Symptoms
Rabies is a deadly virus that infected animals spread through their saliva. It causes flu-like symptoms initially, which progress into fever, muscle spasms, coma, and eventually, death.
Causes
- headache,
- fever,
- malaise (general feeling of not being well),
Prevention
What happens if rabies goes untreated? Rabies is almost always fatal if it is left untreated. In fact, once someone with rabies starts experiencing symptoms, they usually do not survive. This is why it is very important to seek medical attention right away following an animal bite, especially if the bite is from a wild animal.
Complications
This treatment includes extensive washing and local treatment of the wound followed by a course of a potent and effective rabies vaccine. When given in time, PEP can stop the rabies virus from entering the central nervous system and, in turn, prevent the onset of rabies symptoms.
What diseases are caused by rabies?
Why does rabies make animals aggressive?
What happens if rabies is untreated?
Can you cure rabies?

What is rabies in mammals?
What is Rabies? Rabies is a preventable viral disease most often transmitted through the bite of a rabid animal. The rabies virus infects the central nervous system of mammals, ultimately causing disease in the brain and death. The vast majority of rabies cases reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ...
How many proteins are in the rabies genome?
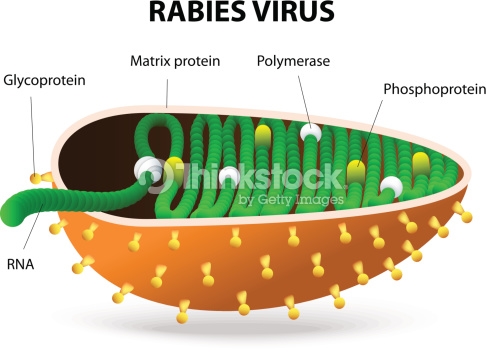
Rhabdoviruses are approximately 180 nm long and 75 nm wide. The rabies genome encodes five proteins: nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix protein (M), glycoprotein (G) and polymerase (L). All rhabdoviruses have two major structural components: a helical ribonucleoprotein core (RNP) and a surrounding envelope. In the RNP, genomic RNA is tightly encased by the nucleoprotein. Two other viral proteins, the phospoprotein and the large protein (L-protein or polymerase) are associated with the RNP.
What is the M protein in rabies?
The glycoprotein forms approximately 400 trimeric spikes which are tightly arranged on the surface of the virus. The M protein is associated both with the envelope and the RNP and may be the central protein of rhabdovirus assembly. The basic structure and composition of rabies virus is depicted in the longitudinal diagram below.
What is the process of fusion of the rabies virus envelope to the host cell membrane?
The fusion of the rabies virus envelope to the host cell membrane (adsorption) initiates the infection process. The interaction of the G protein and specific cell surface receptors may be involved.
What is the rhabdoviridae family?
Within this group, viruses with a distinct “bullet” shape are classified in the Rhabdoviridae family, which includes at least three genera of animal viruses, Lyssavirus, Ephemerovirus, and Vesiculovirus. The genus Lyssavirus includes rabies virus, Lagos bat, Mokola virus, Duvenhage virus, European bat virus 1 & 2 and Australian bat virus.
Where does the virus come from in the salivary gland?
Conversely, virus in the salivary glands buds primarily from the cell membrane into the acinar lumen.
Where does viral polymerase enter the genome?
The viral polymerase enters a single site on the 3’ end of the genome, and proceeds to synthesize full-length copies of the genome. These positive strands of rabies RNA serve as templates for synthesis of full-length negative strands of the viral genome.
What animals can transmit rabies?
Animals that can transmit the rabies virus. Any mammal (an animal that suckles its young) can transmit the rabies virus. The animals most likely to transmit the rabies virus to people include:
What animals are most likely to get rabies?
Animals most likely to transmit rabies in the United States include bats, coyotes, foxes, raccoons and skunks. In developing countries of Africa and Southeast Asia, stray dogs are the most likely to spread rabies to people. Once a person begins showing signs and symptoms of rabies, the disease nearly always causes death.
How do you get rabies from a bat?
But the more common way of getting rabies is from the silver-haired bat .". Jason Howland: The deadly virus is transmitted from the saliva of infected animals to humans, usually through a bite. Dr. Poland: "…. The bat doesn't always bite. Sometimes the saliva will drool onto you, and you could have a minor open cut.
What activities are likely to put you in contact with wild animals that may have rabies?
Activities that are likely to put you in contact with wild animals that may have rabies, such as exploring caves where bats live or camping without taking precautions to keep wild animals away from your campsite. Working in a laboratory with the rabies virus.
What is the causative agent of rabies?
The causative agent of rabies is rabies virus (RV), a negative-stranded RNA virus of the rhabdovirus family. Neuroinvasiveness and neurotropism are the main features that define the pathogenesis of rabies. Although RV pathogenicity is a multigenic trait involving several elements of the RV genome, the RV glycoprotein plays a major role in RV ...
What is the role of glycoprotein in RV pathogenesis?
Although RV pathogenicity is a multigenic trait involving several elements of the RV genome, the RV glycoprotein plays a major role in RV pathogenesis by controlling the rate of virus uptake and trans-synaptic virus spread, and by regulating the rate of virus replication.
What is the role of RV G in apoptosis?
However, the mechanism by which the RV G gene mediates the apoptosis signaling process remains largely unknown. It has been speculated that RV G expression exceeding a certain threshold severely perturbs the cell membrane, resulting in the activation of proteins that trigger apoptosis cascades [59].
What is the primary mechanism involved in RV G-mediated cell death?
Morphological studies with neuron cultures infected with this recombinant RV showed that cell death increased significantly in parallel with the overexpression of RV G and that apoptosis is the primary mechanism involved in RV G-mediated cell death.
What is the role of RNP in the immune system?
The RNP may play a significant role in the establishment of immunologic memory and long-lasting immunity [1,2]. RV has a broad host range and can infect almost all mammals. Although there have been several routes of transmission reported for RV, natural infection most frequently occurs via a bite.
What is the name of the protein that forms the ribonucleoprotein complex?
The N, P and L proteins form, together with the genomic RNA, the ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP). G is the only RV antigen capable of inducing the production of RV-neutralizing antibodies, which are the major immune effectors against a lethal RV infection.
Does RV affect the brain?
RV-infected rat brain also exhibited impairment of both the release and binding of serotonin, a neuro transmitter involved in controlling the sleep cycle, pain perception and behavior [19,20]. In addition to the effects on neurotransmission, RV infection might have effects on ion channels as well.
How does rabies travel?
The Virus Travels through the Body. From numerous studies conducted on rabid dogs, cats, and ferrets, we know that when the rabies virus isintroduced into a muscle through a bite from another animal, it travels from the site of the bite to the brain by moving within nerves. The animal does not appear ill during this time.
Where does rabies go after it has reached the brain?
Late in the disease, after the virus has reached the brain and multiplied there to cause an inflammation of the brain, it moves from the brain to the salivary glands and saliva. Also at this time, after the virus has multiplied in the brain, almost all animals begin to show the first signs of rabies.
How long does it take for rabies to show up in a dog?
Most of these signs are obvious to even an untrained observer, but within a short period of time, usually within 3 to 5 days, the virus has caused enough damage to the brain that the animal begins to show unmistakable signs of rabies. Extensive studies on dogs, cats, and ferrets show that the rabies virus can be excreted in the saliva ...
How long does rabies last after a bite?
The time between the bite and the appearance of symptoms is called the incubation period and it may last for weeks to months. A bite by the animal during the incubation period does not carry a risk of rabies because the virus has not yet made it to the saliva.
How long does it take for an animal to die from a virus?
The animal begins to show signs of the disease. The infected animal usually dies within 7 days of becoming sick. Page last reviewed: October 27, 2017.
Why is there so much variation in the time between exposure and the onset of the disease?
The reason there is so much variation in the time between exposure and the onset of the disease is that many factors come into play , including the site of the exposure, the type of rabies virus, and any immunity in the animal or person exposed.
Can rabies be excreted in saliva?
Extensive studies on dogs, cats, and ferrets show that the rabies virus can be excreted in the saliva of infected animals several days before illness is apparent. Such extensive studies have not been done for wildlife species, but it is known that wildlife species do excrete rabies virus in their saliva before the onset of signs of illness.
What animals are most likely to get rabies?
However, in developed countries domestic animals (dogs, cats, and cattle) only account for 10% of human exposures, while wild animals (skunks, foxes, raccoons, bats, and coyotes) account for the other 90%.
What is the highest risk of rabies?
While all bites should be treated with the same urgency, individuals who have sustained bites on the head, face, neck, and hand , particularly with bleeding, carry the highest risk of developing clinical rabies and are generally associated with shorter incubation periods.
What are the symptoms of rabies during the prodromal period?
Also, during the prodromal period the patient may experience focal symptoms at the portal of innoculation including pain, parasthesias, and pruritus. In the paralytic form of rabies the prodromal period may present with choreiform movements of the bitten limb.
What is the encephalic form of rabies?
Encephalitic rabies. In the encephalitic form of rabies the acute neurological syndrome classically includes painful pharyngeal spasms after exposure to a gust of air (aerophobia) or a drink of water (hydrophobia). The patient may also experience fever, hypersalivation, hyperactivity, fluctuating consciousness, and seizures.
What should you expect to find in a patient with rabies infection?
What should you expect to find? The symptoms found in a patient with rabies infection depend on 1) the form and 2) the stage of the disease. There are two classic forms of rabies: encephalitic and paralytic. A third, much less common form is discussed later.
What are the symptoms of paralytic rabies?
Distinguishing symptoms in paralytic rabies may include a lack of sensation disturbances (with the exception at the bite site), the presence of bladder dysfunction, and persistent fever coinciding with limb weakness. Cerebral involvement may not appear until late in the course making the diagnosis difficult.
What happens during a coma stage of rabies?
During the coma stage the patient may become nonresponsive, and in addition experience worsening hydrophobia, prolonged apnea, and generalized flaccid paralysis which leads to respiratory and cardiovascular collapse. The ultimate end point in the natural history of an untreated rabies infection is death.
What is the cause of rabies?
Rabies is caused by lyssaviruses, including the rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus. It is spread when an infected animal bites or scratches a human or other animal. Saliva from an infected animal can also transmit rabies if the saliva comes into contact with the eyes, mouth, or nose.
What is rabies in humans?
Rabies is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure.
How long does it take for rabies to show symptoms?
The period between infection and the first symptoms (incubation period) is typically 1–3 months in humans. This period may be as short as four days or longer than six years, depending on the location and severity of the wound and the amount of virus introduced. Initial symptoms of rabies are often nonspecific such as fever and headache. As rabies progresses and causes inflammation of the brain and meninges, symptoms can include slight or partial paralysis, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, agitation, abnormal behavior, paranoia, terror, and hallucinations. The person may also have fear of water.
How long should you wash a rabies bite?
Washing bites and scratches for 15 minutes with soap and water, povidone-iodine, or detergent may reduce the number of viral particles and may be somewhat effective at preventing transmission. As of 2016. , only fourteen people had survived a rabies infection after showing symptoms.
How many cases of rabies are caused by dogs?
In countries where dogs commonly have the disease, more than 99% of rabies cases are the direct result of dog bites. In the Americas, bat bites are the most common source of rabies infections in humans, and less than 5% of cases are from dogs. Rodents are very rarely infected with rabies.
What is hydrophobia in rabies?
Hydrophobia is commonly associated with furious rabies, which affects 80% of rabies-infected people. The remaining 20% may experience a paralytic form of rabies that is marked by muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and paralysis; this form of rabies does not usually cause fear of water.
What are the symptoms of rabies?
As rabies progresses and causes inflammation of the brain and meninges, symptoms can include slight or partial paralysis, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, agitation, abnormal behavior, paranoia, terror, and hallucinations. The person may also have fear of water. The symptoms eventually progress to delirium, and coma.
How does rabies spread?
Rabies transmission can occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva. Rabies lyssavirus, like many rhabdoviruses, has an extremely wide host range.
How many rabies viruses are there?
Evolution. All extant rabies viruses appear to have evolved within the last 1500 years. There are seven genotypes of Rabies lyssavirus. In Eurasia cases are due to three of these—genotype 1 (classical rabies) and to a lesser extent genotypes 5 and 6 (European bat lyssaviruses type-1 and -2).
How does rabies lyssavirus enter the host cell?
After receptor binding, Rabies lyssavirus enters its host cells through the endosomal transport pathway. Inside the endosome, the low pH value induces the membrane fusion process, thus enabling the viral genome to reach the cytosol. Both processes, receptor binding and membrane fusion, are catalyzed by the glycoprotein G which plays a critical role in pathogenesis (mutant virus without G proteins cannot propagate).
What are the proteins in the rhabdovirus?
Associated with the nucleocapsid are copies of P (phosphoprotein) and L (large) protein. The L protein is well named, its gene taking up about half of the genome. Its large size is justified by the fact that it is a multifunctional protein. The M (matrix) protein forms a layer between the nucleocapsid and the envelope, and trimers of G (glycoprotein) form spikes that protrude from the envelope. The genomes of all rhabdoviruses encode these five proteins, and in the case of Rabies Lyssavirus they are all of them.
How long does rabies last?
The first symptoms of rabies may be very similar to those of the flu including general weakness or discomfort, fever, or headache. These symptoms may last for days. There may be also discomfort or a prickling or itching sensation at the site of bite, progressing within days to symptoms of cerebral dysfunction, anxiety, confusion, agitation. As the disease progresses, the person may experience delirium, abnormal behavior, hallucinations, and insomnia. Rabies lyssavirus may also be inactive in its hosts body and become active after a long period of time.
What is rabies lyssa?
For other uses, see Rabies (disambiguation). Rabies Virus, scientific name Rabies lyssavirus, is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in humans and animals. Rabies transmission can occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva.
What are the two major structural components of rhabdovirus?
All rhabdoviruses have two major structural components: a helical ribonucleoprotein core (RNP) and a surrounding envelope. In the RNP, genomic RNA is tightly encased by the nucleoprotein. Two other viral proteins, the phosphoprotein and the large protein (L-protein or polymerase) are associated with the RNP.
What is a rabies virus?
Rabies virus is a rod- or bullet-shaped, single-stranded, negative-sense, unsegmented, enveloped RNA virus. The virus genome encodes five proteins. Classification and Antigenic Types. Placement within the family is based on the distinctive morphology of the virus particle.
Where is rabies found?
Today it is found in most countries, with the exception of those regions from which it has not been naturally reported, including many Australian islands, or areas achieving secondary elimination, such as the United Kingdom. Almost all human rabies is caused by the bite of a rabid animal (Fig 61-4).
How does rabies replication occur?
Pathogenesis. After inoculation, rabies virus may enter the peripheral nervous system directly and migrates to the brain or may replicate in muscle tissue , remaining sequestered at or near the entry site during incubation, ...
What is the most significant member of the genus Lyssavirus?
Human pathogens of medical importance are found in the genera Lyssavirus and Vesiculovirus.Only rabies virus, medically the most significant member of the genus Lyssavirus, is reviewed in this chapter.
How is rabies prevented?
Animal rabies is prevented by vaccinating susceptible species, particularly dogs and cats. Mass dog vaccination programs in the United States and Europe were largely responsible for a dramatic reduction in canine and human rabies during the 1940's and 1950s.
What are the stages of rabies?
Clinical Manifestations. Five general stages of rabies are recognized in humans: incubation, prodrome, acute neurologic period, coma, and death ( or, very rarely, recovery) (Fig. 61-1).
How long does it take for rabies to develop?
No specific antirabies agents are useful once clinical signs or symptoms develop. The incubation period in rabies, usually 30 to 90 days but ranging from as few as 5 days to longer than 2 years after initial exposure, is more variable than in any other acute infection.
