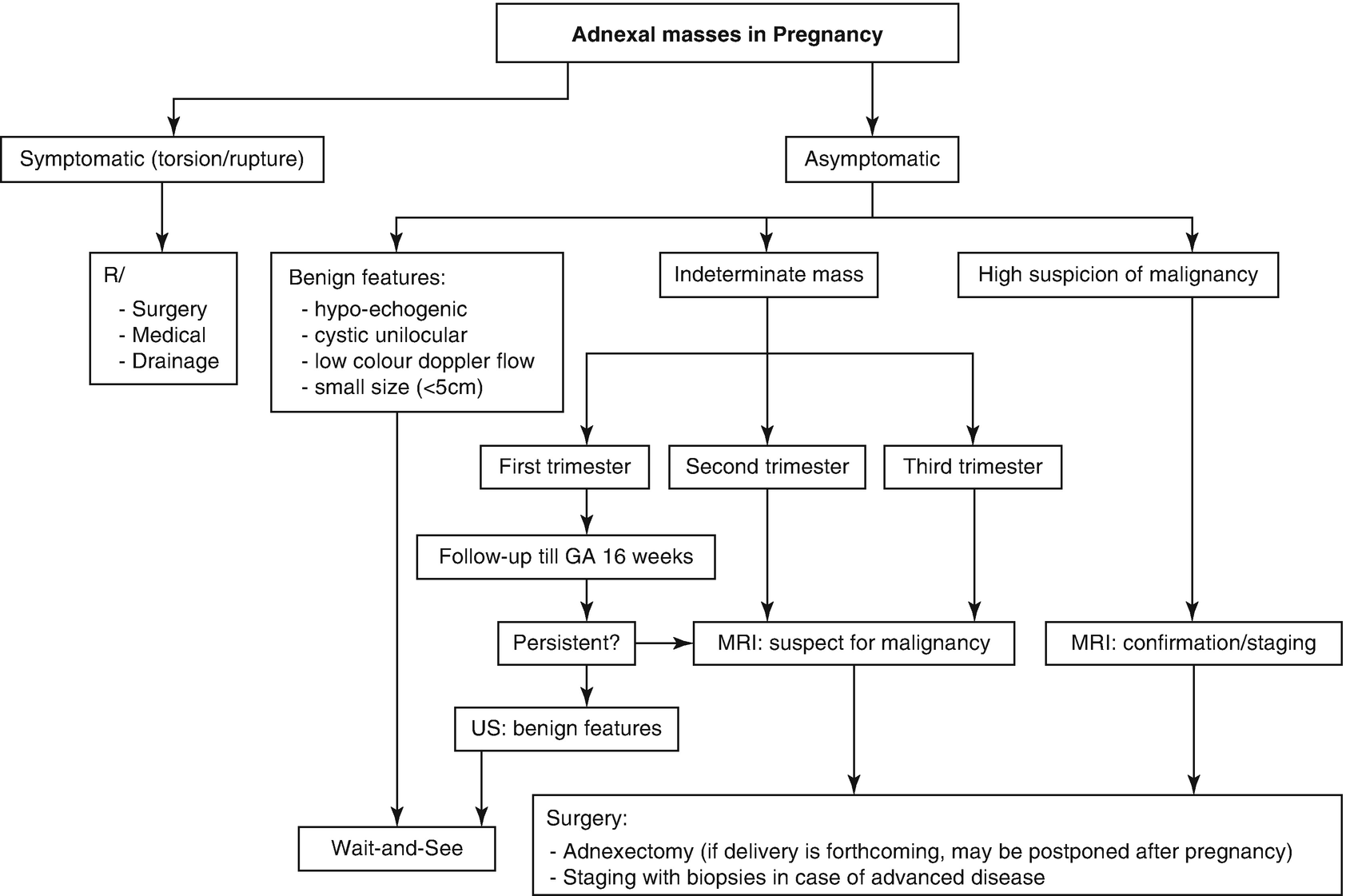
What percentage of adnexal masses are benign?
1. Epidemiology, Signs and Symptoms In the United States, the diagnosis of an adnexal or pelvic mass will occur in five to ten percent of women in their lifetime. Although commonly benign, a small percentage (15 to 20 percent) will be malignant and diagnosis of these at the earliest possible stage is of critical importance.
What is an adnexal mass in a postmenopausal patient?
The adnexal mass in a postmenopausal patient poses an important diagnostic and management dilemma for primary care providers and gynecologists. Postmenopausal women are at a significantly increased risk of gynecologic malignancy; yet even in this population the majority of adnexal masses are benign.
Is an adnexal mass dangerous?
Some adnexal masses are benign tumors or noncancerous growths. These growths won't spread to other body parts and don't usually pose any major threats. They grow slowly and are often only noticed during a routine exam. Ovarian cancer could also cause a pelvic mass.
Can adnexal tumors be cancerous?
Adnexal tumors are most often noncancerous (benign), but they can be cancerous (malignant). Adnexal tumors occur in the: Ovaries. Fallopian tubes. Connective tissue around the ovaries or fallopian tubes.

How do I know if my adnexal cyst is cancerous?
Oftentimes imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI can determine if an ovarian cyst or tumor is benign or malignant. They may also want to test your blood for CA-125, a tumor marker, or preform a biopsy if there is any question. High levels of CA-125 may indicate the presence of ovarian cancer.
What percent of ovarian masses are cancerous?
Overall, they account for 20 to 25% of all tumors, benign as well as malignant, of the ovary. Approximately 3% are malignant. Malignant germ cell tumors include dysgerminomas, endodermal sinus tumors, embryonal carcinomas, and nongestational choriocarcinomas.
What is the most common adnexal mass?
In premenopausal women, physiologic follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts are the most common adnexal masses, but the possibility of ectopic pregnancy must always be considered. Other masses in this age group include endometriomas, polycystic ovaries, tubo-ovarian abscesses and benign neoplasms.
Are adnexal tumors cancerous?
Adnexal tumors are growths of cells that form on the organs and connective tissues around the uterus. Adnexal tumors most often aren't cancerous, but they can be cancerous. Adnexal tumors occur in the: Ovaries.
What is the normal size of adnexal mass?
Results: One hundred and eighty-six women underwent laparoscopic evaluation for an adnexal mass of 10 cm or larger in size. The average preoperative mass size was 12.1 +/- 4.9 cm.
What is the treatment for adnexal mass?
Treatment options for adnexal masses vary depending on the specific diagnosis. Some masses can be treated conservatively, and others may require surgery. Observation is generally recommended when the appearance of the adnexal mass on ultrasonography suggests a benign growth.
Do adnexal masses go away?
The majority of adnexal masses aren't harmful. They won't require treatment unless a woman is experiencing uncomfortable symptoms. Many adnexal masses will resolve themselves without any intervention. In a very small number of cases, the cause of the adnexal mass will be ovarian cancer.
What is the cause of adnexal mass?
What Causes Adnexal Cysts? Fluid-filled cysts on the ovaries are usually caused by hormonal stimulation or bleeding at the time of ovulation (hemorrhagic ovarian cysts).
When should an adnexal cyst be removed?
Large or persistent ovarian cysts, or cysts that are causing symptoms, usually need to be surgically removed. Surgery is also normally recommended if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous or could become cancerous.
Can a solid ovarian mass be benign?
Fibroma. The most common benign solid tumor of the ovary is the fibroma (see Benign Solid Ovarian Tumors). Fibromas are derived from connective tissue and arise from the solid ovarian cortical stroma. Histologically, spindle cells are seen.
What percentage of pelvic masses are cancerous?
Epidemiology, Signs and Symptoms Although commonly benign, a small percentage (15 to 20 percent) will be malignant and diagnosis of these at the earliest possible stage is of critical importance.
Are most pelvic masses benign?
A pelvic mass is also known as an adnexal mass. It is a growth that happens near or in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, and connecting tissues. While they are often benign, they can be cancerous.
What percent of ovarian masses are benign?
Among the ovarian neoplasms, 87.8 % were benign and 10 % were malignant.
Are ovarian masses always cancerous?
Most ovarian germ cell tumors are benign, but some are cancerous and may be life threatening. Less than 2% of ovarian cancers are germ cell tumors. Overall, they have a good outlook, with more than 9 out of 10 patients surviving at least 5 years after diagnosis.
What is the most common benign ovarian tumor?
Benign epithelial tumours are the most common type of benign ovarian tumour. They start from the cells that cover the outer surface of the ovary. Their makeup can be mainly cystic (called cystadenoma), mainly solid (called adenofibroma) or mixed (called cystadenofibroma).
How can you tell if an ovarian tumor is cancerous?
The 2 tests used most often (in addition to a complete pelvic exam) to screen for ovarian cancer are transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and the CA-125 blood test. TVUS (transvaginal ultrasound) is a test that uses sound waves to look at the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries by putting an ultrasound wand into the vagina.
What is an adnexal mass?
What is adnexal mass? An adnexal mass is a lump of tissue in or near the female reproductive system, usually in an ovary or uterine tube. They are called "adnexal" because of their association with the adnexa of the uterus, which are appendages related to the uterus. These appendages include the tissue around the uterus, ovaries, and uterine tubes.
Where is the adnexal mass located?
Managing adnexal mass. When to see a doctor. Discovering a growth or mass can set off alarms in anyone’s head. If it's located in the breast or reproductive area, it's easy to jump to conclusions and assume the worst. A lump near the ovaries or uterus isn’t always a cause for major concern. Sometimes it’s a non-threatening adnexal mass.
How often are pelvic masses cancerous?
Most pelvic masses are not cancerous. Only 5–10 percent of women will be diagnosed with one in their lifetime, and 15–20 percent of those masses are cancerous. The most important action upon discovering a malignant mass is diagnosing it and treating it as soon as possible. The faster a cancerous tumor or growth is diagnosed and removed and treatment begins, the better the outcome will be. The risk of a cancerous adnexal or pelvic mass increases with age, and postmenopausal people are at a greater risk than premenopausal people.
How to manage adnexal mass?
Ways to manage adnexal mass. The location and cause of the adnexal mass will influence what types of treatment are used. People with ovarian cysts can have them surgically removed or wait for the cysts to go away on their own. Benign or malignant tumors are often removed by surgery.
What causes pelvic mass?
Some causes of pelvic masses, like ectopic pregnancies, can lead to the rupture of the uterine tube and cause serious bleeding. Emergency medical care should be sought immediately.
What are the symptoms of adnexal masses?
Pelvic pain. Irregular menstrual cycle. Difficulty urinating or the frequent urge to do so. Constipation. Gastrointestinal problems. The symptoms of adnexal masses often depend on the condition they're associated with, so some may have more severe symptoms than others.
What is the procedure to remove a pelvic mass called?
The surgery that's often used to remove a pelvic mass is called a laparotomy. In a laparotomy, an incision is made in the abdomen to explore potential problems and remove both benign and potentially cancerous growths.
Where does an adnexal mass occur?
An adnexal mass is a growth that occurs in or near the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the connecting tissues. They’re usually benign, but are sometimes cancerous. Some of them are filled with fluid, and some are solid.
How to diagnose adnexal mass?
Adnexal masses are usually diagnosed by a pelvic exam, ultrasound, or both. Often, in cases when the woman isn’t showing any symptoms, the growth is detected during routine exams. Once diagnosed, your doctor will decide if your case is an emergency. Usually it’s not, and your doctor will have time to investigate what’s causing the mass and ...
What tests can be used to determine the cause of adnexal mass?
Imaging and lab tests can be used to determine the underlying cause of the adnexal mass. Your doctor will also probably have you take a pregnancy test to rule out an ectopic pregnancy, since this will need immediate treatment.
What is a benign ovarian tumor?
Benign ovarian tumors. An ovarian tumor is an abnormal lump or growth of cells. They differ from cysts in that they’re solid masses rather than filled with fluid. When the cells inside the tumor aren’t cancerous, it’s a benign tumor. This means it won’t invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body.
What is the most common cancer in women?
Ovarian cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in women. Abnormal cells in the ovary multiply and form a tumor. This tumor has the capacity to grow and spread to other areas of the body. Symptoms are usually present in ovarian cancer and can include:
When should adnexal masses be discovered?
However, adnexal masses are sometimes discovered during a pregnancy when having routine ultrasounds or pelvic exams.
Can you have surgery for a small adnexal mass?
If the adnexal mass is small and you have no symptoms, then it may not require treatment at all. However, your doctor will likely want to monitor you with regular pelvic exams and ultrasounds. Surgery will be needed if: the mass begins to grow. you develop symptoms.
What percentage of women have adnexal mass?
Epidemiology, Signs and Symptoms. In the United States, the diagnosis of an adnexal or pelvic mass will occur in five to ten percent of women in their lifetime. Although commonly benign, a small percentage (15 to 20 percent) will be malignant and diagnosis of these at the earliest possible stage ...
How to rule out pregnancy with adnexal mass?
It is also important to rule out pregnancy when presented with an adnexal or pelvic mass by obtaining a pregnancy test in patients of childbearing age. The most effective diagnostic approach is a combination of physical examination, imaging and serum marker assessment.
What are the symptoms of adnexal mass?
The most common symptoms encountered in a patient with an adnexal or pelvic mass are abdominal fullness, abdominal bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty with bowel movements, and increased frequency of urination, abnormal vaginal bleeding, or pelvic pressure.
What is the most commonly performed imaging study for the suspicion of a pelvic mass?
Metastatic Cancers. The most commonly performed imaging study for the suspicion of a pelvic mass is an ultrasound. It is recommended that transvaginal as well as transabdominal ultrasound be performed whenever possible.
What are the complications of pelvic mass management?
Surgical risks include, but are not limited to bleeding, blood clots, infection, damage to adjacent organs, and anesthesia. For those patients managed conservatively, the major risk would be not intervening in the presence of a cancer. Although not highly specific, most triage strategies for the management of a pelvic mass have excellent negative predictive values, that is, the ability to predict that a patient does not have cancer. Although not 100%, this can be reassuring to both the clinician and the patient.
When did the pelvic mass referral guidelines come out?
In an effort to better delineate the location of surgery for a pelvic mass, the Society of Gynecologic Oncologists (SGO) and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) proposed referral guidelines in 2005.
Why is it important to document the mass?
Masses are not always palpable, but if present, documenting the nature of the mass, including its size, laterality, contour, mobility, presence or absence of tenderness, and location, is important in guiding future surgical decision making as well as contributing to the differential diagnosis.
What are adnexal tumors?
Adnexal tumors occur in the: 1 Ovaries 2 Fallopian tubes 3 Connective tissue around the ovaries or fallopian tubes
How to diagnose adnexal tumor?
Diagnosis of adnexal tumors involves a careful physical exam, imaging tests and, sometimes, surgery. Treatment for adnexal tumors depends on the specific location and types of cells involved.
Why is the adnexal mass important?
The adnexal mass in a postmenopausal patient poses an important diagnostic and management dilemma for primary care providers and gynecologists. Postmenopausal women are at a significantly increased risk of gynecologic malignancy; yet even in this population the majority of adnexal masses are benign. …
What imaging modality is used for adnexal mass?
Tumor markers and imaging can help in the evaluation of adnexal mass in postmenopausal women. Transvaginal ultrasound has long been considered the imaging modality of choice for the evaluation of adnexal masses.
Is adnexal mass benign?
Postmenopausal women are at a significantly increased risk of gynecologic malignancy; yet even in this population the majority of adnexal masses are benign. Evaluation and management of these lesions ...
