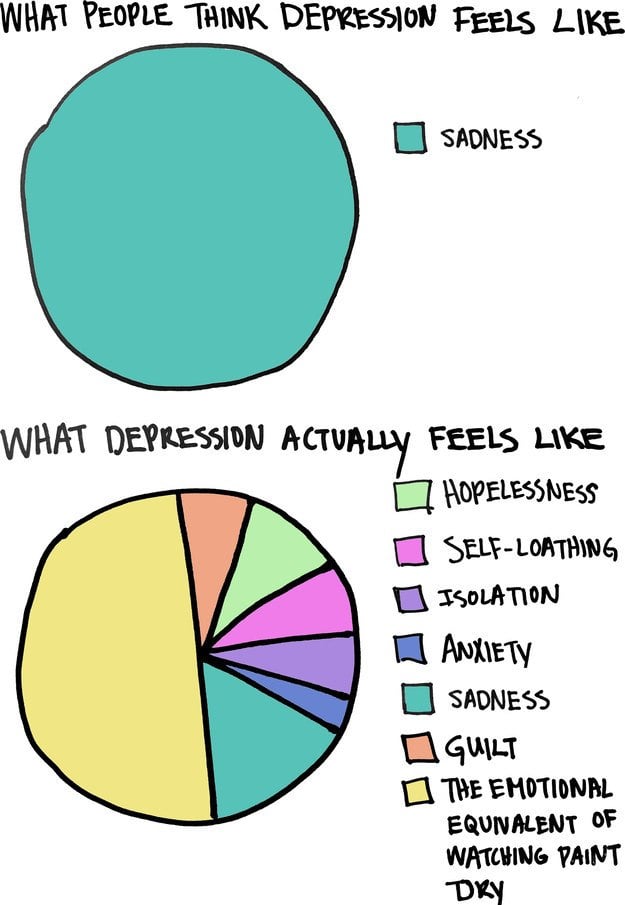
What is depression based on?
“The current standard of care for the treatment of depression is based on what we call the ‘monoamine deficiency hypothesis, ’ essentially presuming that one ...
What does it mean when you think about depression?
When we think about depression, what comes to mind are feelings and emotions – or, for some, the absence of feelings and emotions. In order to really understand depression, however, it’s important to be aware that the condition has physical aspects as well.
How many types of neurotransmitters are there in the human brain?
But according to Dr. Katz, this is only part of the story. There are about 100 types of neurotransmitters overall, and billions of connections between neurons in each person’s brain. There remains much to learn.
Why do nerve cells break apart?
They regulate how the brain changes and develops over a lifetime. When a person experiences chronic stress and anxiety, some of these connections between nerve cells break apart. As a result, communication between the affected cells becomes “noisy,” according to Dr. Krystal.
Is depression a long term disease?
And, since depression is often a long-term disease, people needs long-term treatments for it. “There are clear differences between a healthy brain and a depressed brain,” Dr. Katz says. “And the exciting thing is, when you treat that depression effectively, the brain goes back to looking like a healthy brain.”.
Does depression stem from serotonin?
For years and years, doctors and researchers assumed that depression stemmed from an abnormality within these neurotransmitters, particularly serotonin or norepinephrine. But over time, these two neurotransmitters did not seem to account for the symptoms associated with major depression. As a result, doctors began to look elsewhere.
The Location Of The Stroke Impacts Recovery
If you are a stroke survivor, its important to talk to your neurologist. Ask him/her about the location of your stroke, as it may help you to identify and understand what secondary effects to expect.
Mental Health Awareness: Facts And Figures
The hippocampus is part of the brains limbic system, or whats otherwise known as its emotional centre. The system also contains the amygdala, another part of the brain shown to be affected by depression.
What Part Of The Brain Is Affected By Depression
The body releases cortisol during times of physical and mental stress, including during times of depression. Problems can occur when excessive amounts of cortisol are sent to the brain due to a stressful event or a chemical imbalance in the body.
Areas Of The Brain Affected By Stroke And Symptoms
Below, youll learn about the different parts of the brain that can be impacted by stroke. You will find a short summary of the ;effects of each type of stroke, and you can click the link in each section to learn more.
Effect Of Depression On The Brain
Now its time to have your hands on the information youve been looking for. As per previously mentioned information you might have got an idea about the physical effects of depression. So, depression has a physical impact and symptoms, but can depression cause brain depression? The answer youll find below.
For Many Years People Thought That Antidepressants Worked Primarily Because They Affected The Neurotransmitter Serotonin But The Latest Research Indicates That Antidepressants Influence Neurogenesis By Starting The Formation Of New Nerve Cells
While depression can have serious consequences for the patient, Videbech says there is hope as the brain can be forced to heal itself in many cases.
Conclusion And Future Direction
In vivo MRI scans have made great achievements in the study of psychiatric disorders, which have resulted in the dawn of the understanding of the pathophysiology of psychosis, especially of MDD. Many brain region alterations have been reported, and some crucial circuits have also been revealed via imaging studies.
How does depression affect the brain?
While depression can affect a person psychologically, it also has the potential to affect physical structures in the brain. These physical changes range from inflammation and oxygen restriction, to actual shrinking. In short, depression can impact the central control center of your nervous system. For those interested in learning more about how ...
Which part of the brain shrinks due to depression?
But current studies have shown that the following parts of the brain can be affected: hippocampus. thalamus. amygdala.
What are the effects of oxygen on the brain?
Overall, the brain is highly sensitive to reductions in oxygen, which can lead to: inflammation. brain cell injury. brain cell death. As we’ve learned, inflammation and cell death can lead to a host of symptoms associated with development, learning, memory, and mood.
What happens when the brain is inflamed?
Because brain inflammation can cause the cells of the brain to die, this can lead to a number of complications, including: shrinkage (discussed above) decreased function of neurotransmitters. reduced ability of the brain to change as the person ages (neuroplasticity) Together these can lead to dysfunctions in: brain development.
How does depression affect the nervous system?
In short, depression can impact the central control center of your nervous system. For those interested in learning more about how depression can affect the physical brain, and ways to potentially avoid these changes, we’ve laid it all out for you.
How long does it take for the amygdala to change?
Reduced functionality of the amygdala. This can directly affect mood and emotional regulation. Changes typically take a minimum of eight months.
Which part of the brain controls emotions?
For instance, the prefrontal cortex and amygdala work together to control emotional responses and the recognition of emotional cues in other people. This can potentially contribute to a reduction in empathy in individuals who have postpartum depression (PPD).
Which part of the brain is affected by depression?
For one, we know that the limbic system supports a variety of functions including mood, emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and sense of smell. And, science has told us that three parts of the limbic system are affected by depression: the hippocampus, the thalamus, and the amygdala.
How do emotions affect the brain?
Science has shown that emotions are the result of brain activity. Your brain is full of tiny cells called neurons. Neurons are connected through channels known as synapses. Neurons use synapses to send information to other neurons. They send this information using chemicals or electric pulses.
What part of the brain is the seahorse?
In people with depression, the hippocampus shrinks. An fMRI study on women with a history of depression showed that their hippocampus was, on average, 9% to 13% smaller.
What is the role of the amygdala in the brain?
The amygdala helps organize your emotional responses to stressful events. When this region is too active, it might be hard to control your emotional response to triggers. Finally, depression can have a major impact on communication between your nerve cells. Neurons might send too much information.
Why does the amygdala activate?
The amygdala activates when we recall situations associated with emotions. Imbalance in the amygdala can change your perception of positive memories. A healthy amygdala helps you process your emotions and preserve good and bad memories. Depression can have a negative impact on these three brain regions.
Why is the amygdala important?
Scientists believe the amygdala is important for our emotions and behavior. The amygdala processes fear and can trigger a ‘fight-or-flight’ response. It’s associated with emotions like anger, sorrow, pleasure, fear, and even sexual arousal. The amygdala activates when we recall situations associated with emotions.
What happens when your hippocampus gets smaller?
When your hippocampus gets smaller, you might struggle with executive functioning skills.
How does depression affect the brain?
Physical Effects of Depression on the Brain. Depression is more than feeling down. It may physically change your brain. This can affect how you think, feel, and act. Experts aren’t sure what causes these changes. They think genetics, stress, and inflammation might play a role.
Which part of the brain is responsible for memory?
Hippocampus. That part of your brain is important for learning and memory. It connects to other parts of your brain that control emotion and is responsive to stress hormones. That makes it vulnerable to depression. Prefrontal cortex. This area plays a role in your higher-level thinking and planning.
Why is depression so hard to treat?
Ongoing depression likely causes long-term changes to the brain, especially in the hippocampus. That might be why depression is so hard to treat in some people. But researchers also found less gray matter volume in people who were diagnosed with lifelong major depressive disorder but hadn’t had depression in years.
How to treat depression?
Some people benefit from a mix of all three. Some treatments for mild or serious depression include: Talk therapy.
What are the best treatments for depression?
Here’s what research says about two common depression treatments: Antidepressants. These work on the chemicals in your brain that control stress and emotions. There’s evidence these drugs can help your brain form new connections and lower inflammation. Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT).
Why is it important to get help for depression?
It’s important to get help for your depression. That’s because repeat episodes seem to damage your brain more and more over time. Early treatment might help you avoid or ease some of the following changes.
Does depression cause translocator protein?
Experts aren’t sure if depression or inflammation comes first. But people who have a major depressive episode have higher levels of translocator proteins. Those are chemicals linked to brain inflammation. Studies show these proteins are even higher in people who’ve had untreated major depressive disorder for 10 years or longer.
Which part of the brain is responsible for memory, emotion, and the autonomic nervous system?
The hippocampus is an important part of your brain and is usually considered the center of memory, emotion, and the autonomic nervous system. It responds to stress hormones, and the production of new neurons slows down due to repeated stress.
How to deal with clinical depression?
It is easy to overlook your responsibilities when you are dealing with clinical depression. While you may want to give up your responsibilities at work and at home, you should resist the urge and stay involved all the time. Taking your responsibilities actually keeps you busy and help you maintain a better lifestyle. Successful completion of these responsibilities may also give you a sense of accomplishment that helps counter depression.
How to reverse brain changes?
Now you know the answer, then how to reverse the brain changes? What you eat can affect the way your brain works. If you are already under stress, eating wrong types of foods is only going to make matters worse. Many people tend to overeat when they are depressed, so you need to keep an eye on how much you eat .
Why is it important to have a good brain response to stress?
The way your brain reacts to stress is usually essential for your survival, because it gives you extra energy to fight or flee from dangerous situations. However, if brain chemical levels that increase during stressful situations stay elevated for a long period, it may cause problems such as depression. Depression can make a person feel sad and ...
How to get out of depression?
While you can make lifestyle changes to deal with your depression, it is sometimes necessary to take medications . Talk to your doctor and they will prescribe medications as per your symptoms.
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex?
Located at the front of your brain, the prefrontal cortex plays a big role in executive functions such as decision-making, judgment, and problem solving. It also helps control emotions and memory. Depression can affect its function and weaken it over time. This leads to atrophy of neurons in this area and the prefrontal cortex eventually shrinks.
What is the amygdala?
The amygdala is a part of the limbic system, and this system is a group of structures in the brain and is associated with emotions, including pleasure, anger, fear, sorrow and sexual arousal. The amygdala becomes activated when you recall emotional charged memories.
Which part of the brain receives excitatory inputs from the ACC and outputs to the thala
However, there is evidence that the connections between the ventral striatum and thalamic neurons are present.93The nucleus accumbens is a part of the ventral striatum, which receives excitatory inputs from the ACC and outputs to the thalamus, and has been linked with anhedonia.
Where does the dorsolateral prefrontal circuit originate?
The dorsolateral prefrontal circuit originates from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA seed based 9 and BA 10) and connects to the dorsolateral caudate. The caudate outputs to the lateral dorsomedial globus pallidus and the substantia nigra through the direct or indirect pathway.
Which node controls emotion, memory, and arousal?
Thalamus . The thalamus is considered a complicated sensory information node that controls emotion, memory, and arousal.46Dysfunction and structural disruptions in the thalamus can lead to an amnestic syndrome due to impairments in recall and recognition.47The thalamus is structured as several anatomical parts.
Which nucleus sends out fibers to the substantia nigra?
The subthalamic nuclei accept fibers from the pallidum and motor cortex and send out fibers to the substantia nigra. The lateral dorsal thalamic nucleus sends out fibers to the parietal lobe, and the ventral lateral thalamic nucleus has connections with the cerebellum and the brainstem.
Is depression a disability?
Depression is the leading cause of disability around the world, but little is known about its pathology. Currently, the diagnosis of depression is made based on clinical manifestations, with little objective evidence. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been used to investigate the pathological changes in brain anatomy associated ...
Is the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder complex?
As has been recognized, the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder is complex and changeable. The current review focuses on the significant alterations in the gray and white matter of patients with the depressive disorder to generate a better understanding of the circuits.
