What does the diencephalon do?
The diencephalon is the brain region that gives rise to anterior forebrain structures. Some of these structures include the thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior portion of the pituitary gland, and pineal gland. The diencephalon also encloses a cavity called the third ventricle.
Is the epithalamus part of the diencephalon?
4. The epithalamus The epithalamus is a dorsal part of the diencephalon, which is formed mainly by the habenulas -cellular nuclei with limbic and motor functions- and the pineal gland.
What is the pineal gland made up of?
The pineal gland is a neuroendocrine organ that comprises a part of the epithalamus, one of the three divisions of the diencephalon. Other components of the epithalamus are the stria medullaris, habenular nuclei, posterior commissure and paraventricular nuclei.
What are the 5 parts of the diencephalon?
The Diencephalon: Structure and Function of this Brain Region 1 The hypothalamus. 2 The thalamus. 3 Pituitary gland. 4 The epithalamus. 5 The subtalamus. 6 Retina and optic nerve.
See more

What glands are located in the diencephalon?
Function. The diencephalon is the region of the embryonic vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to anterior forebrain structures including the thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior portion of the pituitary gland, and the pineal gland.
Which structure of the diencephalon contains the pineal gland and secretes melatonin?
The epithalamus is a dorsal posterior segment of the diencephalon, which includes the habenula and their interconnecting fibers, the habenular commissure, the stria medullaris, and the pineal body. A main function of the epithalamus is the secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland.
What are the 4 portion of our brain in diencephalon?
The diencephalon is a small part of the brain that is mostly hidden from view when you are looking at the outside of the brain. It is divided into four parts: the epithalamus, thalamus, subthalamus, and hypothalamus.
What 2 parts make up the diencephalon?
It is the caudal part of the forebrain (prosencephalon) that occupies the central region of the brain. The diencephalon is comprised of the: Epithalamus. Thalamus.
Where is the pineal gland found?
the brainThe pineal gland in humans is a small (100-150mg), highly vascularized, and a secretory neuroendocrine organ. It is located in the mid-line of the brain, outside the blood-brain barrier and attached to the roof of the third ventricle by a short stalk.
Is the pineal gland in the thalamus?
Your pineal gland is located deep in the middle of your brain. It sits in a groove just above the thalamus, which is an area of your brain that coordinates a variety of functions related to your senses.
What are the 3 main parts of the diencephalon?
The three segments of the diencephalon are called prosomere 3, prosomere 2, and prosomere 1, from rostral to caudal. Each of the three prosomeres has alar and basal components, of which the alar parts are most prominent.
What are the 3 parts of the diencephalon and what do they do?
The diencephalon is made up of four main components: the thalamus, the subthalamus, the hypothalamus, and the epithalamus. The hypothalamus is an integral part of the endocrine system, with the key function of linking the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland.
What 3 structures make up the diencephalon?
Step 1. The diencephalon is located between the cerebrum and the brain stem. It consists of the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the subthalamus and the epithalamus.
What are the 7 structures of the diencephalon?
The diencephalon has a central location within the human brain sitting just above the brain stem. It is divided into four main structures—the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus.
Which of the following are contained in the diencephalon?
The diencephalon includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus and subthalamus (Figure 1.3).
Which of the following is not a part of the diencephalon?
Answer and Explanation: Of the above answer choices, the one that is not part of or associated with the diencephalon is the D. arbor vitae. The arbor vitae is the white matter of the cerebellum that lies in the deeper part of the cerebellum and functions to execute fine motor control in the body.
Does the thalamus secrete melatonin?
The thalamus has a strong nonphotic influence on sleep, circadian rhythmicity, pineal melatonin production, and secretion. The opening of the sleep gate for nonrapid eye movement sleep is a thalamic function but it is assisted by melatonin which acts by promoting spindle formation.
How does the pineal gland secrete melatonin?
Melatonin (blue) is produced naturally from the amino acid tryptophan, by the pineal gland (purple) at night-time. Night-time is detected by reduced light entering the eyes (left), and the arrow shows the melatonin secretion signal sent by the optic nerve to the pineal gland once darkness has fallen.
What produces melatonin?
Melatonin is secreted principally by the pineal gland and mainly at nighttime. The primary physiological function is to convey information of the daily cycle of light and darkness to the body.
Where is melatonin produced?
the pineal glandSynthesis of melatonin-the role of light In humans melatonin is produced mainly in the pineal gland and a small portion in the retina.
Function Of The Diencephalon
Each component in the diencephalon is specialized and integral to day-to-day functioning.
Anatomy Of The Diencephalon
The diencephalon is a part of the brain situated in the midbrain and almost entirely covered by the cerebrum.
The Thalamus
The thalamus is the diencephalon’s largest mass of grey matter and is laterally related to the third ventricle.
The Epithalamus
The epithalamus is the most distal section of the diencephalon from which the pineal gland extends posteriorly.
The Subthalamus
The subthalamus is the part of the diencephalon that lies below the back side of the thalamus and laterally to the hypothalamus.
The Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus lies below the thalamus and contains various subdivisions and nuclei.
The Clinical Significance Of The Diencephalon
The diencephalon is obviously a vital part of normal brain functioning.
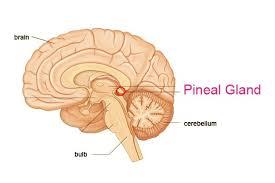
Where is the pineal gland located?
The pineal gland, also called the pineal body, develops as an outward projection from the posterior wall of the third ventricle, below the splenium of corpus callosum . It sits in the groove between the two superior colliculi, and is bilaterally related to the posterior aspects of the two thalami .
What is the pineal gland?
Location and structure. The pineal gland is a neuroendocrine organ that comprises a part of the epithalamus, one of the three divisions of the diencephalon. Other components of the epithalamus are the stria medullaris, habenular nuclei , posterior commissure and paraventricular nuclei. The pineal gland, also called the pineal body, ...
What are the laminae of the pineal gland?
The pineal gland is attached to the rest of the brain by the pineal stalk, which divides into two laminae, the inferior and superior laminae. The inferior and superior laminae contain the posterior commissure and the habenular commissure, respectively.
Why is my pineal gland not working?
Pineal gland function and melatonin secretion can be impaired due to disease or injury of the pineal gland. Pineal gland dysfunction can be caused by pineal tumors, craniopharyngiomas, injuries affecting the sympathetic innervation of the pineal gland, or rare congenital disorders that alter melatonin secretion.
What gland is epiphysis?
Pineal gland (epiphysis): want to learn more about it?
Which gland secretes melatonin?
The pineal gland, or epiphysis is a small cone-like structure that comprises a part of the diencephalon . It is a neuroendocrine gland that secretes the hormone melatonin and several other polypeptide hormones that have a regulatory function on other endocrine glands .
Which glands are involved in the regulation of the pineal gland?
The hormones of the pineal gland have a highly regulatory importance in which they influence the activity of other endocrine glands, namely the pituitary gland , endocrine pancreas , adrenal gland , parathyroid gland and the gonads.
Where is the diencephalon located?
Diencephalon Location. This brain region has a central location within the brain, it is located between the cerebral hemispheres and the brain stem , and through it travel most of the fibers that go to the cerebral cortex. The diencephalon, unlike the telencephalon that ends up forming the cerebral cortex and other internal structures such as ...
What is the largest structure in the diencephalon?
The thalamus. The thalamus corresponds to one of the largest structures in the diencephalon. It is made up mainly of grey matter, rich in neuronal bodies. Nerve impulses pass through the thalamus from the central nervous system to the peripheral and vice versa, this being the place where sensory signals are integrated for subsequent interpretation ...
What is the epithalamus?
The epithalamus is a dorsal part of the diencephalon, which is formed mainly by the habenulas -cellular nuclei with limbic and motor functions- and the pineal gland. It has important functions within the limbic system, connecting it with other parts of the brain, which for example include controlling the circadian rhythm through the pineal gland.
Which part of the body controls the endocrine system?
The hypothalamus is considered one of the largest centers of endocrine control of the human body.. The signals that this part of the diencephalon emits condition a large amount of hormones in the endocrine system, thanks to the release of hormones that they cause in the pituitary gland, also known as the pituitary gland. 2.
What is the midsagittal view of the brain?
Midsagittal view of the brain. Visible are the structures situated on the medial aspect of the cortex as well as subcortical areas, which include the corpus callosum, septum pellucidum, fornix, diencephalon, and brainstem structures. These structures are closely related to each other and can collaborate to carry out specific tasks.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The functions of the hypothalamus are several of vital importance to the functioning of the body, such as homeostasis – the maintenance of normal conditions, such as body temperature, as well as plays a role in sexual desire, hunger and thirst. Also participates in sleep and memory processes, as well as in the function of sex hormones.
What is the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is a part of the diencephalon. is attached to this brain structure. Like the retina, these visual structures are formed from cells of the embryonic diencephalon, but differ from the rest of the neuronal tissue. These structures translate light into nerve impulses, which are then analyzed in the rest of the brain.
What is the in between brain?
a part of the prosencephalon sandwiched between the inferior regions of the cerebral hemisphere. Often referred as the "in-between brain". Contains the epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
Which structure controls the body's temperature?
structure of the diencephalon and it is the master control of the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems, regulates body temperature, controls emotional behavior, food intake, water intake, regulates sleep-wake rhythms.
Which part of the brain is the diencephalon?
Diencephalon occupies the central part of the brain. Anatomically, we can say it has a central position, as a direct extension of the brain stem ( 2 ).
Which part of the diencephalon controls the internal secretion of all glands?
Hypothalamus . The hypothalamus is associated with the pituitary gland which controls the operation of all glands with the internal secretion, i.e. the endocrine system glands. Therefore, we can observe this part of the diencephalon as a bridge between the CNS and the endocrine system. It is located below the thalamus.
What part of the brain is responsible for the connection between the limbic system and other parts of the brain?
Most noteworthy, this part of the diencephalon serves as a connection between the limbic system and other parts of our brain.
What are the causes of diencephalon syndrome?
Scientists found that the occurrence of this syndrome is related to diencephalon insults. Also, it can occur due to an impairment of the pituitary gland itself. Hypothalamus insults also lead to this syndrome. Types of insults that lead to it include radiation therapy, necrosis, and a brain injury.
What is the function of the pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland is located below the hypothalamus. As we have already said, it regulates the hormones. Moreover, it secretes neurohormones .
What is the diencephalon?
Performance focused athletes. Student learning. The diencephalon is one of the two key parts of the forebrain, i.e. prosencephalon in Latin ( 1 ). The second key part is the telencephalon or cerebrum. It is interesting to note that its position is not visible by the naked eye from the outside of the brain surface if the skull was removed.
Which part of the brain is responsible for motor control?
Subthalamus is another crucial part of our brain we must address when elaborating on the diencephalon. Namely, parts of subthalamus are made from the diencephalon tissue. This part of our brain has strong connections with ganglia. As a result, it participates in motoric activity coordination.
