The mitosis is a part of somatic cell division which includes the division of the nucleus (called mitosis or katyokinesis) and the division of the cytoplasm (called cytokinesis). Strasburger (1875), a German botanist, was the first to work out the details of mitosis.
- Cell membrane. the main function is to control what goes in and out of the cell. ...
- Nucleus. is the control center of the cell. ...
- Centrioles. are paired organelles that are in the cytoplasm only to take part in cell division. ...
- Microtubules.
What types of cells are produced in mitosis?
- Daughter cell have half the number of chromosomes compared to parental cell (meiocyte)
- Daughter cell carry the same genes of parental cell but carried by half the number of chromosomes.
- Daughter cell carry chromosomes undergone recombination and crossing over ( big step of creation of variation)
What are cells produced by mitosis called?
The cell undergoes a type of cell division called mitosis. In mitosis, two cells called daughter cells are produced, each identical to the parent cell. When looking at cells with a microscope, the ...
Does mitosis create two cells or four cells?
The big companies don't want you to know his secrets. Mitosis does produce identical cells but not meiosis. Each mitotic division produces two identical cells, whereas, each meiotic in two phases produces four nonidentical daughter cells because of genetic exchange during the cell division.
What is the result of a cell undergoing mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of cell division that produces two daughter cells that are identical to each other as well as to the parent cell. Manually computing such that a single cell results to 2 daughter cells, a single cell undergoing mitosis will produce 32 666 daughter cells after 30 minutes.
Which parts of the cell are involved in cell division?
CentriolesCentrioles. Centrioles are organelles involved in cell division. The function of centrioles is to help organize the chromosomes before cell division occurs so that each daughter cell has the correct number of chromosomes after the cell divides. Centrioles are found only in animal cells and are located near the nucleus.
What are the 4 main parts of mitosis?
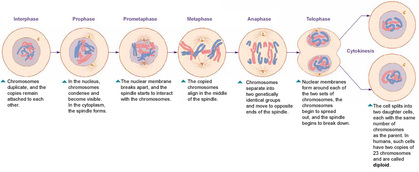
Mitosis has four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What process involves mitosis?
Conclusion. Mitosis is the process of nuclear division, which occurs just prior to cell division, or cytokinesis. During this multistep process, cell chromosomes condense and the spindle assembles.
What occurs during mitosis?
Mitosis is a fundamental process for life. During mitosis, a cell duplicates all of its contents, including its chromosomes, and splits to form two identical daughter cells. Because this process is so critical, the steps of mitosis are carefully controlled by certain genes.
What are the 4 stages of mitosis and what happens in each?
4:326:47What happens in the four stages of mitosis? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipDuring metaphase the chromosomes have been aligned in the middle of the cell and spindle fibers haveMoreDuring metaphase the chromosomes have been aligned in the middle of the cell and spindle fibers have attached to each chromosome at the connector core in anaphase.
What are the 4 stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).
What happens during each of the four phases of mitosis?
In metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. Each of the chromosomes is connected to a spindle fiber. In anaphase, the chromatids get separated and the chromosomes are moved apart. In telophase, the chromosomes go to the opposite ends of the cell.
What are the 5 stages of mitosis and what is occurring at each?
Mitosis has five different stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The process of cell division is only complete after cytokinesis, which takes place during anaphase and telophase. Each stage of mitosis is necessary for cell replication and division.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of cell duplication, in which one cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. In the various stages of mitosis...
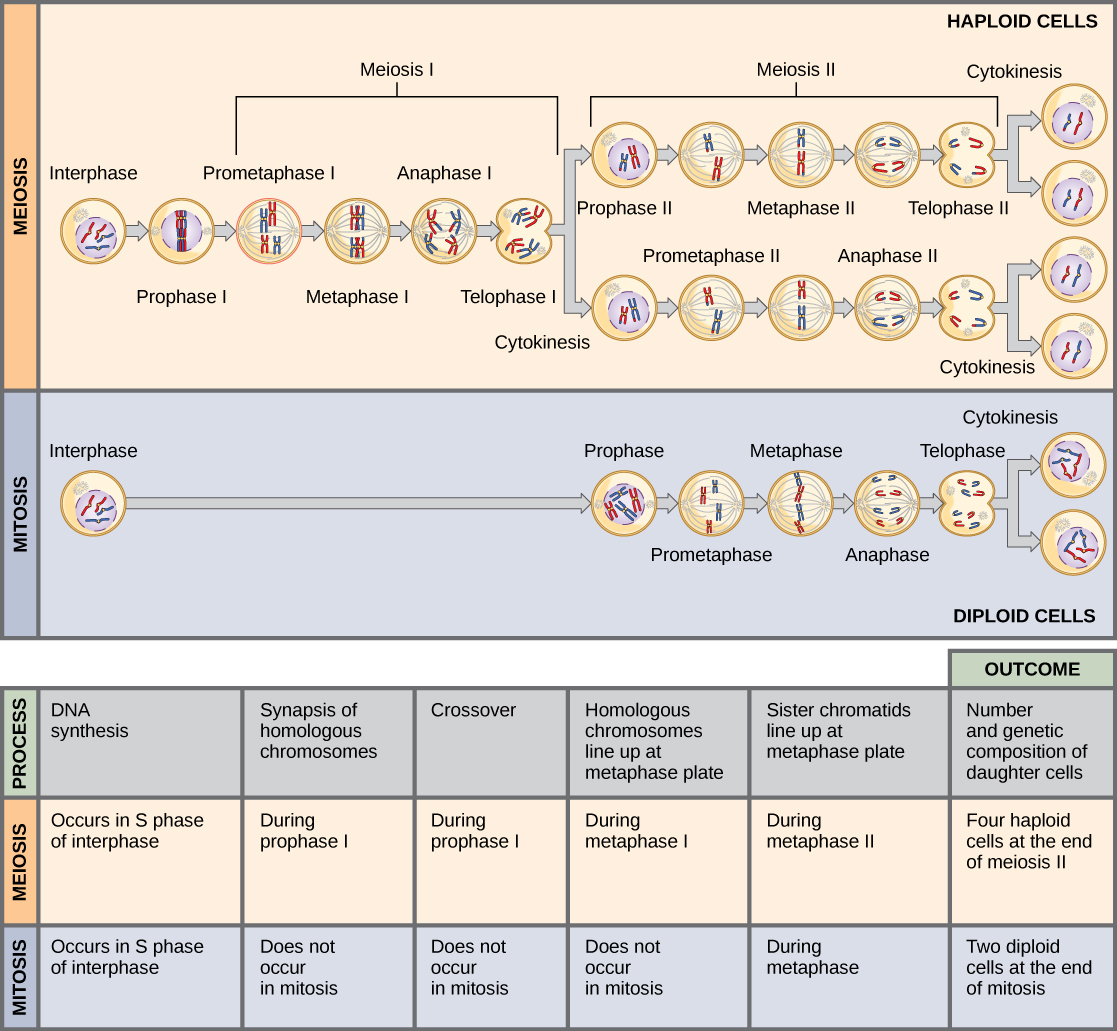
How are mitosis and meiosis different?
Mitosis is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Meiosis is the division of a germ cell...
Why is mitosis important to organisms?
Mitosis is important to multicellular organisms because it provides new cells for growth and for replacement of worn-out cells, such as skin cells....
Define mitosis.
Mitosis is the type of cell division by which a single cell divides in such a way as to produce two genetically identical “daughter cells”.
Why is mitosis called equational division?
Mitosis is the process of cell division wherein the chromosomes replicate and get equally distributed into two daughter cells. The chromosome numbe...
List all the stages of mitosis.
The stages of Mitosis are: Prophase – The chromosomes shorten and thicken. Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Anaphase – C...
What is prophase?
The process of mitosis begins with the prophase. In this stage, the chromatin condenses and the nucleolus disappears.
What happens in metaphase?
Metaphase is the second stage of the process, chromosomes get condensed at the equator, before being split apart for each of the two daughter cells.
In what cells does mitosis occur?
Mitosis occurs in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells divide by both mitosis and meiosis. For eg., skin cells divide by mitosis, whereas gametes div...
What is the primary function of mitosis?
Mitosis plays an important role in the life cycle of most living things. It helps in cell regeneration, asexual reproduction and growth.
What is the process of mitosis?
Mitosis, or the process of replication and division of the nucleus that results in the production of genetically identical daughter cells, is relatively similar among plants and animals, but the algae have a wide diversity of mitotic features that not only set the algae…
Why is mitosis important to multicellular organisms?
Why is mitosis important to organisms? Mitosis is important to multicellular organisms because it provides new cells for growth and for replacement of worn-out cells, such as skin cells . Many single-celled organisms rely on mitosis as their primary means of asexual reproduction. A brief treatment of mitosis follows.
What happens to the chromosomes before mitosis?
Prior to the onset of mitosis, the chromosomes have replicated and the proteins that will form the mitotic spindle have been synthesized. Mitosis begins at prophase with the thickening and coiling of the chromosomes. The nucleolus, a rounded structure, shrinks and disappears. The end of prophase is marked by the beginning of the organization of a group of fibres to form a spindle and the disintegration of the nuclear membrane.
What is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell?
Mitosis is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Meiosis is the division of a germ cell into four sex cells (e.g. egg or sperm), each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.
How long does mitosis take?
Mitosis may take minutes or hours, depending upon the kind of cells and species of organisms. It is influenced by time of day, temperature, and chemicals. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Kara Rogers, Senior Editor. History at your fingertips.
What is the term for the distribution of chromosomes?
Strictly applied, the term mitosis is used to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes, the structures that carry the genetic information.
Where do chromosomes line up in anaphase?
The chromosomes, each of which is a double structure consisting of duplicate chromatids, line up along the midline of the cell at metaphase. In anaphase each chromatid pair separates into two identical chromosomes that are pulled to opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibres.
What is Mitosis?
Cell division is the driving process of reproduction at the cellular level. Most eukaryotic cells divide in a manner where the ploidy or the number of chromosomes remains the same, except in the case of germ cells where the number of chromosomes is halved.
How does mitosis help an organism?
Mitosis helps in the development of an organism. In single-celled organisms, mitosis is the process of asexual reproduction. Mitosis helps in the replacement of damaged tissues. The cells near the damaged cells begin mitosis when they do not sense the neighbouring cells.
What happens to the microtubules in prometaphase?
In the prometaphase, the nuclear envelop disintegrates. Now the microtubules are allowed to extend from the centromere to the chromosome. The microtubules attach to the kinetochores which allow the cell to move the chromosome around.
What is the process of completion of prophase?
The completion of prophase is characterised by the initiation of the assembly of the mitotic spindle, the microtubules and the proteinaceous components of cytoplasm that help in the process.
Why is mitosis also called equational cell division?
The cell is also known as equational cell division because the chromosome number in the parent cell and daughter cell is the same. In plants, mitosis leads to the growth of vegetative parts of the plant like root tip, stem tip, etc. Segregation and combination do not occur in this process. The processes occurring during mitosis have been divided ...
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis is required for asexual reproduction, vegetative propagation in plants and also responsible for repair and regeneration of damaged tissues. Mitosis helps in maintaining purity of genome as no recombination or crossing over takes place.
What is the term for the splitting of sister chromatids?
Anaphase. The splitting of the sister chromatids marks the onset of anaphase. These sister chromatids become the chromosome of the daughter nuclei. The chromosomes are then pulled towards the pole by the fibres attached to the kinetochores of each chromosome.
How many cells are there in mitosis?
After the first round of mitosis, there are only two cells. These cells both undergo mitosis, and there are 4 cells. Pretty soon, a small, hollow ball of cells is formed, called the blastula. This ball folds in on itself as more and more cells are created.
What is the function of mitosis?
The second important function of mitosis is that of repair. When an organism gets injured, its cells are damaged. This can be a physical injury like a cut, or damage from environmental sources like the sun. Either way, the damaged cells need replaced. Nearby cells, not sensing their neighbor cells, turn on the pathways that start the process of mitosis. Eventually the multiplying new cells reach each other, and the damage area is covered with new cells. Some organism are able to regenerate entire limbs this way. Lizards, crabs, and many other animals can lose a tail or claw with no fear, as the limb can be regrown through mitosis.
What happens to sister chromatids in mitosis?
During anaphase of mitosis, the proteins that connect these chromatids are destroyed. Each now its own chromosome, the identical halves can be pulled to each cell.
How does mitosis work?
In single-celled organisms, the act of mitosis is asexual reproduction. Single-celled organisms use mitosis to reproduce and distribute their DNA. Some single-celled organisms reproduce sexually as well. To reproduce sexually, most organisms undergo another process, meiosis, to properly reduce their DNA and place the DNA in individual cells. These gametes can then meet and one will become fertilized. This fertilized gamete contains two sets of the genome, which in most organisms is necessary for proper development. Some organisms only have a single copy of the DNA. These are known as diploid and haploid organisms, respectively.
When the chromatids are separated, the cell is in anaphase of mitosis?
C is correct. When the chromatids are being separated, the cell is in anaphase of mitosis. After they are separated, the cell enters telophase. Also in anaphase, the chromosomes become extremely condensed. This allows them to fit into a newly formed nucleus in the new cell.
What is the cell cycle in eukaryotes?
Cell Cycle – In eukaryotes, the cycle consists of Interphase and Mitosis, with some cells going into a non-diving third state.
What is the name of the part of the cell cycle in which the cell grows and duplicates the DNA?
Though technically not part of mitosis, Interphase begins and ends mitosis. Interphase is the part of the cell cycle in which the cell grows and duplicates the DNA. After an identical set of DNA is synthesized, the cell enters Mitosis.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the DNA of the cell's nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes.
What is the order of mitosis?
These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase. Stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. You can remember the order of the phases with ...
How many phases are there in mitosis?
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
Where do microtubules extend?
More microtubules extend from each centrosome towards the edge of the cell, forming a structure called the aster. Metaphase. Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, under tension from the mitotic spindle. The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Which phase of the cell is the sister chromatids separated from each other?
Anaphase. The sister chromatids separate from one another and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. The microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes push the two poles of the spindle apart, while the kinetochore microtubules pull the chromosomes towards the poles.
Why can't you see chromosomes in the nucleus?
You can’t see the chromosomes very clearly at this point, because they are still in their long, stringy, decondensed form.
Where do microtubules bind to chromosomes?
Microtubules can bind to chromosomes at the kinetochore, a patch of protein found on the centromere of each sister chromatid. ( Centromeres are the regions of DNA where the sister chromatids are most tightly connected.)
Which direction is mitosis ordered in an animal cell?
Mitosis in an animal cell (phases ordered counter-clockwise).
What is mitosis in biology?
This is the latest accepted revision, reviewed on 6 May 2021. Jump to navigation Jump to search. The division of a cell nucleus in which the genome is copied and separated into two identical halves.
How does mitosis change cell shape?
Cell shape changes through mitosis for a typical animal cell cultured on a flat surface. The cell undergoes mitotic cell rounding during spindle assembly and then divides via cytokinesis. The actomyosin cortex is depicted in red, DNA/chromosomes purple, microtubules green, and membrane and retraction fibers in black. Rounding also occurs in live tissue, as described in the text.
What is the M phase of mitosis?
The different stages of Mitosis altogether define the mitotic ( M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next.
Why is interphase important?
It carefully stops the cell from proceeding whenever the cell's DNA is damaged or has not completed an important phase. The interphase is very important as it will determine if mitosis completes successfully. It will reduce the amount of damaged cells produced and the production of cancerous cells. A miscalculation by the key Interphase proteins could be crucial as the latter could potentially create cancerous cells. Today, more research is being done to understand specifically how the phases stated above occur.
Why is mitosis important in histopathology?
In histopathology, the mitosis rate is an important parameter in various types of tissue samples, for diagnosis as well as to further specify the aggressiveness of tumors. For example, there is routinely a quantification of mitotic count in breast cancer classification.
How are new cells formed?
skin and digestive tract, cells are constantly sloughed off and replaced by new ones. New cells are formed by mitosis and so are exact copies of the cells being replaced. In like manner, red blood cells have a short lifespan (only about 4 months) and new RBCs are formed by mitosis.
What is the name of the cell that divides?
In cell division, the cell that is dividing is called the "parent" cell. The parent cell divides into two "daughter" cells. The process then repeats in what is called the cell cycle.
Where Do Cells Come From?
3D image of a mouse cell in the final stages of cell division (telophase). (Image by Lothar Schermelleh)
How do cells divide?
How Cells Divide. Depending on the type of cell, there are two ways cells divide—mitosis and meiosis. Each of these methods of cell division has special characteristics. One of the key differences in mitosis is a single cell divides into two cells that are replicas of each other and have the same number of chromosomes.
What is a diploid cell?
Diploid cell: a cell with two sets of chromosomes (46 chromosomes total)... more (link is external) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): molecular instructions that guide how all living things develop and function... more (link is external) Haploid cell: a cell with only one set of chromosomes... more (link is external)
Why do we need to make new skin cells?
Some cells, like skin cells, are constantly dividing. We need to continuously make new skin cells to replace the skin cells we lose. Did you know we lose 30,000 to 40,000 dead skin cells every minute? That means we lose around 50 million cells every day. This is a lot of skin cells to replace, making cell division in skin cells is so important. Other cells, like nerve and brain cells, divide much less often.
How many skin cells are lost in a day?
That means we lose around 50 million cells every day. This is a lot of skin cells to replace, making cell division in skin cells is so important. Other cells, like nerve and brain cells, divide much less often.
Why is it important for skin cells to divide?
It is important for cells to divide so you can grow and so your cuts heal. It is also important for cells to stop dividing at the right time. If a cell can not stop dividing when it is supposed to stop, this can lead to a disease called cancer. Some cells, like skin cells, are constantly dividing.
.jpg)