The Columbian Exchange of Plants, Animals, and Diseases
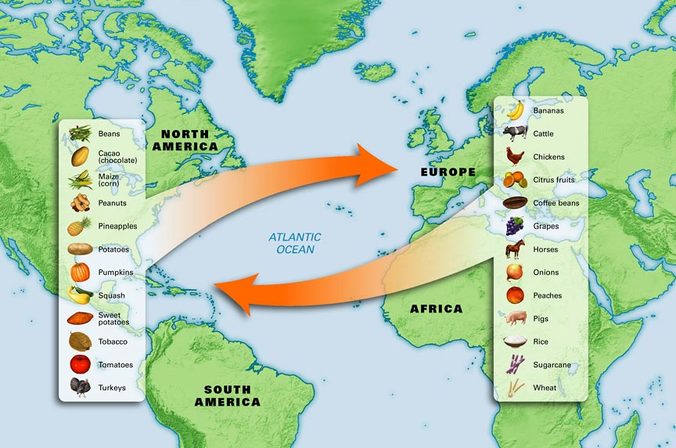
- 1) New World to Old World Plants (partial list) avocado, beans, pepper, cocoa, cashew, berries (black raspberry), corn, peanut, pecan, pineapple, potato, pumpkin, rubber, various squash, sunflower, sweet potato, tobacco, tomato, vanilla, zucchini. Animals (partial list) Diseases guinea pig, llama, turkey. Chagas disease (a tropical unicellular parasite), syphilis ...
- 2) Old World to New World
What plants did Columbus bring to Europe from the New World?
Crops and Introduced Wild Plants. Columbus took many crops and wild plants from the New World and brought them to Europe. Some of these are potatoes, tomatoes, and maize. Asia also received new vegetables from the New World such as chili and potatoes.
What crops were brought to Europe from the New World?
Columbus took many crops and wild plants from the New World and brought them to Europe. Some of these are potatoes, tomatoes, and maize. Asia also received new vegetables from the New World such as chili and potatoes.
How did plants get to the New World?
Within about 50 years, Europeans transported the spuds back across the ocean to North America. Other plants moved from Europe to the New World. On Columbus's second voyage to the Americas, he brought with him seeds for such plants as wheat, salad greens, grapes and sugarcane. Each grew well in the fertile American soil.
What foods were introduced to the New World?
With the discovery of the New World, Europe secured enormous tracts of fertile land suited for the cultivation of popular crops such as sugar, coffee, soybeans, oranges, and bananas. Upon introduction of these crops, the Americas quickly became the main suppliers of these foods to most of the world. What animals were introduced to the New World?
What brought change to the New World and the Old World?
Why did Europeans plant large farm fields?
What was North America like in the 1500s?
Why did the Europeans force the American Indians to work on their land?
How did tobacco spread?
Why did the explorers travel to the New World?
What was the name of the corn that spread across the continent?
See 4 more
About this website

What plants went from the New World to the Old World?
The exchange introduced a wide range of new calorically rich staple crops to the Old World—namely potatoes, sweet potatoes, maize, and cassava. The primary benefit of the New World staples was that they could be grown in Old World climates that were unsuitable for the cultivation of Old World staples.
What was brought from the New World to the Old World?
Christopher Columbus introduced horses, sugar plants, and disease to the New World, while facilitating the introduction of New World commodities like sugar, tobacco, chocolate, and potatoes to the Old World. The process by which commodities, people, and diseases crossed the Atlantic is known as the Columbian Exchange.
What plants were in the Old World?
They brought European crops such as barley and rye. They brought wheat, which was originally from the Middle East . They brought plants that had originally come from Asia, including sugar, bananas, yams, citrus fruit, coffee, rice, and sugarcane.
What are 3 important plants that were transferred from the Old World to the New World in the Columbian Exchange?
Corn, pumpkins, tobacco, Perhaps the Americas simply had fewer species of large mammals that could be tamed.
What foods came from the New and Old World?
Food historian Lois Ellen Frank calls potatoes, tomatoes, corn, beans, squash, chili, cacao, and vanilla the "magic eight" ingredients that were found and used only in the Americas before 1492 and were taken via the Columbian Exchange back to the Old World, dramatically transforming the cuisine there.
What plants and animals were brought from the Old World to the New World as part of the Columbian Exchange?
The Columbian Exchange facilitated the transfer of all of the major domesticated animals from the Old World to the Americas: cattle, horses, sheep, goats, and pigs. The few domesticated species in Pre-Columbian America included the dog and the alpaca.
What did the old world bring?
Europeans brought deadly viruses and bacteria, such as smallpox, measles, typhus, and cholera, for which Native Americans had no immunity (Denevan, 1976). On their return home, European sailors brought syphilis to Europe.
Are tomatoes Old World or New World?
It's hard to imagine, but Christopher Columbus—an Italian—had never seen tomatoes. Why? Because they're indigenous to the Americas.
What vegetables came from the Old World?
There are vegetables well known today in the list such as cucumber, chickpeas, celery, carrots, cabbage, leeks, peas, lettuce, garlic, onions, shallots, as well as familiar aromatic herbs as mint, sage, cumin, anise, parsley, savory, coriander.
Is onion from the Old World or New World?
Foods That Originated in the New World: artichokes, avocados, beans (kidney and lima), black walnuts, blueberries, cacao (cocoa/chocolate), cashews, cassava, chestnuts, corn (maize), crab apples, cranberries, gourds, hickory nuts, onions, papayas, peanuts, pecans, peppers (bell peppers, chili peppers), pineapples, ...
What are 3 animals that were brought from the New World to the Old?
The main ones, aside from llamas and alpacas, were dogs, turkeys, and guinea pigs. The introduction of horses made hunting buffalo much easier for the Plains Indians.
Which species plants and animals came from the Old World to the New World?
Europeans introduced such domestic animals as cattle, pigs, chickens, goats, and sheep to North America, with the intent of using the animal meat for food, and hides or wool for clothing. They also inadvertently brought pest animals and plants, such as rats and assorted weeds.
What are 10 significant items that traveled from the New World to the Old World?
The Americas' farmers' gifts to other continents included staples such as corn (maize), potatoes, cassava, and sweet potatoes, together with secondary food crops such as tomatoes, peanuts, pumpkins, squashes, pineapples, and chili peppers.
What animals were brought from the New World to the Old World?
The main ones, aside from llamas and alpacas, were dogs, turkeys, and guinea pigs. The introduction of horses made hunting buffalo much easier for the Plains Indians.
What things were brought to the New World?
The Europeans brought technologies, ideas, plants, and animals that were new to America and would transform peoples' lives: guns, iron tools, and weapons; Christianity and Roman law; sugarcane and wheat; horses and cattle. They also carried diseases against which the Indian peoples had no defenses.
Columbian Exchange - The Old World Meets The New World
7. Crops and Introduced Wild Plants . Columbus took many crops and wild plants from the New World and brought them to Europe. Some of these are potatoes, tomatoes, and maize.
What technology did the New World give to the Old World?
Answer (1 of 28): “What technology did the New World give to the Old World?” I’m guessing you mean technology from the time of discovery, not technology in the modern day since such modern technology is pervasive around the world and much of it builds in small increments on discoveries from else...
The Columbian Exchange, Native Americans and the Land, Nature ...
Essays on American environmental history. Nature Transformed is an interactive curriculum enrichment service for teachers, offering them practical help in planning courses and presenting rigorous subject matter to students. Nature Transformed explores the relationship between the ways men and women have thought about their surroundings and the ways they have acted toward them.
Why did the New World have so few people?
The New World had only a few, possibly because humans had been present there and had lived in dense populations, cities, for a short time compared to the Old. Possibly of greater importance is the relative lack of domesticated herd animals in America, one of our richest sources of disease micro-organisms.
Was there a disease in the New World before 1492?
There were infections in the New World before 1492 that were not present in the Old (Chargas' disease, for instance). There were those it shared with the Old World, certainly one or more of the treponematoses (a category including syphilis) and possibly tuberculosis; but the list is short, very short.
What plants did Columbus bring to Europe?
Columbus took many crops and wild plants from the New World and brought them to Europe. Some of these are potatoes, tomatoes, and maize. Asia also received new vegetables from the New World such as chili and potatoes.
What animals did the Spaniards bring to the New World?
The Spaniards brought along with them their livestock as well as domesticated pets to the New World. Soon cargo ships were loaded with donkeys, mules, goats, chickens, large dogs, cats, pigs, cattle, horses, bees, and sheep. Some of these animals like the horse altered the history of many native Indian tribes.
What were the changes that Europeans brought to the New World?
The Europeans brought to the New World significant changes to the lives of the Amerindians. These changes affected the native population in many negative aspects. The decimation of entire Amerindian populations was not uncommon due to slavery or diseases foreign to them. Misunderstandings and search for gold were settled by the genocide of entire cities. Some Spanish governors were, however, honest in their role as they dispensed justice. The introduction of Christianity and the cultural awareness brought about by the Europeans still is felt today.
What did Columbus do when he saw how easily he could be enslaved?
When Columbus saw how easily they could be enslaved he wasted no time in the process. He originally started enslaving native peoples in the West Indies. During his years in the New World, Columbus began propagating his policies of forced labor using the indigenous Americans for reaping profit.
What was the significance of the Spanish colonization?
The colonization involved the annexation of several South American countries as Spanish protectorates and colonies under the rule of Spanish governors. The domination was more to the benefit of Spain than the New World. The Spanish rule in the Americas brought justice, freedom, and equality.
How long did Spain control the New World?
The 350 years of Spanish military control of the New World produced so much gold and silver and other precious gems that it made Spain a major European power. Gold was sent back to Spain and used as decorations inside churches and cathedrals.
Where is the Columbian Exchange?
Columbian Exchange - The Old World Meets The New World. A Monument Dedicated to Christopher Columbus in Barcelona, Spain. 10. Columbus's Landfall and Contact. Christopher Columbus, Italian navigator, and explorer first made landfall in the New World on October 12, 1492. His original aim was to sail to the West Indies using a new route ...
What brought change to the New World and the Old World?
The exchange of plant and animal species brought change to the New World and the Old World. People on both continents gained much, including animal-produced clothing materials and bountiful new agricultural crops that would become dietary mainstays. They also lost a great deal.
Why did Europeans plant large farm fields?
Europeans were more likely to plant large farm fields, often burning acres of forest and meadows to make way for agricultural plots. Where forests once stood and animals thrived, farm fields fragmented the land. Europeans systematically removed native plants to make way for the introduced crops.
What was North America like in the 1500s?
When the Europeans landed in the New World in the late 1400s and early 1500s, North America was an untamed wilderness filled with mysterious flowers, trees, birds, and mammals. Christopher Columbus wrote of the scent of a breeze from the shores of North America as "the sweetest thing in the world." Other explorers similarly reported of the biological wealth of this unknown continent: flocks of birds so thick they blocked out the noonday sun; fishes so large and numerous that they sometimes hampered river navigation; enormous stands of pines, oaks and chestnuts; and meadows so vast that their boundaries were beyond sight.
Why did the Europeans force the American Indians to work on their land?
Often the success of the European settlers also spelled misery for the American Indians. As Europeans came to rely more and more on the introduced crops and their productive but invasive agricultural practices, they began to see the Indians as either hindrances to the expansion of agriculture or as potential farm workers. The Indians were thus forced to work the land for the benefit of the Europeans or were pushed—sometimes violently—from land that Europeans began to claim as their own.
How did tobacco spread?
Tobacco's spread throughout Europe was similarly quick. Explorers introduced it to Spain in about 1500, smoking became popular shortly thereafter, and farmers began to cultivate the plant in 1531. By 1556, the plant appeared in France, and within a decade, it was present in England. Its use spread both as a recreational pastime and as an important medicinal herb. Its supposed curative properties ranged from headaches to toothaches, and lockjaw to cancer. By the end of the century, tobacco use had spread nearly around the globe despite mainly religious-based attempts to ban or control its cultivation and/or use.
Why did the explorers travel to the New World?
The explorers were in the New World to find items of economic benefit to their countries and saw the new land as a resource to be exploited and a wilderness to be tamed. The first explorers to North America came with hopes of finding a passageway to the East Indies, and eventually opening a lucrative trade route with the spice-rich islands. Although they were unsuccessful in this regard, they were able to discover many new and useful plants and animals, which they were only too happy to transport back to their homelands.
What was the name of the corn that spread across the continent?
Called ma-hiz by the Indians of Central America, its name was later corrupted to "maize" in Europe. By the time the New World was discovered in 1492, corn had spread across the continent as far north as Canada.
