How much of Malaysia is covered by forest?
Malaysia’s land surface was once almost entirely covered with forest. Today, forests still cover about 54%of the total land area. However, deforestation is a major concern as the country is still rapidly developing. From 2001 to 2019, there was a reduction of about 8.12 million hectares of forest cover in Malaysia.
What are the different types of rainforests in Malaysia?
Malaysian rainforests contain several different forest types throughout the region. According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), these include lowland dipterocarp forest, hill dipterocarp forest, upper hill dipterocarp forest, oak-laurel forest, montane ericaceous forest, peat swamp forest, mangrove forest, freshwater swamp forest, heath forest, ...
Is deforestation a major concern in Malaysia?
However, deforestation is a major concern as the country is still rapidly developing. From 2001 to 2019, there was a reduction of about 8.12 million hectares of forest cover in Malaysia. This is equivalent to a 28% decrease in tree cover since 2000.
How many species are there in Malaysia?
Biodiversity and Protected Areas: Malaysia has some 1671 known species of amphibians, birds, mammals and reptiles according to figures from the World Conservation Monitoring Centre. Of these, 13.9% are endemic, meaning they exist in no other country, and 9.3% are threatened.
Where is the rainforest in Malaysia?
What are the threats to the Malaysian rainforest?
How much of the world's land is forest?
What is the WWF Malaysia?
See 1 more
About this website
What percentage of Malaysia is forest?
Malaysia's land surface was once almost entirely covered with forest. Today, forests still cover about 54% of the total land area. However, deforestation is a major concern as the country is still rapidly developing. From 2001 to 2019, there was a reduction of about 8.12 million hectares of tree cover in Malaysia.
How big is the rainforest in Malaysia?
Taman Negara Rainforest is one of the oldest rainforests in the world. It has been around for 130 million years, which means the forest, once upon a time, used to accommodate dinosaurs. Spanning over a 4343 sq. km, Taman Negara is one of Malaysia's premier and the most popular tourist destinations.
What is the percentage of rainforests?
Tropical rainforest now covers about six percent of Earth's land surface.
Is Malaysia a rainforest country?
Malaysia has one of the most complex tropical rainforest ecosystems in the world. The country as a whole has a tropical maritime climate. It is also a relatively small country, and with a land area of only about 33 million ha, is about the size of the British Isles.
Why is Malaysia an important rainforest?
Ecological Significance Malaysian rainforests support a vast diversity of plant and animal life, including approximately 200 mammal species (such as the rare Malayan tiger, Asian elephant, Sumatran rhinoceros, Malayan tapir, gaur, and clouded leopard), over 600 species of birds, and 15,000 plants.
What is the rate of deforestation in Malaysia?
From 2001 to 2021, Malaysia lost 8.67Mha of relative tree cover, equivalent to a 30% decrease since 2000 and 2.0% of the global total.
What percentage of rainforest is left?
36 %Of the approximately 14.5 million square kilometres of tropical rainforest that once covered Earth's surface, only 36 % remains intact. Just over a third, 34 %, is completely gone and the last 30 % is in various forms of degradation. Of the current rainforest cover, almost half (45 %) is in a degraded state.
What percentage of Earth is tropical rainforest?
Tropical rainforests cover only 7% of the Earth's land surface but contain over 50% of the worlds wildlife.
What is the biggest rainforest in the world?
The AmazonThe Amazon is the world's largest rainforest. It's home to more than 30 million people and one in ten known species on Earth. See some of this region's splendor in our new video.
What is Malaysia known for?
What is Malaysia Famous For?The Petronas Towers. One of Malaysia's most recognisable and iconic landmarks is the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur. ... Stunning Coastal Landscape. ... Malacca City. ... Gunung Mulu National Park. ... Batu Caves. ... Multiculturalism. ... Malaysian Food. ... 7 Interesting Facts about Johor Bahru.More items...•
What type of forest is Malaysia?
Major Forest Types. Major forest types in Malaysia include the lowland dipterocarp forest, the hill dipterocarp forest, the upper hill dipterocarp forest, the oak-laurel forest, the montane ericaceous forest, the peat swamp forest and the mangrove forest.
Why is the Malaysian rainforest being destroyed?
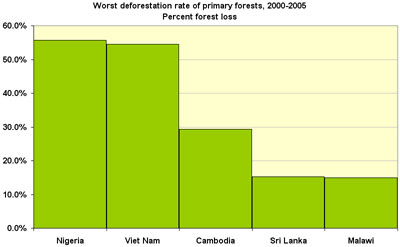
As well as unsustainable logging practices, Malaysia's forests are under threat from rapid deforestation, illegal removal of forest products and encroachment. Its deforestation rate is accelerating faster than in any other tropical country, and between 1990 and 2010, it lost 8.6%, or 1,920,000ha of its forest cover.
Why is the Malaysian rainforest being destroyed?
As well as unsustainable logging practices, Malaysia's forests are under threat from rapid deforestation, illegal removal of forest products and encroachment. Its deforestation rate is accelerating faster than in any other tropical country, and between 1990 and 2010, it lost 8.6%, or 1,920,000ha of its forest cover.
What big cats are in Malaysia?
Peninsular Malaysia holds four big cats: the Indochinese tiger, the Malayan tiger, the Indochinese leopard and also the clouded leopard. Another major predator is the sunbear.
What animal can only be found in Malaysia?
Malayan TigerMalayan Tiger (Source) The national animal of Malaysia, the Malaysian Tiger is also recognized as a symbol of bravery in the country. Without a doubt, the Malayan Tiger is the pride of Malaysia.
What animals are in a Malaysian jungle?
Animals include orangutan, Malayan weasel, leopard, Bornean gibbon, tarsier, bearded pig, elephant, rhinoceros hornbill and mountain serpent-eagle.
THE 10 BEST Malaysia Forests (with Photos) - Tripadvisor
Quite nearby the city for 30 mins drive uphill on the way to ulu yam passing by Empangan Batu (water reservoir). Minimal entrance fee at RM1 for an adult and RM0.50 for a kid.
10 rainforest resorts in Malaysia you should check out - CNN
Malaysia is blessed with beautiful rainforests -- on its amazing islands, highlands and along its stunning coastlines. The best thing? You can live within them. Here are 10 you should check out.
What’s Happening to the Rainforests in Malaysia: Deforestation and ...
When I am trekking through forests, peaks and natural foliage in other parts of the world: I often come across visitors who have visited Malaysia and get wild-eyed about Borneo and Taman Negara where they talk about the oldest rainforests, especially the tall Borneo’s dipterocarps, the tallest rainforest trees in the world, reaching up to unbelievable height of 60-70m, even 90m (as tall as a ...
How much of Malaysia's land is deforested?
Today, forests still cover about 54%of the total land area. However, deforestation is a major concern as the country is still rapidly developing. From 2001 to 2019, there was a reduction of about 8.12 million hectares of forest cover in Malaysia. This is equivalent to a 28% decrease in tree cover since 2000.
What is WWF Malaysia?
WWF-Malaysia supports the implementation of the national and state policies through our Sabah Landscapes Programme (SLP), which has three pillars: Protect, Produce and Restore. SLP aims to support the achievement under of the sustainable development goals by integrating the protection of forests, wildlife and rivers with RSPO certified production of palm oil, and restoration of ecological corridors and riparian reserves. Through the programme, WWF-Malaysia will work in three priority landscapes such as Tabin, Tawau and Lower Sugut. Subsequent conservation efforts will also continue in Central Forest, Kalabakan and Ulu Padas-Nabawan landscapes. Learn More
How much of the Earth's surface is covered by forests?
Forests cover 30% of the Earth’s surface and contain much of the biological diversity found on land – they harbour over two-thirds of known terrestrial species, many of which are threatened.
Which region has the most biodiversity?
The rainforests of Southeast Asia, including Malaysia, are believed to be the oldest and among the most biologically diverse in the world.
Is Borneo a biodiversity hotspot?
To conservationists, Borneo is one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. The ambitious conservation programme, Heart of Borneo that some may have heard of encompasses not just any area in Borneo, but highland forests at the core, or heart, of the island.
How much of Malaysia is forested?
According to the U.N. FAO, 62.3% or about 20,456,000 ha of Malaysia is forested, according to FAO. Of this 18.7% ( 3,820,000 ) is classified as primary forest, the most biodiverse and carbon-dense form of forest. Malaysia had 1,807,000 ha of planted forest.
How much carbon is in Malaysia's forests?
Malaysia's forests contain 3,212 million metric tons of carbon in living forest biomass. Biodiversity and Protected Areas: Malaysia has some 1671 known species of amphibians, birds, mammals and reptiles according to figures from the World Conservation Monitoring Centre. Of these, 13.9% are endemic, meaning they exist in no other country, ...
How much forest cover did Malaysia lose in 2010?
Change in Forest Cover: Between 1990 and 2010, Malaysia lost an average of 96,000 ha or 0.43% per year. In total, between 1990 and 2010, Malaysia lost 8.6% of its forest cover, or around 1,920,000 ha. Malaysia's forests contain 3,212 million metric tons of carbon in living forest biomass.
What was Malaysia's growth driven by?
Growth was almost exclusively driven by exports - particularly of electronics. As a result, Malaysia was hard hit by the global economic downturn and the slump in the information technology (IT) sector in 2001 and 2002.
How many species of vascular plants are there in Malaysia?
Malaysia is home to at least 15500 species of vascular plants, of which 23.2% are endemic. 4.1% of Malaysia is protected under IUCN categories I-V. In May 2011, Sassan Saatchi of Caltech's Jet Propulsion Lab and colleagues published a paper in PNAS with new carbon stock estimates for global tropical forests.
How much of Malaysian Borneo is covered by rainforest?
We estimate that only about 22% of the land area of Malaysian Borneo is still covered by forests that have not been logged, and that’s being conservative. The sheer extent of logging, that logging roads penetrate almost the entire area of remaining forests in Sabah and Sarawak may be a surprise to many – that’s because most previous studies have used low resolution imagery to map forests, and you simply can’t ‘see’ logging unless you use high resolution imagery like we did.
What would satellite imagery do to Malaysia?
Mannan added that more up-to-date satellite imagery would help countries like Malaysia better manage forest resources, including identifying areas that should be set aside for protection .
Why is logging so bad in Borneo?
One reason the impact of logging has been greater in Borneo than regions like Latin America and Central Africa is the nature of the island’s forests, which have a high density of commercially exploitable dipterocarp trees. Therefore loggers in Malaysian Borneo extract a much higher volume of trees per hectare, causing considerable damage and requiring longer harvest cycles. Low returns between harvests increase pressure to convert logged-over forests for timber and oil palm plantations.
What is the challenge for Sabah and Sarawak?
The challenge for Sabah and Sarawak however will be making the transition away from forestry and plantation agriculture. At present there is intense political pressure to turn over non-productive logged-over forests for conversion to plantations rather than wait for them to recover or turn them over for protected areas. While both states have considerable offshore energy reserves, revenue flows from those resources accrue to the central government. So neither Sabah nor Sarawak can currently rely on Brunei’s economic model.
What is the difference between Brunei and Sabah?
Unlike Sabah and Sarawak, it has largely left its forests for the birds. The difference in policy offers a stark contrast when it comes to forest cover: nearly two-thirds of its forest cover is “intact” and only 15 percent is classified as “degraded” or “severely degraded.”
How many miles of roads are there in Sarawak?
The study uncovered some 226,000 miles (364,000 km) of roads across Sabah and Sarawak, and found that roughly 80 percent of the two states have been impacted by logging or clearing. At best, only 45,400 square kilometers of forest ecosystems in the region remain intact.
Is excluding logging from primary forests a conservation strategy?
The authors argue that Brunei’s example shows that excluding logging from primary forests is a far more effective conservation strategy than trying to manage old-growth forests through reduced-impact logging.
Where is the majority of Malaysia's forest?
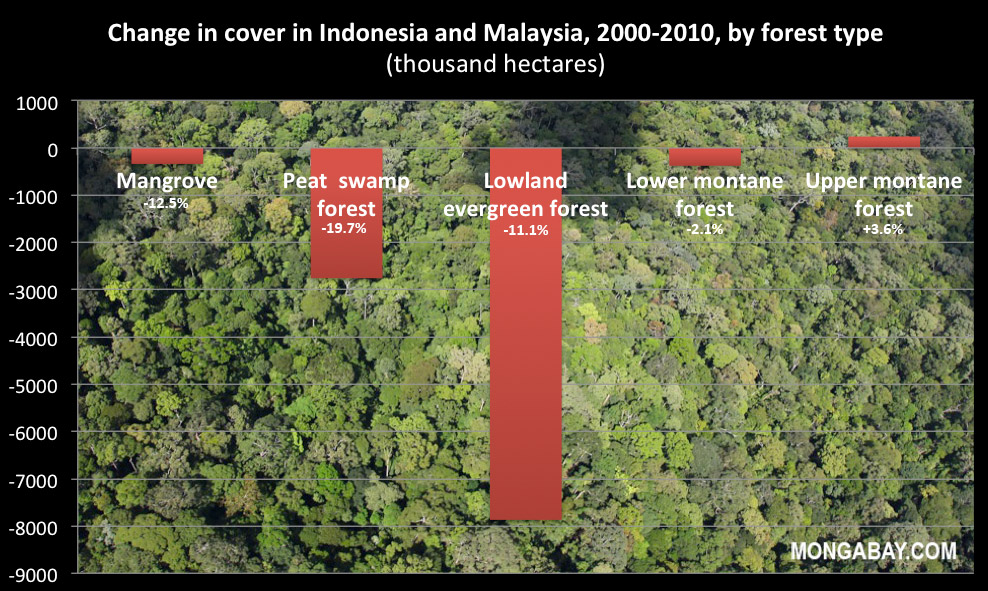
Most of Malaysia's remaining primary forest exists on the island of Borneo in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, but the majority of the forest area in Malaysian Borneo —especially the lowlands—has been selectively logged, resulting in reduced biodiversity.
How much of Malaysia's forest is pristine?
Forest cover has fallen dramatically in Malaysia since the 1970s. While FAO says that forests still cover more than 60 percent of the country, only 11.6 percent of these forests are considered pristine.
What was the impact of the attacks on Penan?
The attacks on the Penan brought international attention to the logging of Borneo's forests but appear to have had relatively little long-term impact, since logging increased dramatically in the following years. Mining. Decades of mining in peninsular Malaysia have left a heavy mark on the environment.
Why is the forest cover in Malaysia declining?
Declining forest cover in Malaysia results primarily from urbanization, agricultural fires, and forest conversion for oil-palm plantations and other forms of agriculture. Logging, which is generally excluded in deforestation figures from FAO, is responsible for widespread forest degradation in the country, and green groups have blamed local timber companies for failing to practice sustainable forest management. In late 2005—despite photographic evidence suggesting otherwise—the Samling Group denied claims from NGOs accusing the timber giant of recklessly harvesting timber in one of its Sarawak concessions on the island of Borneo.
What did Malaysia do to open up the rainforest?
Transmigration. Like Indonesia, the Malaysian government sponsored transmigration programs to open up rainforest for cash crop production. Between 1956 and the 1980s, Malaysia converted more than 15,000 square kilometers of forest for resettlement programs.
How much forest has Malaysia lost?
In total, Malaysia lost an average of 140,200 hectares—0.65 percent of its forest area—per year since 2000. For comparison, the Southeast Asian country lost an average of 78,500 hectares, or 0.35 percent of its forests, annually during the 1990s.
How many acres of forest was floodbed by Bakun Dam?
In the 1990s, the government overturned a High Court decision that would have prevented Bakun dam, a huge hydroelectric project that would flood 170,000 acres (69,000 hectares) of forest. The $2-billion-dollar project has since been plagued with cost overruns and delays.
Where is the rainforest in Malaysia?
The Malaysian rainforest eco-region extends across peninsular Malaysia to the extreme southern tip of Thailand.
What are the threats to the Malaysian rainforest?
Threats. The clearing of forest land by humans is the primary threat to the Malaysian rainforest ecosystem and its inhabitants. Lowland forests have been cleared to create rice fields, rubber plantations, oil palm plantations, and orchards. In conjunction with these industries, logging has boomed as well, and the development ...
How much of the world's land is forest?
Currently, forests cover about 59.5 percent of the total land area.
What is the WWF Malaysia?
WWF-Malaysia's Forest for Life Programme works to improve forest preservation and management practices throughout the region, paying special attention to the restoration of degraded areas where critical forest corridors are required by wildlife for safe travel throughout their habitats.