How many people have periodontal disease?
Top Gum Disease & Oral Health Care Statistics In America!
- Periodontitis affects 70% of individuals over 65 in the United States.
- Women are more likely than males to get periodontal disease.
- In the United States, periodontal disease is more prevalent in those living below poverty.
- Over 47% of Americans above 30 have severe gum disease.
How serious is periodontal gum disease?
Without the correct treatment, periodontal disease can eventually result in tooth loss and bone loss. It is a particularly serious condition that has also been linked to many other systemic diseases which include cardiovascular disease and diabetes gum disease.
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease?
The good news is that it is possible to cure periodontal disease. Below are some of the aspects of periodontal disease treatment that can be expected. Behavior Change. This is one of the first things the dentist will recommend as part of your treatment. Because plaque is the root cause of periodontal disease, it is essential that it is removed every day.
What is primary cause of periodontal disease is?
Plaque is the primary cause of gum disease. However, other factors can contribute to periodontal disease. These include: Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and monthly menstruation, make gums more sensitive, which makes it easier for gingivitis to develop.

What percentage of population has periodontitis?
The prevalence of periodontal (gum) disease continues to be an important public health problem in the United States as 2 in 5 adults are affected by some form of this disease.
What percent of the US has periodontal disease?
The CDC's analysis showed that 47.2 percent of Americans, totaling 64.7 million people, have gum disease that could be characterized as mild, moderate or severe. In adults who are 65 or older, the rate of gum disease rises to 70.1 percent.
Is periodontal disease a big deal?
Periodontitis (per-e-o-don-TIE-tis), also called gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Periodontitis can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth loss.
How many people are diagnosed with periodontal disease?
Nearly half (46%) of all adults aged 30 years or older show signs of gum disease; severe gum disease affects about 9% of adults.
How fast does periodontal disease progress?
The progression of periodontal disease is slow but steady. It only takes four days for plaque to reach its maximum extent, so you'll be able to physically see signs of gingivitis on day 5. Advanced stages of this disease can be seen in as little as a few weeks if you have not tried to reverse the gingivitis.
Can you live with periodontal disease?
Living with periodontal disease can cause aesthetic complications and bone loss of a serious nature. Unlike other injuries, periodontal disease does not cause any pain. It is a silent disease when the teeth gum becomes inflamed and bleeds.
Can periodontitis be stopped?
Periodontitis can be stopped if caught and treated early enough. Treatment is typically very successful. If you have periodontitis, regular follow-ups with a dentist are essential to ensure that the disease doesn't continue.
Will periodontitis be cured?
Periodontitis can only be treated but cannot be cured. Gingivitis, on the other hand, can be prevented by maintaining proper oral hygiene practices and visiting the dentist for checkups and exams.
What happens if you don't treat periodontitis?
Periodontitis (also called periodontal disease) is gum disease. This infection damages the soft tissue around your teeth and wears away the bone supporting them. If left untreated, the disease eventually ruins the bone, loosening the teeth and causing them to fall out.
Is periodontitis completely preventable?
Although periodontal disease is the most prevalent infectious oral condition but is treatable and preventable.
What does early stage gum disease look like?
In its early stages, inflammation around the gums is observable, with gum tissues appearing red and swollen. Gums that are easily irritated or that bleed during tooth brushing indicate the presence of Gingivitis.
How long does it take for gingivitis to turn into periodontitis?
Slight Periodontal Disease Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease. At this stage, your gums will start to pull away or "recede" from your teeth.
What percentage of adults have gum recession?
Almost half, 47.2%, of all adults aged 30 years and older have some form of gum disease. Gum disease increases with age. 70.1% of adults 65 years and older have periodontal disease. Smoking can put you at risk for gum problems.
How common is advanced periodontal disease?
Advanced periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis, is extremely common among American adults.
Will periodontitis be cured?
Periodontitis can only be treated but cannot be cured. Gingivitis, on the other hand, can be prevented by maintaining proper oral hygiene practices and visiting the dentist for checkups and exams.
Can periodontitis be reversed?
Periodontitis can't be reversed, only slowed down, while gingivitis can be reversed. This is why it's important to catch it in its early stages and prevent it from moving on to periodontitis. Below are some ways you can reverse gingivitis so it doesn't progress into something more serious.
How many people have periodontal disease?
47.2% of adults aged 30 years and older have some form of periodontal disease . Periodontal disease increases with age, 70.1% of adults 65 years and older have periodontal disease. This condition is more common in men than women (56.4% vs 38.4%), those living below the federal poverty level (65.4%), those with less than a high school education ...
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal diseases are mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults. Periodontal disease and tooth decay are the two biggest threats to dental health.
What is the most serious form of tooth decay?
In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults. Periodontal disease and tooth decay are the two biggest threats to dental health.
What happens when bacteria in your mouth is on your teeth?
Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus.
How to treat gingivitis?
Gingivitis can be controlled and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and sometimes corrective surgery.
How to get rid of gum disease?
Brush and floss every day to remove the bacteria that cause gum disease.
Can tartar build up on gums be removed?
Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health professional can remove the tartar and stop the periodontal disease process.
How to prevent gum disease?
To help prevent or control gum disease, it is important to brush daily and floss regularly. Also, make sure to see your dentist for routine checkups. Almost half, 47.2%, of all adults aged 30 years and older have some form of gum disease.
What is it called when your gums pull away from your teeth?
That's called gingivitis. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums pull away from the teeth and form spaces (called "pockets") that become infected. This can cause loss of the bone that holds teeth in place, and eventually tooth loss.
Why do my gums bleed?
It's typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on teeth and harden. In its early stage, the gums can become red, swollen, and may bleed easily. That's called gingivitis. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums pull away from the teeth and form spaces ...
Does smoking cause gum disease?
Smoking can put you at risk for gum problems. In fact, 64.2% of current smokers have gum disease . Sources : MedlinePlus: Learning about Gum Disease ; National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research: Preventing Gum Disease ; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Periodontal Disease.
How many people have gum disease?
The study confirmed that almost 50 percent of adults in the U.S., who are over the age of 30, have the advanced form of periodontal disease, or gum disease.
What is gum disease?
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It is a major cause of tooth loss in adults. Because gum disease is usually painless, you may not know you have it.
How old do you have to be to have a dental checkup?
Having regular dental exams is vital in preventing and reversing gum disease. The study findings recommended that all adults over the age of 30 should have annual comprehensive periodontal evaluations and assessments by a dental professional.
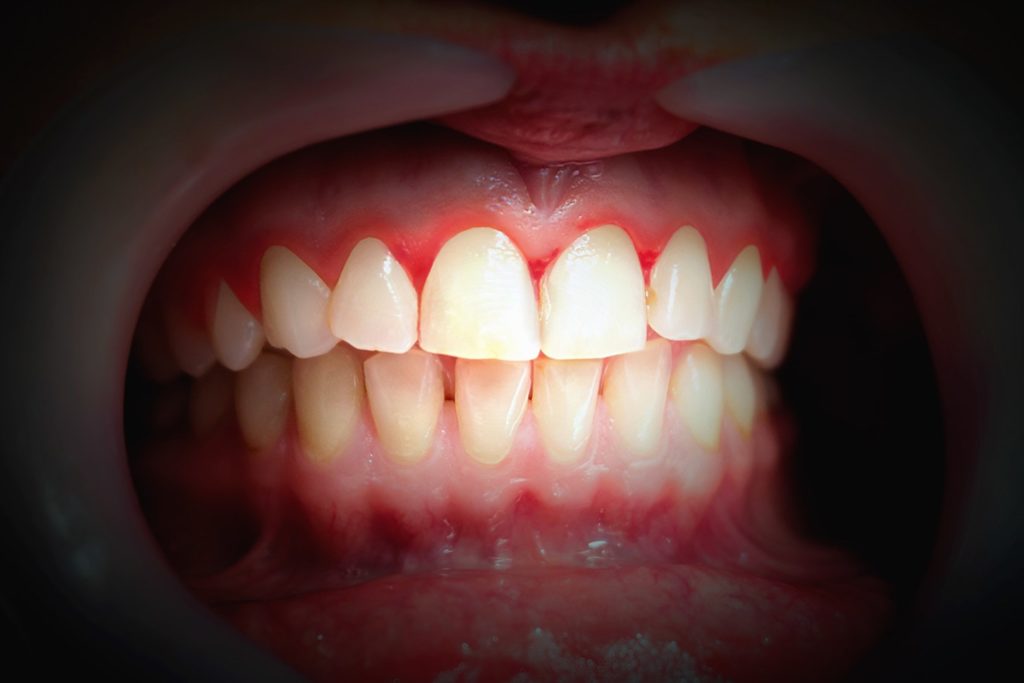
What Is Periodontal Disease?
- Periodontal diseases are mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may...
Causes
- Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus. Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health profession…
Warning Signs
- The following are warning signs of periodontal disease: 1. Bad breath or bad taste that won’t go away 2. Red or swollen gums 3. Tender or bleeding gums 4. Painful chewing 5. Loose teeth 6. Sensitive teeth 7. Gums that have pulled away from your teeth 8. Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite 9. Any change in the fit of partial dentures
Risk Factors
- Certain factors increase the risk for periodontal disease: 1. Smoking 2. Diabetes 3. Poor oral hygiene 4. Stress 5. Heredity 6. Crooked teeth 7. Underlying immuno-deficiencies—e.g., AIDS 8. Fillings that have become defective 9. Taking medications that cause dry mouth 10. Bridges that no longer fit properly 11. Female hormonal changes, such as with pregnancy or the use of oral c…
Prevention and Treatment
- Gingivitis can be controlled and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and some…
What Is The CDC Doing About Periodontal Disease?
- The CDC is currently working with key partner organizations such as the American Academy of Periodontology and the American Dental Association to improve and sustain surveillance of periodontal disease in the adult U.S. population. The efforts of the CDC include (1) developing measures for use in surveillance of periodontal disease at the state and local levels, (2) improvin…
Podcasts About Periodontal Disease and Diabetes
- Listen to Summary: Periodontal Disease and Diabetes Podcast. Provides valuable information on the impact of periodontal disease and its link to diabetes (Length 1:36). View transcript. Listen to Periodontal Disease and Diabetes Podcast. Informative interview of two dental professionals about periodontal disease, diabetes complications, and the influence of poor oral health on bloo…
Additional Resources
- Periodontal (Gum) Diseases: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment. [PDF–1.26 M]external icon. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research consumer brochure. Bethesda, MD. Reprinted January 2006. American Academy of Periodontologyexternal icon Journal articles on periodontal disease
Reference
- 1Eke PI, Dye B, Wei L, Thornton-Evans G, Genco R. Prevalence of Periodontitis in Adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J Dent Res. Published online 30 August 2012:1–7. View full textexternal icon. Top of Page