What is the hypoglossal canal?
Hypoglossal canal. Occipital bone. The hypoglossal canal is a foramen in the occipital bone of the skull. It is hidden medially and superiorly to each occipital condyle. The hypoglossal nerve traverses the canal.
Where does the hypoglossal nerve enter the brain?
The hypoglossal canal is formed during the embryological stage of development in mammals. The hypoglossal canal transmits the hypoglossal nerve from its point of entry near the medulla oblongata to its exit from the base of the skull near the jugular foramen.
When do the two branches of the hypoglossal nerve join?
In some people, the two branches of the hypoglossal nerve don't join together until after exiting the hypoglossal canal, which, in those people, includes two openings instead of one. The hypoglossal nerve is purely a motor nerve; it doesn't send any sensory information to and from the brain.
What is the pathophysiology of hypoglossal nerve damage?
Penetrating injuries to the neck, and various lesions of the skull base may also affect the nucleus of the hypoglossal nerve. An injury of the nerve manifests as flaccid paralysis and atrophy of the ipsilateral muscles of the tongue followed with speech impairment.

Which cranial nerve passes through the hypoglossal canal?
Function. The hypoglossal canal transmits the hypoglossal nerve from its point of entry near the medulla oblongata to its exit from the base of the skull near the jugular foramen.
Does the hypoglossal nerve pass through the hypoglossal canal?
The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, passes through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue.
What foramen does the hypoglossal nerve pass through?
The hypoglossal nerve passes through the dura by itself, the ninth, tenth and eleventh nerves pass through the dura together to enter the jugular foramen. Nerves nine, ten and eleven leave through this part of the jugular foramen. The hypoglossal nerve leaves through this opening, the hypoglossal canal.
Where is the hypoglossal canal?
occipital condyleThe hypoglossal canal is located between the occipital condyle and jugular tubercle and runs obliquely forwards (posteromedial to anterolateral) allowing the hypoglossal nerve to exit the posterior cranial fossa.
What does the hypoglossal nerve supply?
The hypoglossal nerve enables tongue movement. It controls the hyoglossus, intrinsic, genioglossus and styloglossus muscles. These muscles help you speak, swallow and move substances around in your mouth.
Does the hypoglossal nerve go through the foramen magnum?
The posterior fossa dura is innervated by the upper three cervical spinal nerves that give off ascending meningeal branches, entering via the foramen magnum (C3), hypoglossal canal, and jugular foramen (C2 and C3). The nerves originating from C3 supply the dura mater in the anterior part of the posterior cranial fossa.
What passes through the foramen magnum?
Apart from the spinal cord, its associated meninges and cerebrospinal fluid, the foramen magnum also transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, dural veins and the spinal roots of the accessory nerve (CN XI).
What passes through the jugular foramen?
Cranial nerves IX, X, and XI, originate from the brainstem and exit the cranium via the jugular foramen. These nerves originate from the medulla, the inferior most portion of the brainstem.
What nerve passes through the foramen magnum?
Cranial nerve XICranial nerve XI, or the accessory nerve, originates from the upper spinal cord and medulla and enters the skull through the foramen magnum.
Which cranial nerve passes through the optic canal?
cranial nerve II[1] The optic canal connects the orbit to the middle cranial fossa and transmits the optic nerve, ophthalmic artery, meningeal sheaths, and sympathetic nerve fibers. The optic nerve, also known as the cranial nerve II, transmits visual signal from the retina to the visual cortex.
What passes through condylar canal?
Through the condylar canal, the occipital emissary vein connects to the venous system including the suboccipital venous plexus, occipital sinus and sigmoid sinus. It is not always present, and can have variations of being a single canal or multiple smaller canals in cluster.
What nerves pass through the Cribriform Foramina?
Olfactory foramina in the cribriform plate: These holes make up a very important part of the pathway of the first cranial nerve (CNI), the olfactory nerve. Nerve endings in the top of our nose, responsible for our sense of smell, pass through these holes in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone.
Does the hypoglossal nerve cross over?
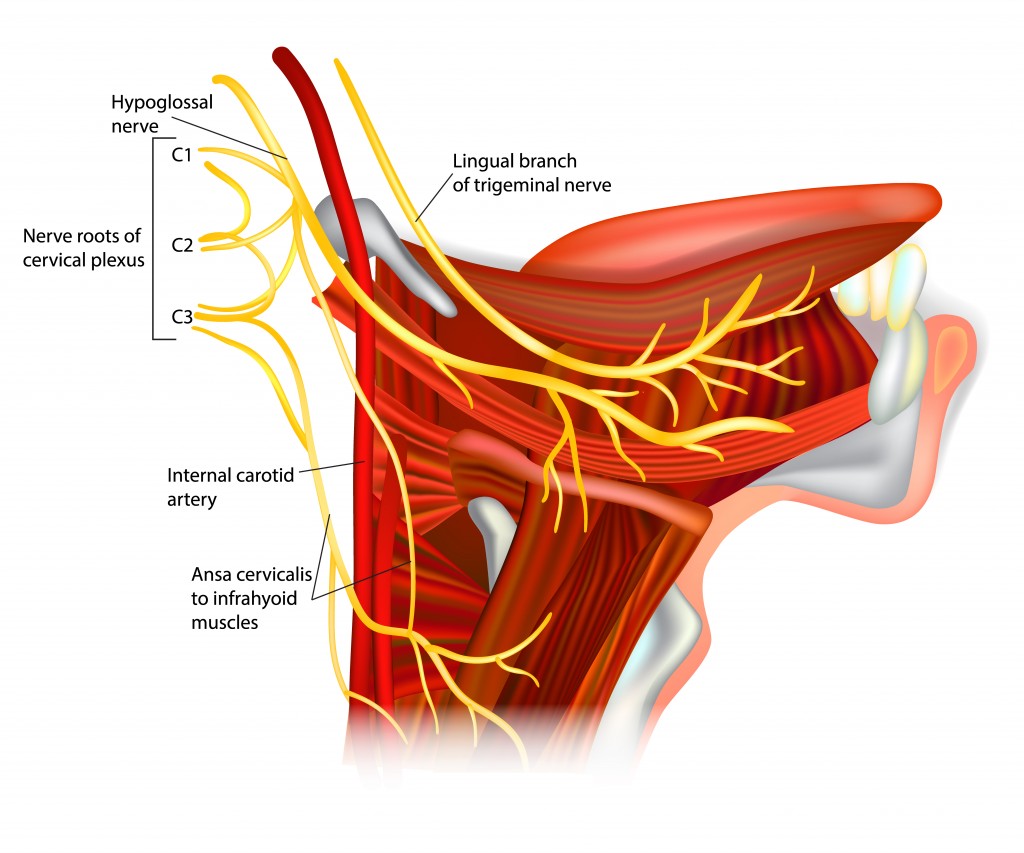
It first crosses over the carotid triangle, and then over the submandibular triangle of the neck. See how the hypoglossal nerve takes a sudden horizontal course once it reaches the occipital artery. You will recognize it as a nerve crossing the carotid vessels right after the bifurcation of the common carotid artery.
What passes through condylar canal?
Through the condylar canal, the occipital emissary vein connects to the venous system including the suboccipital venous plexus, occipital sinus and sigmoid sinus. It is not always present, and can have variations of being a single canal or multiple smaller canals in cluster.
Where is the hypoglossal canal?
The hypoglossal canal is a foramen in the occipital bone of the skull. It is hidden medially and superiorly to each occipital condyle. The hypoglossal nerve traverses the canal.
What is the function of the hypoglossal canal?
Function. The hypoglossal canal has recently been used to try to determine the antiquity of human speech. Researchers have found that hominids who lived as long as 2 million years ago had the same size canal as that of modern-day chimpanzees; some scientists thus assume they were incapable of speech.
How did the hypoglossal canal help humans?
The hypoglossal canal has recently been used to try to determine the antiquity of human speech. Researchers have found that hominids who lived as long as 2 million years ago had the same size canal as that of modern-day chimpanzees; some scientists thus assume they were incapable of speech. However, archaic H. sapiens 400,000 years ago had the same size canal as that of modern humans, meaning they could have been capable of speech. Some Neanderthals also had the same size hypoglossal canal as archaic H. sapiens. However recent studies involving several primate species have failed to find conclusive evidence of a relationship between its size and speech.
Where is the hypoglossal nerve located?
It transmits the hypoglossal nerve from its point of entry near the medulla oblongata to its exit from the base of the skull near the jugular foramen. It lies in the epiphyseal junction between the basiocciput and the jugular process of the occipital bone.
What is the proximal portion of the hypoglossal nerve?
Its proximal portion is often divided by a fibrous (sometimes ossified) septum, which separates the two roots of the hypoglossal nerve (these have formed by the convergence of numerous rootlets). These roots merge within the canal and a single nerve emerges.
Where is the hypoglossal canal located?
The hypoglossal canal is located between the occipital condyle and jugular tubercle and runs obliquely forwards (posteromedial to anterolateral) allowing the hypoglossal nerve to exit the posterior cranial fossa . Its proximal portion is often divided by a fibrous (sometimes ossified) septum, which separates the two roots of the hypoglossal nerve ...
What is the ISBN for Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied?
1. McMinn. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. Churchill Livingstone. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
What nerves do not branch off?
The hypoglossal nerve doesn't branch off until it reaches the muscles of the tongue, at which time it sends off numerous small branches to innervate those muscles.
What nerve is responsible for chewing and swallowing?
The hypoglossal nerve supplies all of the motor function to your tongue. It's the 12th cranial nerve. 1 Damage to this nerve can affect speech, chewing, and swallowing. The prefix hypo is of Greek origin and means "under.". Glossal, also from the Greek, mean "tongue.".
Which nerve controls the tongue?
The hypoglossal nerve controls two sets of muscles. One set is extrinsic (on the exterior of the tongue) while the other set is intrinsic (fully contained within the tongue). The extrinsic muscles include: Genioglossus: Makes up the bulk of the tongue and allows you to stick your tongue out and move it side to side.
Which nerve is purely a motor nerve?
The hypoglossal nerve is purely a motor nerve; it doesn't send any sensory information to and from the brain.
Which nerves do not join together?
A branch of the cervical plexus runs inside the sheath of the hypoglossal nerve, but the fibers of these two nerves don't join together in any way. The hypoglossal nerve doesn't branch off until it reaches the muscles of the tongue, at which time it sends off numerous small branches to innervate those muscles.
Where does the hypoglossal nerve run?
That's where it meets up with the cervical plexus. The hypoglossal nerve then runs between the carotid artery and the jugular vein, down into the neck, where it crosses the sternocleidomastoid muscle and runs along the mylohyoid muscle.
What are the intrinsic muscles?
The intrinsic muscles include: 1 . Superior longitudinal: A thin muscle right underneath the mucous membranes in the back of the tongue; works with the inferior longitudinal to retract the tongue and make it short and thick. Inferior longitud inal: A narrow band under the surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and the hyoglossus muscles;
What nerve crosses the carotid vessels?
See how the hypoglossal nerve takes a sudden horizontal course once it reaches the occipital artery. You will recognize it as a nerve crossing the carotid vessels right after the bifurcation of the common carotid artery.
What nerves are used to reach the suprahyoid and infrahyoid?
These spinal nerves basically “use” the hypoglossal nerve to reach the suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles. When the nerve exits the cranium, it enters the retrostyloid space, which is a part of the lateral pharyngeal space. In this space, the nerve is closely related to all lateral pharyngeal elements, such as:
What is the purpose of corticobulbar fibers?
The corticobulbar fibers intended for this connection to innervate the contralateral nucleus of the hypoglossal nerve. This means that the damage of the corticobulbar fibers manifests as paralysis of the muscles of the contralateral side of the tongue.
What is the space where the nerve exits the cranium?
When the nerve exits the cranium, it enters the retrostyloid space, which is a part of the lateral pharyngeal space. In this space, the nerve is closely related to all lateral pharyngeal elements, such as:
What is the lateral pharyngeal space?
When the nerve exits the cranium, it enters the retrostyloid space, which is a part of the lateral pharyngeal space. In this space, the nerve is closely related to all lateral pharyngeal elements, such as: 1 The internal carotid artery 2 The internal jugular vein 3 The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) 4 The vagus nerve (CN X) 5 The accessory nerve (CN XI)
How to test hypoglossal nerve?
To test the function of the hypoglossal nerve, a physician should ask their patient to protrude their tongue. The tongue should then be palpated to check the tone of the muscles as well as the ability of sensation.
Where does the hypoglossal nerve enter the sublingual area?
Finally, the hypoglossal nerve together with the secretory duct of the submandibular gland passes through the intermuscular crack, between the anterior edge of the hyoglossus muscle and the posterior edge of the mylohyoid muscle, and enters the sublingual area where it splits into its terminal lingual branches.
Overview
Function
The hypoglossal canal transmits the hypoglossal nerve from its point of entry near the medulla oblongata to its exit from the base of the skull near the jugular foramen.
Structure
The hypoglossal canal lies in the epiphyseal junction between the basiocciput and the jugular process of the occipital bone.
Embryonic variants sometimes lead to the presence of more than two canals as the occipital bone is formed.
The hypoglossal canal is formed during the embryological stage of development in mammals.
Clinical significance
Study of the hypoglossal canal aids in the diagnosis of a variety of tumors found at the base of the skull, including: large glomus jugulare neoplasms, myelomas, and the occasional meningioma. Studies of the hypoglossal canal revolve around the development of safe drilling techniques to conduct surgery on that area of the brain.
Research
The hypoglossal canal has recently been used to try to determine the antiquity of human speech. Researchers have found that hominids who lived as long as 2 million years ago had the same size canal as that of modern-day chimpanzees; some scientists thus assume they were incapable of speech. However, archaic H. sapiens 400,000 years ago had the same size canal as that of modern humans, meaning they could have been capable of speech. Some Neanderthals also ha…
Additional images
• Hypoglossal canal
• Base of the skull. Upper surface.
• Median sagittal section through the occipital bone and first three cervical vertebræ.
External links
• Anatomy figure: 22:5b-15 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
• cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (XII)
• "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.