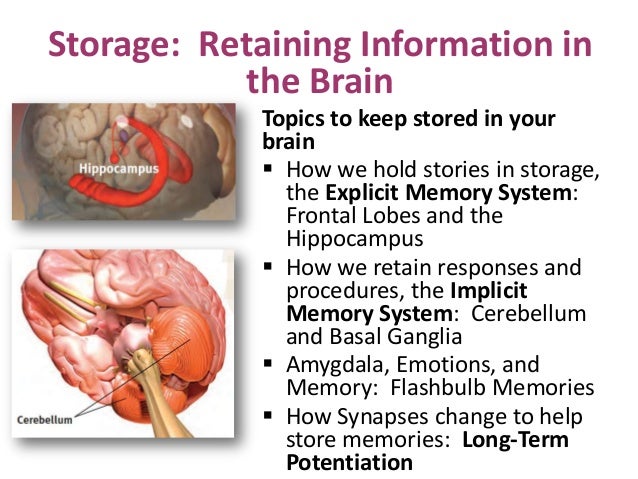
Which part of the brain is most involved in creating implicit memories?
Explicit memory depends mostly on the temporal and frontal parts of your brain. The hippocampus in the temporal lobe is crucial. It is the first structure to be damaged by Alzheimer’s disease. Implicit memory relies on various structures in the brain, depending on the type of knowledge involved.
What is an example of implicit memory?
Other examples of implicit memory may include:
- Knowing how to use utensils and dress yourself each day
- Navigating a familiar area such as your house or neighborhood
- Recalling how to boil water to fix dinner, or drive a car
- Remembering the words to a popular song after hearing the first few notes
Which area of the brain is associated with memory?
There are five main areas associated with memory: the hippocampus, neocortex, amygdala, basal ganglia and cerebellum. The hippocampus is associated with declarative and episodic memory. The hippocampus is associated with declarative and episodic memory.
How to improve memory with brain training?
Tips for Brain Games and Brain Exercises
- Participate in new types of exercise or learning a new sport. ...
- Learn memory techniques such as how to create a memory palace or chunking. ...
- Try brain game apps. Apps like BrainHQ, CogniFit, or Cogmed Working Memory Training create a memory training program for you.
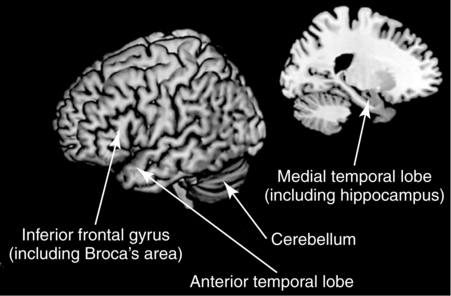
What part of the brain controls implicit learning?
In particular, the medial temporal lobe and the basal ganglia are found to be differentially engaged in explicit versus implicit learning conditions, and as learning progresses, the learner's dependence on the temporal lobe declines rapidly [7].
What does the cerebellum do implicit memory?
The cerebellum plays a large role in implicit memories (procedural memory, motor learning, and classical conditioning). For example, an individual with damage to their hippocampus will still demonstrate a conditioning response to blink when they are given a series of puffs of air to their eyes.
What causes implicit memory?
Implicit memory is sometimes referred to as unconscious memory or automatic memory. Implicit memory uses past experiences to remember things without thinking about them. The performance of implicit memory is enabled by previous experiences, no matter how long ago those experiences occurred.
Is the amygdala involved in implicit memory?
We refer to the role of the amygdala in implicit and explicit memories. The amygdala is involved in emotional aspects of learning and memory.
What are the 4 functions of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum, which stands for 'little brain', is a hindbrain structure that controls balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills, and it is thought to be important in processing some types of memory.
What is the main function of the cerebellum?
Your cerebellum is part of your brain that helps coordinate and regulate a wide range of functions and processes in both your brain and body. While it's very small compared to your brain overall, it holds more than half of the neurons (cells that make up your nervous system) in your whole body.
What functions does the cerebellum control?
The cerebellum is primarily responsible for muscle control, including balance and movement. It also plays a role in other cognitive functions such as language processing and memory.
How does the cerebellum help in learning?
Using all its tools, the cerebellum can learn to recognize situations and to generate optimized behavioural responses to them. Thus, the cerebellum helps to perfect and speed up the motor activity and behavioural repertoire.