Full Answer
How many cells do you start with in meiosis?
In meiosis, however, you start with a diploid cell that divides twice to produce four haploid cells. What does 2n 4 mean in mitosis? In this example, a diploid body cell contains 2n = 4 chromosomes, 2 from mom and two from dad. In humans, 2n = 46, and n = 23.
What is the beginning cell in meiosis?
Meiosis is the process by which gametes (sex cells) are generated in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are produced in male and female gonads and contain one-half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. New gene combinations are introduced in a population through the genetic recombination that occurs during meiosis.
Do all cells undergo the process of meiosis?
The cells normally go through meiosis and mitosis after going through the G2 phase. Types of cells that undergo mitosis and meiosis. All the different types of sex cells undergo meiosis while mitosis only occurs in no sex cells or what is known as somatic cells.
What cells are the outcomes of meiosis?
When a cell undergoes meiosis,the outcome of the process is FOUR HAPLOID CELLS. Meiosis refers to a form of cell division which always results in the formation of four daughter cells. The four daughters cells produce have diploid cells which contains half the original of chromosomes from the parents.

What stage of the cell cycle does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in the primordial germ cells, cells specified for sexual reproduction and separate from the body's normal somatic cells. In preparation for meiosis, a germ cell goes through interphase, during which the entire cell (including the genetic material contained in the nucleus) undergoes replication.
Is meiosis part of the M phase?
(A) In mitosis, diploid cells replicate chromosomes during S phase and segregate sister chromatids during M phase, so that diploid daughter cells are produced. (B) In meiosis, two chromosome-segregation phases, meiosis I and meiosis II, follow a single round of DNA replication during the premeiotic S phase.
What phase does mitosis and meiosis?
In meiosis, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase occur twice. The first round of division is special, but the second round is more like mitosis. In mitosis, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase occur once.
Is M phase mitosis or meiosis?
mitosisCell division occurs during M phase, which consists of nuclear division (mitosis) followed by cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis). The DNA is replicated in the preceding S phase; the two copies of each replicated chromosome (called sister chromatids) remain glued together by cohesins.
What type of division is meiosis?
cell divisionThere are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Most of the time when people refer to “cell division,” they mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells. Mitosis is a fundamental process for life.
What happens in G1 phase?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What happens in G2 phase of cell cycle?
During the second gap phase, or G 2start subscript, 2, end subscript phase, the cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles, and begins to reorganize its contents in preparation for mitosis.
What are the 4 stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).
How many stages of meiosis are there?
Meiosis I occurs in five stages: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, and ends with cytokinesis. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis I except there is no "S" phase. “The chromatids of each chromosome are no longer identical because of recombination” (The Biology Project, 1997b, para 8).
How many chromosomes are in a chromatid in meiosis?
Meiosis II separates the chromatids producing two daughter cells each with 23 chromosomes (haploid), and each chromosome has only one chromatid (Cells Alive!, 1994a). Meiosis II occurs in five stages: prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II, and ends as a Gamete (n). It is then ready to fertilize (a sperm cell) or be fertilized (an egg ...
How many chromatids are in each daughter cell?
Each of the daughter cells is now haploid (23 chromosomes), but each chromosome has two chromatids (The Biology Project, 1997b). Telophase I. The nuclear membrane begins to form around the daughter nuclei. Each daughter nucleus contains two sister chromatids for each chromosome attached to a common centromere.
Why are the sister chromatids not identical?
Because of crossing over, the two sister chromatids are not identical. Cytokinesis. When the cleavage furrow begins to form, this marks the start of cytokinesis (cell division). The resulting daughter cells are hapliod (1N). Meiosis II is similar to mitosis; however, there is no "S" phase.
What is a chromosome with only one chromatid?
A chromosome with only one chromatid heads toward each pole (The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc, n.d.). Telophase II. Chromosomes with only one chromatid begin to condense and the nuclear envelope begins to form around the sets of daughter chromosomes (The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc, n.d.). Gamete (n).
What is a cell with two sets of chromosomes called?
Cells that have two sets of chromosomes are called diploid (2n) cells and cells that have one set of chromosomes are called haploid (n) cells. “In meiosis I, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells.
What happens when a daughter cell is cleavage furrow?
When the cleavage furrow begins to form, this marks the start of cytokinesis. It contracts and splits the cells completely . The four daughter cells are now all haploid (1N) and have the right amount of DNA. They are ready to develop into sperm or eggs now (STCC Foundation Press, 2006).
What is the process of meiosis?
To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs.
What phase of meiosis is haploid?
In meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate, making haploid cells with non-duplicated chromosomes. Phases of meiosis II. Prophase II: Starting cells are the haploid cells made in meiosis I. Chromosomes condense. Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
What happens to homologues in anaphase I?
In anaphase I, the homologues are pulled apart and move apart to opposite ends of the cell. The sister chromatids of each chromosome, however, remain attached to one another and don't come apart. Finally, in telophase I, the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles of the cell.
How are sister chromatids captured?
The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles. In metaphase II, the chromosomes line up individually along the metaphase plate. In anaphase II, the sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Why do chromosomes become haploid in meiosis?
The number of chromosomes becomes haploid in meiosis I, because the actual sister chromatids are not pulled apart by spindle fibers. For example, if a cell was undergoing meiosis, and had a total of 4 chromosomes in it, then 2 of them would go to one daughter cell, and 2 of them would go to the other daughter cell.
What happens before entering meiosis?
Before entering meiosis I, a cell must first go through interphase. As in mitosis, the cell grows during G phase, copies all of its chromosomes during S phase, and prepares for division during G phase.
How many genes are in a homologous chromosome?
Two homologous chromosomes carry different versions of three genes. One has the A, B, and C versions, while the other has the a, b, and c versions. A crossover event in which two chromatids—one from each homologue—exchange fragments swaps the C and c genes. Now, each homologue has two dissimilar chromatids.
What happens in metaphase 1 of meiosis?
In metaphase I of meiosis, the alleles are separated, allowing for this phenomenon to happen. In meiosis II, they will be separated into individual gametes. In mitosis, all the chromosomes line up on their centromeres, and the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into new cells.
Where does meiosis occur?
Human meiosis occurs in the sex organs. Male testis produce sperm and female ovaries produce eggs. Before these gametes are made, however, the DNA must be reduced. Humans have 23 distinct chromosomes, existing in homologous pairs between maternal and paternal DNA, meaning 46 chromosomes.
What is the first step in meiosis?
Prophase I , the first step in meiosis I, is similar to prophase in mitosis in that the chromosomes condense and move towards the middle of the cell. The nuclear envelope degrades, which allows the microtubules originating from the centrioles on either side of the cell to attach to the kinetochores in the centromeres of each chromosome.
Why is meiosis necessary?
Meiosis is necessary for many sexually-reproducing animals to ensure the same number of chromosomes in the offspring as in the parents. The act of fertilization includes two cells fusing together to become a new zygote. If the number of alleles of each gene is not reduced to 1 in the gametes that produce the zygote, ...
What is the process of reducing the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction?
What is Meiosis ? Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm.
Where do homologous chromosomes line up in meiosis?
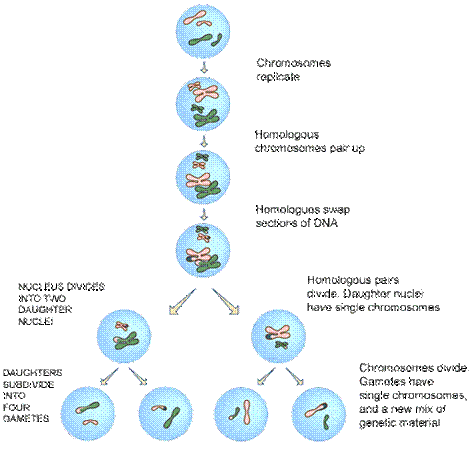
In metaphase I of meiosis I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate, near the center of the cell. This step is referred to as a reductional division. The homologous chromosomes that contain the two different alleles for each gene are lined up to be separated. As seen in the diagram above, while the chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate with their homologous pair, there is no order upon which side the maternal or paternal chromosomes line up. This process is the molecular reason behind the law of segregation.
Where do alleles come from in meiosis?
In meiosis, the lining up of homologous chromosomes leaves 2 alleles in the final cells, but they are on sister chromatids and are clones of the same source of DNA.
What are the two stages of meiosis?
In meiosis two divisions take place which results in formation of four haploid daughter cells. The two stages of meiosis are-. Meiosis I- Homologous pairs of chromosomes separate during meiosis I. 2. Meiosis II- Sister chromatids are formed due to replication in ‘S’ phase are separated during Meiosis-II.
What happens during meiosis?
Meiosis results in the formation of four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes. This process takes place in gametes formation which are involved in sexual reproduction in higher organisms.
What is the type of cell division that takes place after the interphase in higher organisms?
Ans: Meiosis is the type of cell division that takes place after the interphase in higher organisms. It is also called reductional division. It helps in the formation of haploid cells like germ cells which fuse to form a zygote. Q.5.
What happens in each of the haploid daughter cells resulting from meiosis I?
During this stage, the nuclear membrane disintegrates and centrioles move apart from each other to the opposite poles. This happens in each of the haploid daughter cells resulting from meiosis I. Metaphase II. Sister chromatids are lined by the spindle fibers on the equator to form a metaphase plate.
What is the name of the pair of chromosomes that form a synaptonemal complex?
Paired chromosomes are called dyad. These chromatids undergo vertical splitting and form tetrad. To hold this pair together, a synaptonemal complex is formed. Sister chromatids refer to the arms of one chromosome whereas non-sister chromatids refer to the arms of two homologous chromosomes.
What is the process of cell division called?
Meiosis involves the cell division which results in formation of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes compared to the single parent cell. Meiosis is also called REDUCTIONAL DIVISION.
What is the process of a haploid cell from a diploid cell called?
As two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell division are involved in meiosis, it gives us four-daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes. Since chromosome number gets halved, it is also called reductional division. 1. Meiosis is a process that gives rise to a haploid cell from a diploid one. 2.